Korean J Adult Nurs.
2015 Apr;27(2):211-222. 10.7475/kjan.2015.27.2.211.
The Path Model based on Senescent Sleep Model for Sleep in Community-dwelling Older Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Cheongju University, Cheongju, Korea. arkim@cju.ac.kr
- 2Division of Nursing, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2298135
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2015.27.2.211
Abstract
- PURPOSE
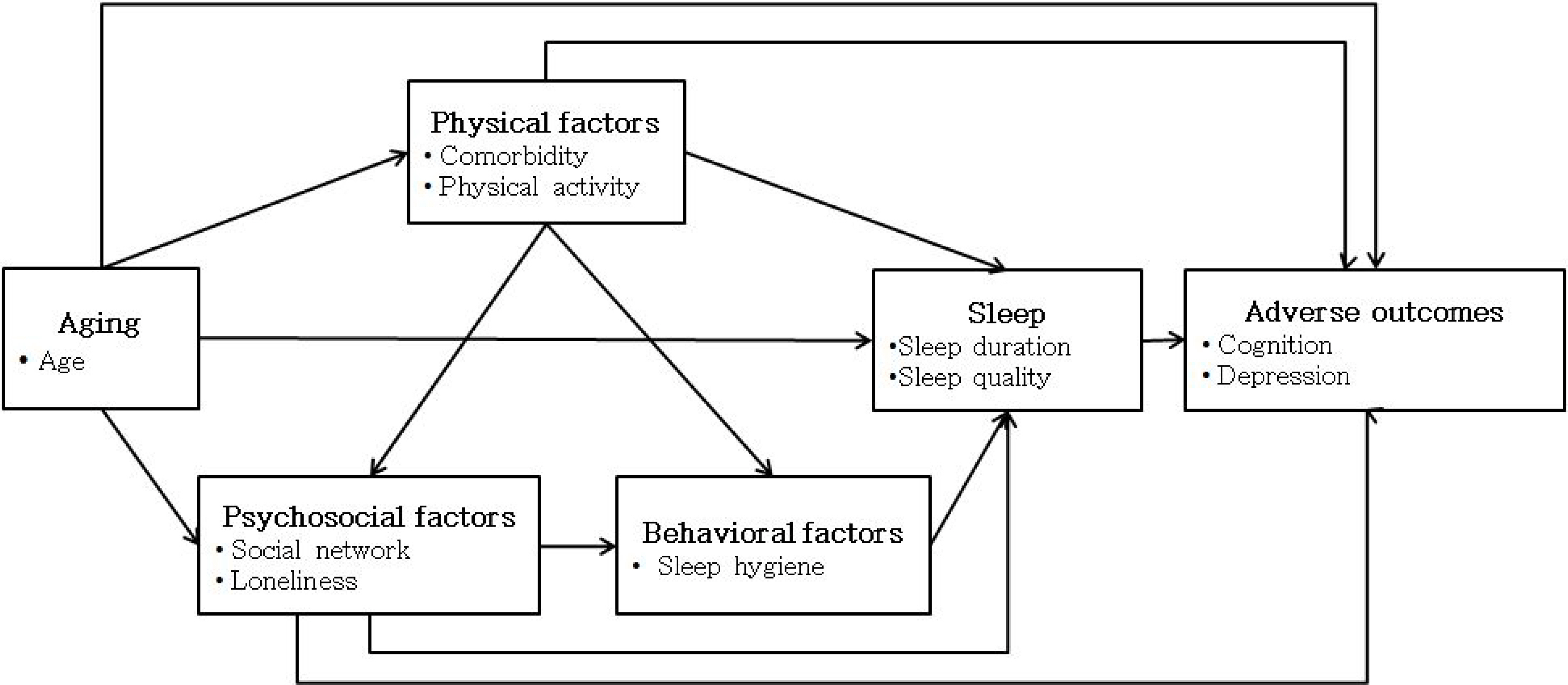
This study was conducted to test the model for sleep in community-dwelling older adults. The hypothetical model based on a senescent sleep model was constructed using the multiple influencing factors of sleep and associated adverse outcomes of changes in sleep in the older adults.
