Korean J Urol.
2006 May;47(5):527-535. 10.4111/kju.2006.47.5.527.
Duloxetine versus Placebo for the Treatment of Korean Women with Stress Predominant Urinary Incontinence
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Yongdong Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Samsung Cheil Hospital & Woman's Healthcare Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Incheon Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 7Department of Urology, Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Lilly Korea, Ltd, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Lilly Research Laboratories, Indianapolis, IN, USA. viktrupla@lilly.com
- KMID: 2294140
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2006.47.5.527
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare duloxetine with placebo for the treatment of Korean women with stress urinary incontinence (SUI).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
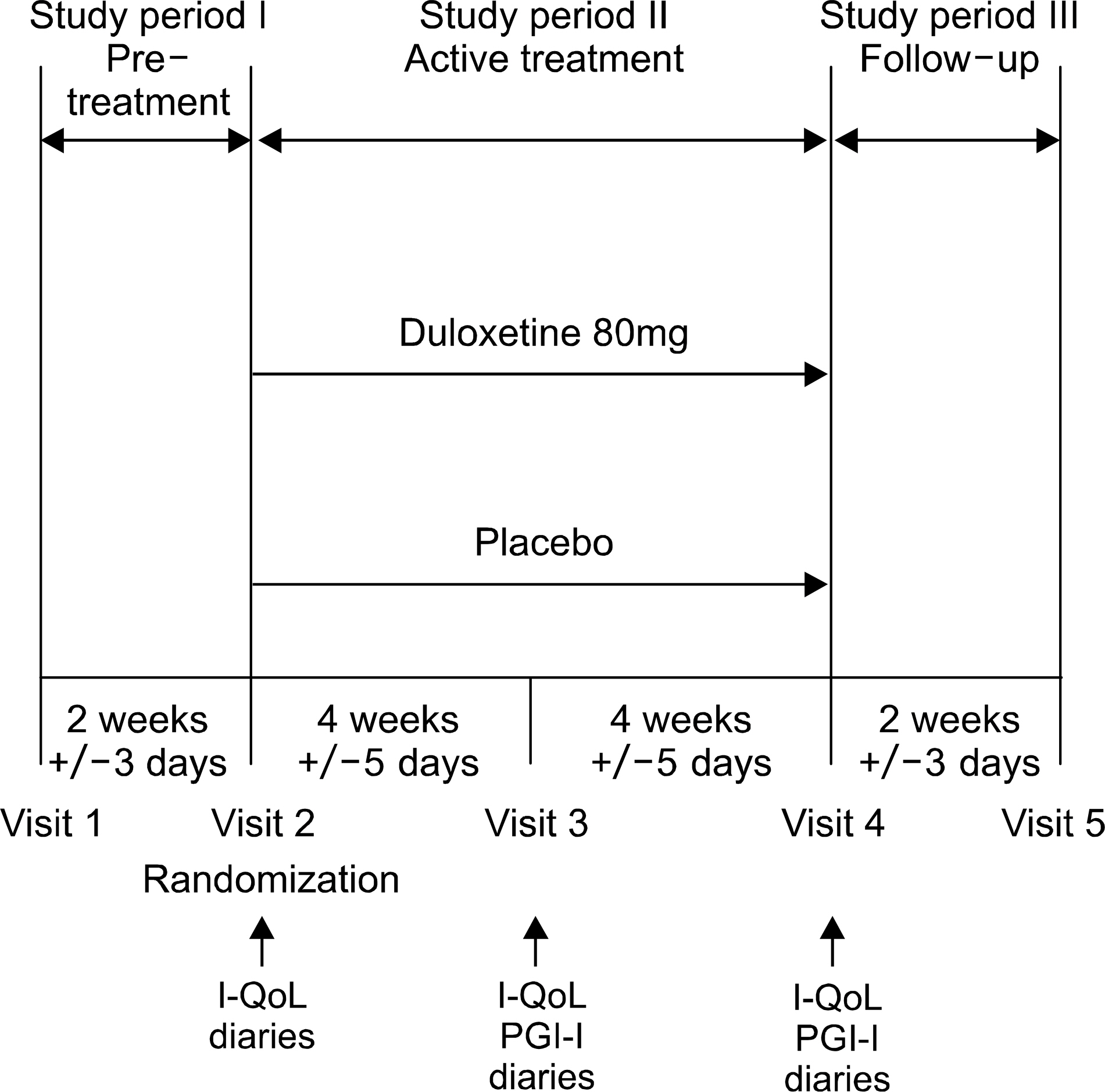
This was a phase 3, double-blind, stratified, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled, multi-center study investigating efficacy and safety of a of duloxetine compared with placebo in the treatment of SUI. After a 2-week no-drug screening period, women ages 29-69 were randomly assigned to placebo (n=60) or duloxetine (n=61) as 40mg twice daily for 8 weeks followed by a 2 week no-drug period. Women were seen at 4-week intervals. The primary efficacy variable was percent change in incontinence episodes frequency (IEF)/week. Secondary variables included percent change in, changes in Incontinence Quality of Life (I-QoL) total and 3 sub-scale scores, and Patient Global Impression of Improvement (PGI-I) ratings. Safety was evaluated by treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE), discontinuations due to adverse events, vital signs measurements, and clinical laboratory tests.
RESULTS
