Korean J Hematol.
2006 Dec;41(4):272-281. 10.5045/kjh.2006.41.4.272.
Identification of Leukemia Surface Proteins Using a Proteomic Technique
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hematology-Oncology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. jangjh@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2305214
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2006.41.4.272
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Numerous cell surface proteins of leukemia cells such as CD33 and CD52 have been identified as diagnostic and therapeutic targets. Thus the profiling of the cell surface proteome and proteins restricted to specific leukemia(s) can provide a way to identify novel targets for leukemia diagnosis and therapy. However, there is a lack of data pertaining to the comprehensive analysis of surface membrane proteins because there are few effective strategies for profiling surface membrane proteomes.
METHODS
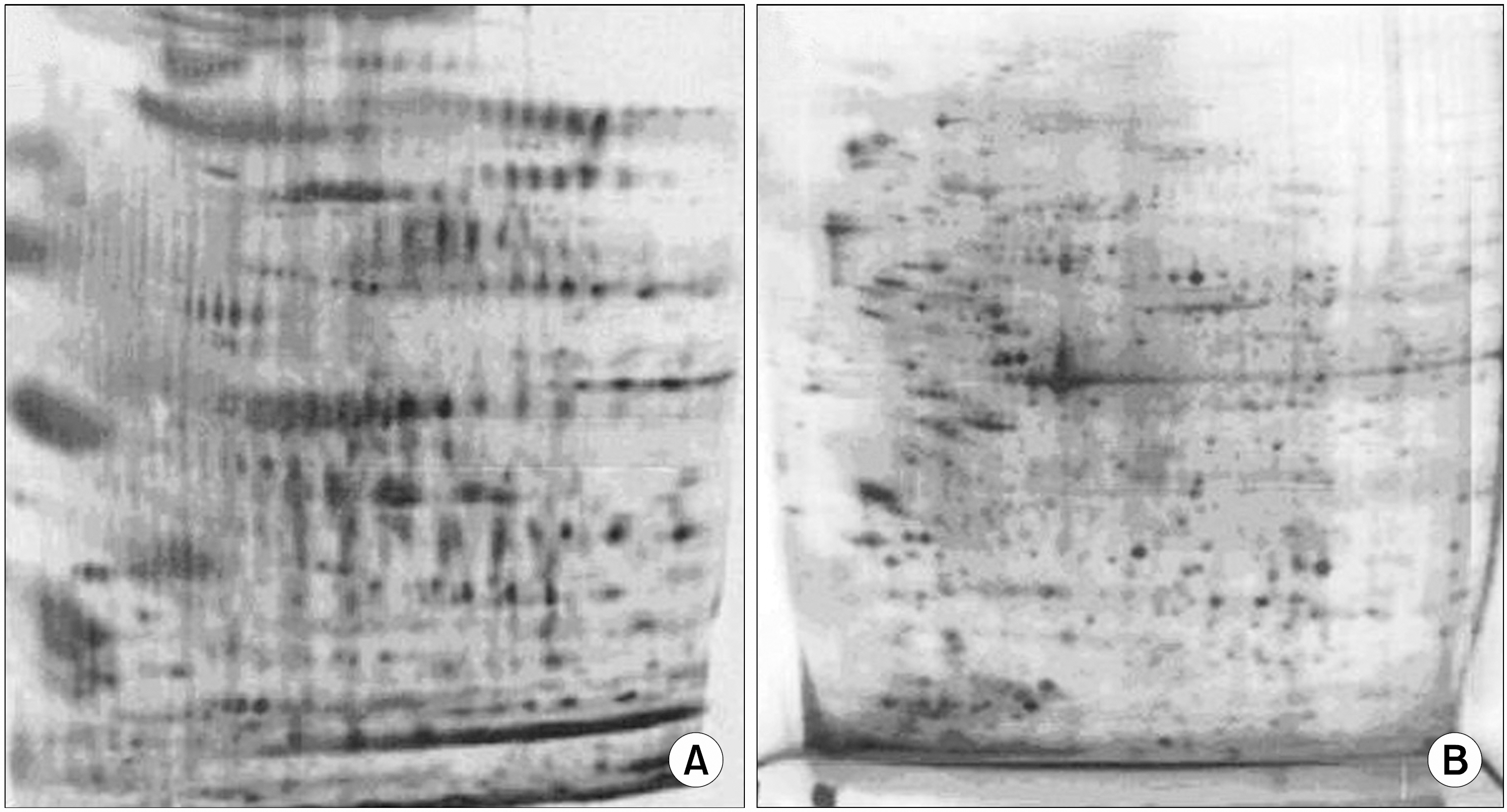
We report on the application of quantitative proteomic techniques that incorporate affinity-capture and purification on monomeric avidin columns to identify all biotinylated cell surface proteins from leukemia cell lines.