METHODS
Data were collected from 203 community-dwelling older adults living in Korea, and analyzed using IBM SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0.
RESULTS
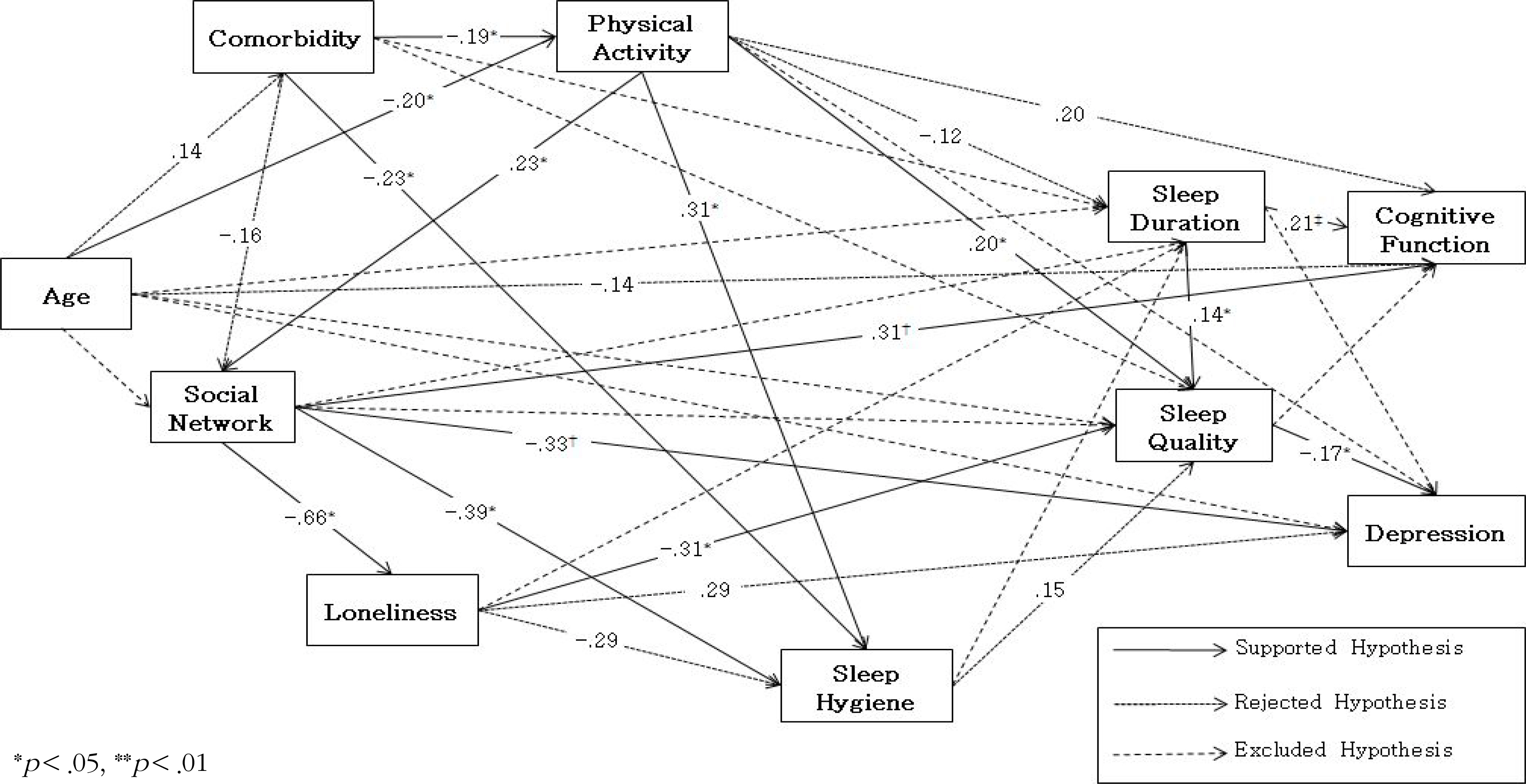
Increased age and multiple comorbidities were associated with decreased physical activities. Decreased physical activities were associated with smaller social networks, and smaller social networks were associated with higher level of loneliness. Multiple comorbidities, decreased physical activities, larger social networks, and higher level of loneliness were associated with maladaptive sleep hygiene. Decreased physical activities, higher level loneliness, and shorter actual sleep duration were associated with worse sleep quality. Smaller social networks and shorter actual sleep duration were associated with lower cognitive functions. Smaller social networks, higher loneliness, and worse sleep quality were associated with more severe depressive symptoms.
