Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm.
2013 Apr;8(1):32-37. 10.14777/kjutii.2013.8.1.32.
Effect of the Severity of Chronic Prostatitis Symptoms on Premature Ejaculation among Korean Males in Their 40-50s
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea. msk0701@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2289250
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14777/kjutii.2013.8.1.32
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to analyze the effect of the severity of chronic prostatitis symptoms on premature ejaculation among Korean males in their 40-50s.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From September 2011 to December 2012, we conducted a survey targeting 319 Koreans who had undergone medical examinations in our institution, using National Institute of Health chronic prostatitis symptom index (NIH-CPSI) and premature ejaculation diagnostic tool (PEDT).
RESULTS
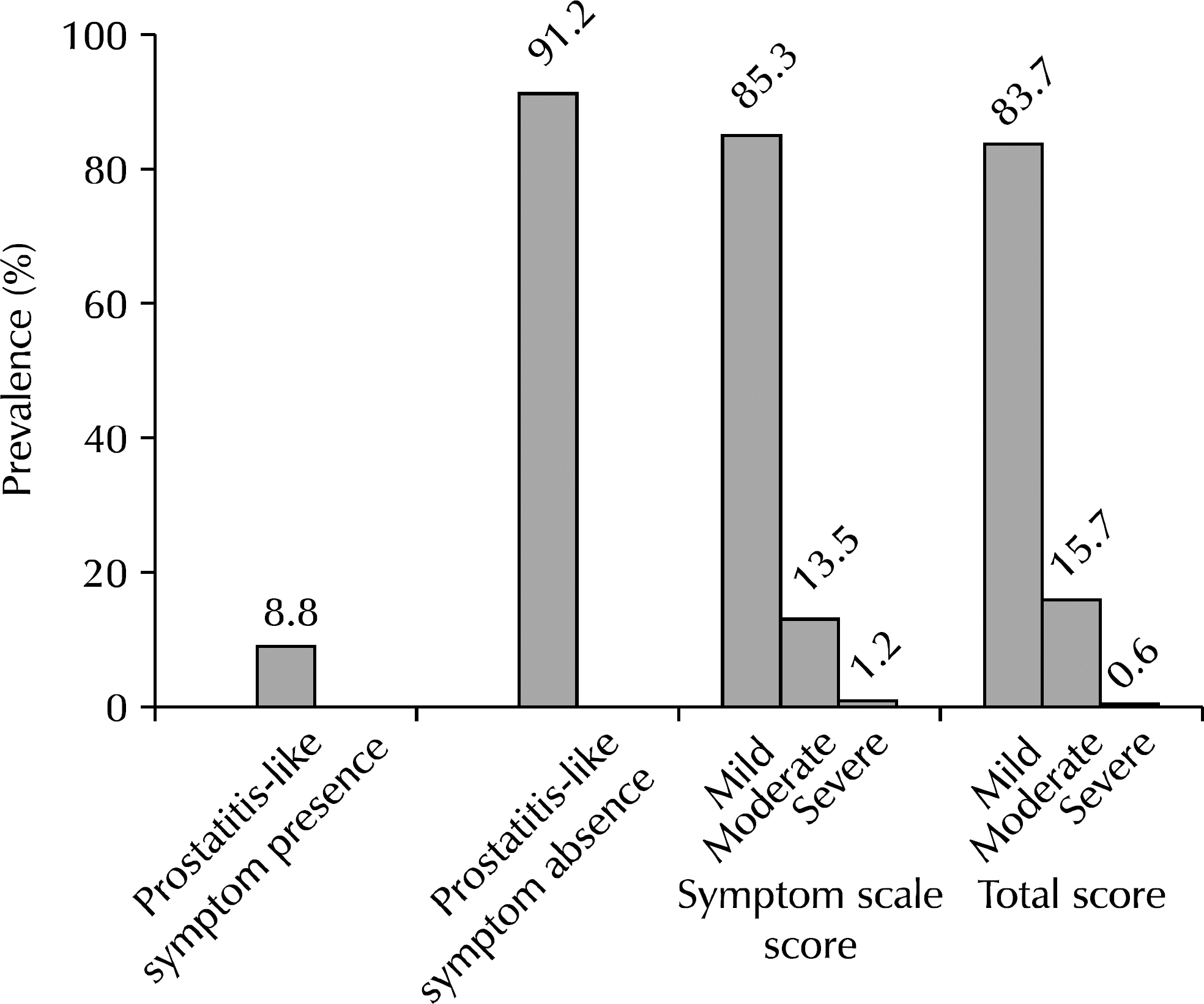
The average age of 319 volunteers was 50.8 years (40-59), the average total NIH-CPSI score was 8.6+/-6.2. And total PEDT score was 7.7+/-5.0. Twenty eight persons had chronic prostatitis-like symptoms (8.8%). Statistically significant differences in the prevalence of premature ejaculation were observed between persons with chronic prostatitis-like symptoms (82%) and those without (37.5%). In the same manner, the prevalence of premature ejaculation was higher in the moderate and severe symptom groups than in the mild symptom groups according to the symptom scale score (pain plus voiding score) and total score of NIH-CPSI (mild: 38.2%, moderate/severe: 59.6% by symptom scale score and mild: 36.7%, moderate/severe: 65.4% by total score). In univariate and multivariate analyses, presence or absence of chronic prostatitis-like symptoms and classification according to total NIH-CPSI score were independent predictive factors for the prevalence of premature ejaculation on PEDT.