RESULTS
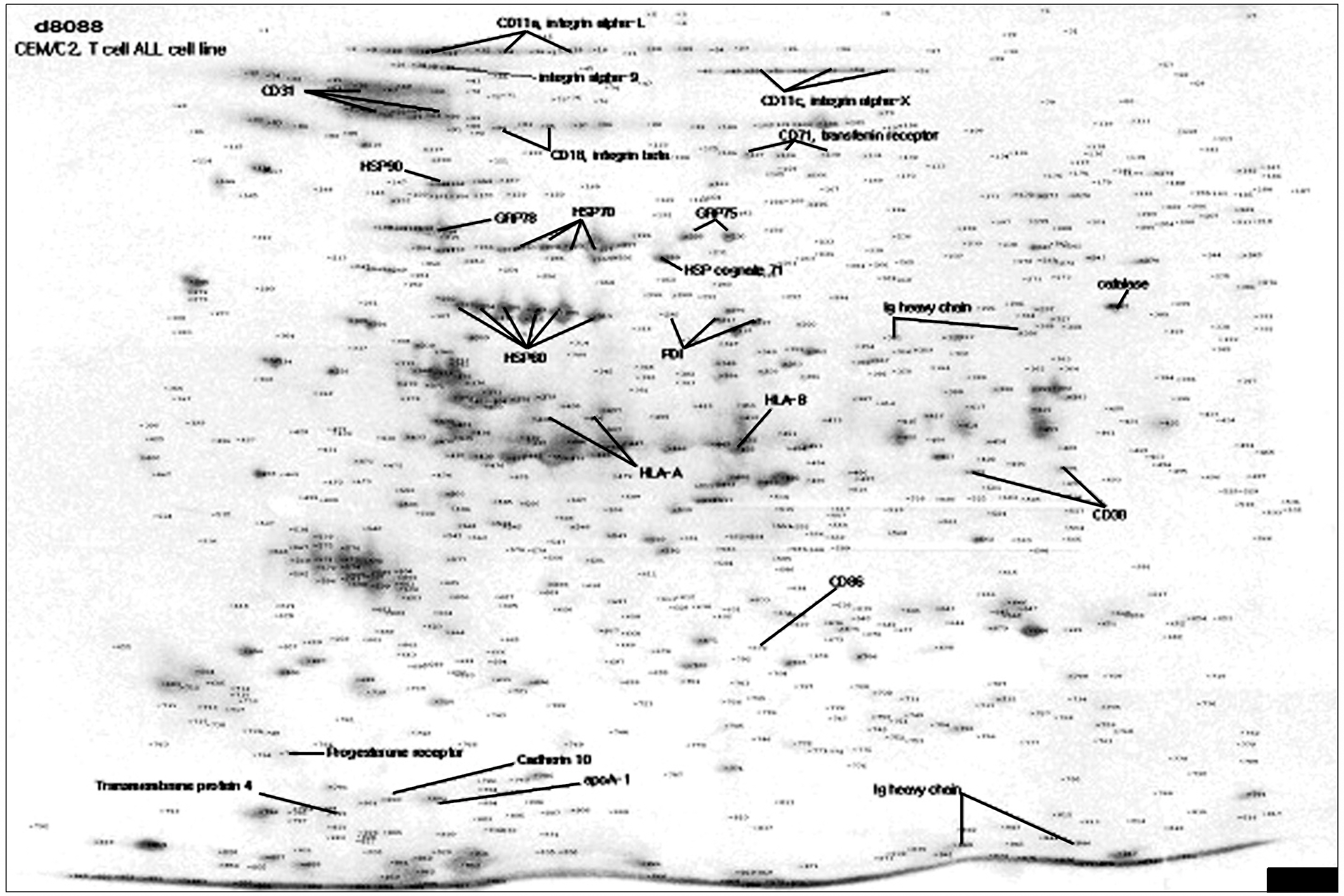
An analysis of a subset of biotinylated proteins among the different human leukemia cell lines using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization and tandem mass spectrometry identified, among others, some widely expressed proteins in leukemia cells, such as CD11a, CD11c, CD18, CD31, CD44, and CD147, as well as a set of proteins identified as chaperone proteins, including HSP90, GRP78, GRP75, HSP70, HSP60 and protein disulfide isomerases. On the basis of their known functional roles, several of these proteins may participate in the progression of leukemogenesis and should be considered as potential markers of leukemia.