CONCLUSION
These findings suggest that the sleep improvement interventions not only with physical perspectives but psychosocial ones for older adults may improve depressive symptoms as well as sleep quality.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Factors Influencing the Practice of Respiratory Infection Prevention for the Elderly in Rural Areas
Myung Soon Kwon, Jeong Soon Yu
J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2019;30(4):460-470. doi: 10.12799/jkachn.2019.30.4.460.The Factors Associated with Depression in the Elderly Male: Based on the 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Doonam Oh, Chul-Gyu Kim
Korean J Adult Nurs. 2015;27(5):583-593. doi: 10.7469/kjan.2015.27.5.583.
Reference
-
1.Random House Webster's College Dictionary. New York: Random House Reference;2005.2.Jung KH., Oh YH., Lee YK., Sohn CK., Park BM., Lee SY, et al. 2011 Korean national survey on older adults. Policy report. Korea: Ministry for Health and Welfare;2012 April. Report No.: 11-1352000-000672-12.3.Jaussent I., Bouyer J., Ancelin ML., Akbaraly T., Peres K., Ritchie K, et al. Insomnia and daytime sleepiness are risk factors for depressive symptoms in the elderly. Sleep. 2011. 34(8):1103–10. http://dx.doi.org/10.5665/SLEEP.1170.
Article4.Kang S., Kim JS. Experiences of insomnia of the elderly women in community. Journal of Qualitative Research. 2010. 11(1):13–25.5.Keage HA., Banks S., Yang KL., Morgan K., Brayne C., Matthews FE. What sleep characteristics predict cognitive decline in the elderly? Sleep Medicine. 2012. 13(7):886–92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2012.02.003.
Article6.Nebes RD., Buysse DJ., Halligan EM., Houck PR., Monk TH. Self-reported sleep quality predicts poor cognitive performance in healthy older adults. Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences & Social Sciences. 2009. 64B(2):180–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbn037.
Article7.Ohayon MM., Carskadon MA., Guilleminault C., Vitiello MV. Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep. 2004. 27(7):1255–73.
Article8.Holfeld B., Ruthig JC. A longitudinal examination of sleep quality and physical activity in older adults. Journal of Applied Gerontology. 2012. Forthcoming.http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0733464812455097.
Article9.Tu X., Cai H., Gao YT., Wu X., Ji BT., Yang G, et al. Sleep duration and its correlates in middle-aged and elderly chinese women: the shanghaiwomen's health study. Sleep Medicine. 2012. 13(9):1138–45. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2012.06.014.10.Yao KW., Yu S., Cheng S., Chung I. Relationships between personal, depression, socialnetwork factors and sleepquality in community-dwelling older adults. Journal of Nursing Research. 2008. 16(2):131–9.11.McHugh JE., Lawlor BA. Perceived stress mediates the relationship betweenemotionalloneliness andsleepquality over time in older adults. British Journal of Health Psychology. 2013. 18(3):546–55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8287.2012.02101.x.12.Monk TH., Buysse DJ., Billy BD., Fletcher ME., Kennedy KS., Schlarb JE, et al. Circadian type and bed-timing regularity in 654 retired seniors: correlations with subjective sleep measures. Sleep. 2011. 34(2):),. 235–9.
Article13.vaz Fragoso CA., Gill TM. Sleep complaints in community-living older persons: a multifactorial geriatric syndrome. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2007. 55(11):1853–66.