CONCLUSIONS
Significant statistical relationships were observed between NIH-CPSI and PEDT in Korean males in their 40-50s who have chronic prostatitis-like symptoms or were classified into moderate and severe symptom groups according to total NIH-CPSI score.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ku JH, Lee SH, Jeon YS, Kim ME, Lee NK, Park YH. Epidemiologic study of chronic prostatitis-like symptoms surveyed among young men in the area of Taejeon and Chungnam: prevalence and influence of weather. Korean J Urol. 2002; 43:318–21.2. Roberts RO, Lieber MM, Rhodes T, Girman CJ, Bostwick DG, Jacobsen SJ. Prevalence of a physician-assigned diagnosis of prostatitis: the olmsted county study of urinary symptoms and health status among men. Urology. 1998; 51:578–84.
Article3. Pontari MA. Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urol Clin North Am. 2008; 35:81–9.
Article4. Litwin MS, McNaughton-Collins M, Fowler FJ Jr, Nickel JC, Calhoun EA, Pontari MA, et al. The National Institutes of Health chronic prostatitis symptom index: development and validation of a new outcome measure. Chronic Prostatitis Collaborative Research Network. J Urol. 1999; 162:369–75.5. Nickel JC, Downey J, Ardern D, Clark J, Nickel K. Failure of a monotherapy strategy for difficult chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol. 2004; 172:551–4.
Article6. Propert KJ, Alexander RB, Nickel JC, Kusek JW, Litwin MS, Landis JR, et al. Chronic Prostatitis Collaborative Research Network. Design of a multicenter randomized clinical trial for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urology. 2002; 59:870–6.
Article7. Taylor BC, Noorbaloochi S, McNaughton-Collins M, Saigal CS, Sohn MW, Pontari MA, et al. Urologic Diseases in America Project. Excessive antibiotic use in men with prostatitis. Am J Med. 2008; 121:444–9.
Article8. McMahon CG. Treatment of premature ejaculation with sertraline hydrochloride: a single-blind placebo controlled crossover study. J Urol. 1998; 159:1935–8.
Article9. Symonds T, Perelman MA, Althof S, Giuliano F, Martin M, May K, et al. Development and validation of a premature ejaculation diagnostic tool. Eur Urol. 2007; 52:565–73.
Article10. Shamloul R, el-Nashaar A. Chronic prostatitis in premature ejaculation: a cohort study in 153 men. J Sex Med. 2006; 3:150–4.11. Screponi E, Carosa E, Di Stasi SM, Pepe M, Carruba G, Jannini EA. Prevalence of chronic prostatitis in men with premature ejaculation. Urology. 2001; 58:198–202.
Article12. Xing JP, Fan JH, Wang MZ, Chen XF, Yang ZS. Survey of the prevalence of chronic prostatitis in men with premature ejaculation. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2003; 9:451–3.13. Liang CZ, Hao ZY, Li HJ, Wang ZP, Xing JP, Hu WL, et al. Prevalence of premature ejaculation and its correlation with chronic prostatitis in Chinese men. Urology. 2010; 76:962–6.
Article14. Gonen M, Kalkan M, Cenker A, Ozkardes H. Prevalence of premature ejaculation in Turkish men with chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Androl. 2005; 26:601–3.
Article15. Nickel JC, Downey J, Hunter D, Clark J. Prevalence of prostatitis-like symptoms in a population based study using the National Institutes of Health chronic prostatitis symptom index. J Urol. 2001; 165:842–5.
Article16. Waldinger MD. The neurobiological approach to premature ejaculation. J Urol. 2002; 168:2359–67.
Article17. Waldinger MD. Lifelong premature ejaculation: from authority-based to evidence-based medicine. BJU Int. 2004; 93:201–7.
Article18. Gurkan L, Oommen M, Hellstrom WJ. Premature ejaculation: current and future treatments. Asian J Androl. 2008; 10:102–9.
Article19. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Text revision DSM-IV-TR. 4th ed.Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association;2000.20. St Lawrence JS, Madakasira S. Evaluation and treatment of premature ejaculation: a critical review. Int J Psychiatry Med. 1992; 22:77–97.
Article21. World Health Organization. The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders: diagnostic criteria for research. Geneva (IL): World Health Organization;1993.22. Opsomer RJ, Guerit JM, Wese FX, Van Cangh PJ. Pudendal cortical somatosensory evoked potentials. J Urol. 1986; 135:1216–8.
Article23. Cho IR. Premature ejaculation and prostatitis. Proceeding of the 1st KAUPPC (The Korean Association of Urological Professional Primary Clinician) symposium on premature ejaculation. Seoul. 1997. 15–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Prevalence of the Symptoms of the Prostate Syndrome Patients Under 50
- The Effect Of Herb Cream(Ss-Cream) On Premature Ejaculation
- Prevalence of Premature Ejaculation in Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
- Reliability of Penile Biothesiometry, Vibration-Induced Ejaculation Test, Bulbocavernous Reflex Latency Test, and Dorsal Nerve Somatosensory Evoked Potential Test to Evaluate Penile Hypersensitivity and Nerve Conduction Pathway in Premature Ejaculation
- Clomipramine in the Treatment of Premature Ejaculation