CONCLUSION
Comprehensive profiling of the leukemia cell surface proteome provides an effective approach for the identification of commonly occurring proteins as well as proteins with restricted expression patterns to a specific cell line.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Jemal A., Murray T., Samuels A., Ghafoor A., Ward E., Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin. 2003. 53:5–26.
Article2). Dyer MJ., Hale G., Hayhoe FG., Waldmann H. Effects of CAMPATH-1 antibodies in vivo in patients with lymphoid malignancies: influence of antibody isotype. Blood. 1989. 73:1431–9.
Article3). Giles FJ. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin: promise and challenge in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2002. 2:630–40.
Article4). Wellhausen SR., Peiper SC. CD33: biochemical and biological characterization and evaluation of clinical relevance. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2002. 16:139–43.5). Bernstein ID. CD33 as a target for selective ablation of acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Lymphoma. 2002. 2(Suppl 1):S9-S11.
Article6). Jacobson BS., Stolz DB., Schnitzer JE. Identification of endothelial cell-surface proteins as targets for diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nat Med. 1996. 2:482–4.
Article7). Harvey S., Zhang Y., Landry F., Miller C., Smith JW. Insights into a plasma membrane signature. Physiol Genomics. 2001. 5:129–36.
Article8). Sabarth N., Lamer S., Zimny-Arndt U., Jungblut PR., Meyer TF., Bumann D. Identification of surface proteins of Helicobacter pylori by selective biotinylation, affinity purification, and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:27896–902.
Article9). Jang JH., Hanash S. Profiling of the cell surface proteome. Proteomics. 2003. 3:1947–54.
Article10). Wilbur DS., Pathare PM., Hamlin DK, et al. Development of new biotin/streptavidin reagents for pretar-geting. Biomol Eng. 1999. 16:113–8.11). Diamandis EP., Christopoulos TK. The biotin-(strept) avidin system: principles and applications in biotechnology. Clin Chem. 1991. 37:625–36.12). Gharahdaghi F., Weinberg CR., Meagher DA., Imai BS., Mische SM. Mass spectrometric identification of proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gel: a method for the removal of silver ions to enhance sensitivity. Electrophoresis. 1999. 20:601–5.
Article13). Belov L., de la Vega O., dos Remedios CG., Mulligan SP., Christopherson RI. Immunophenotyping of leukemias using a cluster of differentiation antibody microarray. Cancer Res. 2001. 61:4483–9.14). Freedman AS. Cell surface antigens in leukemias and lymphomas. Cancer Invest. 1996. 14:252–76.
Article15). Kishihara K., Penninger J., Wallace VA, et al. Normal B lymphocyte development but impaired T cell maturation in CD45-exon6 protein tyrosine phosphatase-deficient mice. Cell. 1993. 74:143–56.
Article16). Jennings CD., Foon KA. Recent advances in flow cytometry: application to the diagnosis of hematologic malignancy. Blood. 1997. 90:2863–92.
Article17). Jiang XM., Fitzgerald M., Grant CM., Hogg PJ. Redox control of exofacial protein thiols/disulfides by protein disulfide isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1999. 274:2416–23.
Article18). Tager M., Kroning H., Thiel U., Ansorge S. Membrane-bound proteindisulfide isomerase (PDI) is in-volved in regulation of surface expression of thiols and drug sensitivity of B-CLL cells. Exp Hematol. 1997. 25:601–7.19). Lawrence DA., Song R., Weber P. Surface thiols of human lymphocytes and their changes after in vitro and in vivo activation. J Leukoc Biol. 1996. 60:611–8.
Article20). Dill KA., Chan HS. From Levinthal to pathways to funnels. Nat Struct Biol. 1997. 4:10–9.
Article21). Ellis RJ. The general concept of molecular chaper-ones. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1993. 339:257–61.
Article22). Harada M., Kimura G., Nomoto K. Heat shock proteins and the antitumor T cell response. Biotherapy. 1998. 10:229–35.
Article23). Vabulas RM., Braedel S., Hilf N, et al. The endoplasmic reticulum-resident heat shock protein Gp96 activates dendritic cells via the Toll-like receptor 2/4 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:20847–53.
Article24). Vabulas RM., Ahmad-Nejad P., Ghose S., Kirschning CJ., Issels RD., Wagner H. HSP70 as endogenous stimulus of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor signal pathway. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:15107–12.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A study on the immunologic surface markers of acute leukemia
- Proteomic Screening of Antigenic Proteins from the Hard Tick, Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae)
- Identification of proteins regulated by chlorogenic acid in an ischemic animal model: a proteomic approach
- Identification of surface antigens of Trichomonas vaginalis
- Proteomic Identification of Proteins Suggestive of Immune-Mediated Response or Neuronal Degeneration in Serum of Achalasia Patients