Article14.Ayotte BJ., Margrett JA., Hicks-Patrick J. Physical activity in middle-aged and young-old adults the roles of self-efficacy, barriers, outcome expectancies, self-regulatory behaviors and social support. Journal of Health Psychology. 2010. 15(2):173–85. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1359105309342283.15.Yamanaka Y., Hashimoto S., Tanahashi Y., Nishide SY., Honma S., Honma K. Physical exercise accelerates reentrainment of human sleep-wake cycle but not of plasma melaton in rhythm to 8-h phase-advanced sleep schedule. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory. Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 2010. 298(3):R681–91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00345.2009.16.Milanovic Z., Pantelic S., Trajkovic N., Sporis G., Kostic R., James N. Age-relateddecrease in physical activity and functional fitness among elderly men and women. Clinical Interventions in Aging. 2013. 8:549–56. http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S44112.17.Lieverse R., de Vries R., Hoogendoorn AW., Smit JH., Hoogen-dijk WJ. Socialsupportand social rhythm regularity in elderly patients with major depressive disorder. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. 2013. 21(11):1144–53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jagp.2013.01.052.18.Theeke LA., Goins RT., Moore J., Campbell HT. Loneliness, depression, social support, and quality of life in older chronically ill appalachians. The Journal of Psychology. 2012. 146(1-2):155–71.
Article19.Mesas AE., Lopez-Garc a E., Leon-Munoz LM., Graciani A., ́í ́̃Guallar-Castillon P., Rodr guez-Artalejo F. The association ́í between habitual sleep duration and sleep quality in older adults according to health status. AgeandAgeing. 2011. 40(3):318–23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afr004.20.Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 2nd ed.New York: Guilford Press;2005. p. 20–208.21.Montgomery-Downs HE., Insana SP., Bond JA. Movement toward a novel activity monitoring device. Sleep Breath. 2012. 16(3):913–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11325-011-0585-y.
Article22.Buysse DJ., Reynolds CF., Monk TH., Berman SR., Kuper DJ. The pittsburghsleep quality index: A newinstrumentfor psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research. 1989. 28(2):193–213.23.Charlson ME., Pompei P., Ales K., MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity inlongitudinal studies: development and validation. Journal of Chronic Diseases. 1987. 40(5):373–83.24.Oh JY., Yang YJ., Kim BS., Kang JH. Validity and reliability of Korean version of international physical activity questionnaire (IPAQ) short form. Journal of the Korean Academy of Family Medicine. 2007. 28(7):532–41.25.Hong M., Casado BL., Harrington D. Validation of Korean versions of the lubben social network scales in Korean Americans. Clinical Gerontologists. 2011. 34(4):319–34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/07317115.2011.572534.
Article26.Kim OS. Koreanversion ofthe revised UCLA loneliness scale: reliability and validity test. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 1997. 27(4):871–9.27.Mastin DF., Bryson J., Corwyn R. Assessment of sleep hygiene using the sleep hygiene index. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 2006. 29(3):223–7.
Article28.Kwon YC., Park JH. Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE-K) partI: developmentofthe test for the elderly. Journal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1989. 28(1):125–35.29.Cho MJ., Bae JN., Suh GH., Hahm BJ., Kim JK., Lee DW, et al. Validation of Geriatric Depression Scale, Koreanversion(GDS) in the assessment of DSM--R major depression. ⅢJournal of Korean Neuropsychiatric Association. 1999. 38(1):48–62.30.Kang YH., Kim MY., Lee GJ., Jung DY., Ma RW. Astudy of social support, loneliness, sleepquality, and perceivedhealthstatus among community-dwelling older adults. Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing. 2012. 26(2):303–13. http://dx.doi.org/10.5932/JKPHN.2012.26.2.303.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sleep Patterns of Older Residents in Long-Term-Care Facilities: A Comparison with Older Adults in Home-Care Services and Community-Dwelling Older Adults
- Sleep Disorders in the Elderly
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Sleep Disturbance in Community Dwelling Adults in Korea
- The Effects of a Brief Intervention for Insomnia on Community Dwelling Older Adults
- Factors Related to Suicidal Ldeation in Community-Dwelling Older Adults with Multimorbidity Using Data From the 2017 Korean Community Health Survey