There were statistically significant improvements with duloxetine compared with placebo in IEF (duloxetine baseline 16.4IEF/wk, endpoint 7.7IEF/wk, median percent reduction=50.0% vs placebo baseline 13.3IEF/ wk, endpoint 8.8IEF/wk, median percent reduction=37.1%, p=0.033), and avoidance and limiting behavior subscale (p=0.006) in I-QoL. TEAEs were reported significantly more often in the duloxetine group compared with the placebo group (82.0% vs 31.7%; p<0.001); common AEs (>or=5% in duloxetine-treated subjects and p<0.05) were nausea, dizziness, anorexia, fatigue, lethargy, abdominal discomfort, and constipation. Discontinuation rates because of AEs were 34.4% for duloxetine and 8.3% for placebo.
CONCLUSIONS
These data provide evidence for the safety and efficacy of duloxetine for the treatment for Korean women with SUI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Abrams P., Cardozo L., Khoury S., Wein A. International Consultation on Incontinence. 3rd ed.Plymouth: Health Publication Ltd;2005.2.Oh SJ., Park WH., Park CH., Paick JS., Seo JT., Lee YS, et al. Prevalence of urinary incontinence and incontinence-related quality of life in Korean women: a population-based study. J Korean Continence Soc. 2003. 7:73–80.
Article3.Chen GD., Lin TL., Hu SW., Chen YC., Lin LY. Prevalence and correlation of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder in Taiwanese women. Neurourol Urodyn. 2003. 22:109–17.
Article4.Ju CC., Swan LK., Merriman A., Choon TE., Viegas O. Urinary incontinence among the elderly people of Singapore. Age Ageing. 1991. 20:262–6.
Article5.Ma SS. The prevalence of adult female urinary incontinence in Hong Kong Chinese. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 1997. 8:327–31.
Article6.Yu HJ., Chen J., Lai MK., Chan KA., Chie WC. High prevalence of voiding symptoms in Taiwanese women. Br J Urol. 1998. 82:520–3.
Article7.Minassian VA., Drutz HP., Al Badr A. Urinary incontinence as a worldwide problem. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2003. 82:327–38.
Article8.Ueda T., Tamaki M., Kageyama S., Yoshimura N., Yoshida O. Urinary incontinence among community-dwelling people aged 40 years or older in Japan: prevalence, risk factors, knowledge and self-perception. Int J Urol. 2000. 7:95–103.
Article9.Fultz NH., Burgio K., Diokno AC., Kinchen KS., Obenchain R., Bump RC. Burden of stress urinary incontinence for community-dwelling women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003. 189:1275–82.
Article10.Kinchen KS., Burgio K., Diokno AC., Fultz NH., Bump R., Obenchain R. Factors associated with women' s decisions to seek treatment for urinary incontinence. J Womens Health. 2003. 12:687–98.11.Thor KB., Katofiasc MA. Effects of duloxetine, a combined serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, on central neural control of lower urinary tract function in the chloralose-anesthetized female cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995. 274:1014–24.12.Norton PA., Zinner NR., Yalcin I., Bump RC. Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002. 187:40–8.
Article13.Dmochowski RR., Miklos JR., Norton PA., Zinner NR., Yalcin I., Bump RC. Duloxetine versus placebo for the treatment of North American women with stress urinary incontinence. J Urol. 2003. 170:1259–63.
Article14.van Kerrebroeck P., Abrams P., Lange R., Slack M., Wyndaele JJ., Yalcin I, et al. Duloxetine versus placebo in the treatment of European and Canadian women with stress urinary incontinence. BJOG. 2004. 111:249–57.15.Millard RJ., Moore K., Rencken R., Yalcin I., Bump RC. Duloxetine vs placebo in the treatment of stress urinary incontinence: a four-continent randomized clinical trial. BJU Int. 2004. 93:311–8.
Article16.Wyman JF., Fantl JA., McClish DK., Bump RC. Comparative efficacy of behavioral interventions in the management of female urinary incontinence. Continence Program for Women Research Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1998. 179:999–1007.17.Kondo A., Yokoyama E., Koshiba K., Fukui J., Gotoh M., Yoshikawa Y, et al. Bladder neck support prosthesis: a nonoperative treatment for stress or mixed urinary incontinence. J Urol. 1997. 157:824–7.
Article18.Bodell DM., Leach GE. Needle suspension procedures for female incontinence. Urol Clin North Am. 2002. 29:575–84.
Article19.Rodriguez LV., Raz S. Prospective analysis of patients treated with a distal urethral polypropylene sling for symptoms of stress urinary incontinence: surgical outcome and satisfaction determined by patient driven questionnaires. J Urol. 2003. 170:857–63.20.Patrick DL., Martin ML., Bushnell DM., Yalcin I., Wagner TH., Buesching DP. Quality of life of women with urinary incontinence: further development of the incontinence quality of life instrument (I-QoL). Urology. 1999. 53:71–6.
Article21.Yalcin I., Bump RC. Validation of two global impression questionnaires for incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003. 189:98–101.
Article22.Os SJ., Park HG., Lim SH., Hong SK., Martin ML., Ting BL, et al. Translation and linguistic validation of Korean version of the incontinence quality of life (I-QoL) instrument. J Korean Continence Soc. 2002. 6:10–23.23.Cardozo L., Drutz HP., Baygani SK., Bump RC. Pharmacological treatment of women awaiting surgery for stress urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 2004. 104:511–9.
Article24.Komaroff AL., Fagioli LR., Doolittle TH., Gandek B., Gleit MA., Guerriero RT, et al. Health status in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and in general population and disease comparison groups. Am J Med. 1996. 101:281–90.
Article25.Lenderking WR., Nackley JF., Anderson RB., Testa MA. A review of the quality-of-life aspects of urinary urge incontinence. Pharmacoeconomics. 1996. 9:11–23.
Article26.Bump R., Yalcin I., Voss S. The effect of duloxetine dose escalation and tapering on the incidence of adverse events (Ae) in women with stress urinary incontinence. Int Continence Soc. 2005.27.Yalcin I., Bump RC. The effect of previous treatment experience and incontinence severity on the placebo response of stress urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004. 191:194–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Overactive Bladder Successfully Treated with Duloxetine in a Female Adolescent
- The Effect of Auricular Acupressure on Urinary Incontinence, Quality of Life, and Sleep Quality in Elderly Women with Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Two Cases of New Operative Technique in Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Female Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Continence Self-Efficacy to Increase PFM Exercise Adherence in SUI