J Clin Neurol.
2009 Jun;5(2):97-100. 10.3988/jcn.2009.5.2.97.
Stroke Mimicking Encephalopathy as an Initial Manifestation of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Stroke & Neural Stem Cell Laboratory in the Clinical Research Institute, Stem Cell Research Center, Seoul National Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Program in Neuroscience, Neuroscience Research Institute of the SNUMRC, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Epidemic Intelligence Service, Korea Center for Disease Control & Prevention, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Center for Alcohol and Drug Addiction Research, Seoul National Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2287662
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2009.5.2.97
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Systemic lymphoma can be difficult to recognize due to its diverse manifestations. Paraneoplastic leukoencephalopathy has rarely been reported in the context of lymphoma.
CASE REPORT
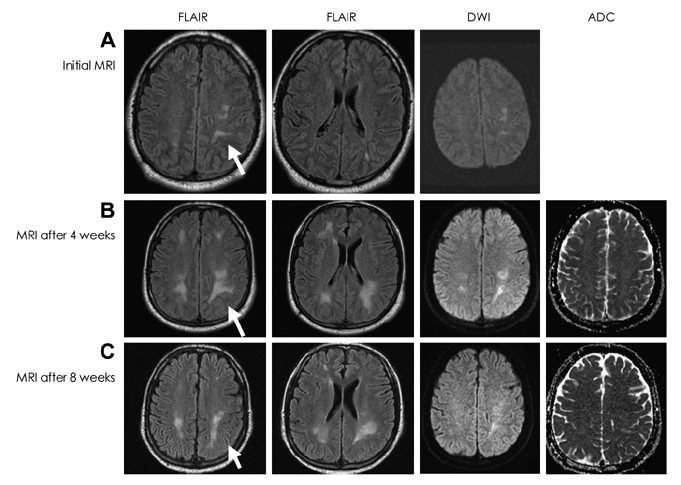
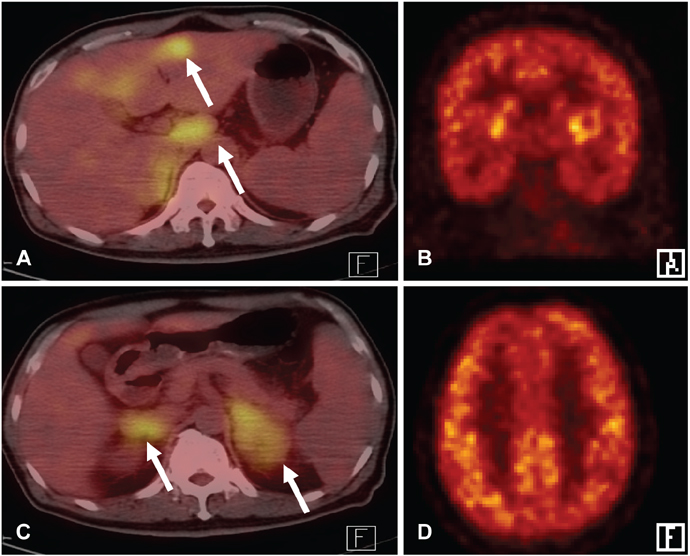
We report a 45-year-old man with systemic lymphoma whose initial manifestation was sudden-onset leukoencephalopathy, mimicking stroke. This patient, who was eventually diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, initially presented with sudden cognitive impairment and gait disturbance. Radiological studies suggested a paraneoplastic leukoencephalopathy. Chemotherapy for lymphoma resulted in clinical and radiological improvement.
CONCLUSIONS
The presented case indicates that diffuse large B-cell lymphoma may initially appear as a treatable leukoencephalopathy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Intravascular lymphoma as a Potential Cause of Recurrent Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source
Kyung Ah Woo, Dallah Yoo, Keun-Hwa Jung
J Clin Neurol. 2019;15(3):415-417. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2019.15.3.415.
Reference
-
1. Glass J. Neurologic complications of lymphoma and leukemia. Semin Oncol. 2006. 33:342–347.
Article2. Yoon JH, Bang OY, Kim HS. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in AIDS: proton MR spectroscopy patterns of asynchronous lesions confirmed by serial diffusion weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient mapping. J Clin Neurol. 2007. 3:200–203.
Article3. Phanthumchinda K, Rungruxsirivorn S. Encephaloradiculopathy: a non-metastatic complication of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Assoc Thai. 1991. 74:288–291.4. Gonzales N, Jarboe E, Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Bosque P. Acute multifocal CNS demyelination as first presentation of systemic malignancy. Neurology. 2005. 65:166.
Article5. Song DK, Boulis NM, McKeever PE, Quint DJ. Angiotropic large cell lymphoma with imaging characteristics of CNS vasculitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 23:239–242.6. Brecher K, Hochberg FH, Louis DN, de la Monte S, Riskind P. Case report of unusual leukoencephalopathy preceding primary CNS lymphoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998. 65:917–920.
Article7. Lövblad KO, Laubach HJ, Baird AE, Curtin F, Schlaug G, Edelman RR, et al. Clinical experience with diffusion-weighted MR in patients with acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998. 19:1061–1066.8. Fleming JO, Keegan BM, Parisi JE. A 52-year-old man with progressive left-sided weakness and white matter disease. Neurology. 2007. 69:600–606.
Article9. Karaarslan E, Arslan A. Diffusion weighted MR imaging in non-infarct lesions of the brain. Eur J Radiol. 2008. 65:402–416.
Article10. Baehring JM, Henchcliffe C, Ledezma CJ, Fulbright R, Hochberg FH. Intravascular lymphoma: magnetic resonance imaging correlates of disease dynamics within the central nervous system. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005. 76:540–544.
Article11. Palmedo H, Urbach H, Bender H, Schlegel U, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Matthies A, et al. FDG-PET in immunocompetent patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma: correlation with MRI and clinical follow-up. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006. 33:164–168.
Article12. Tenembaum S, Chitnis T, Ness J, Hahn JS. International Pediatric MS Study Group. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Neurology. 2007. 68(16):Suppl 2. S23–S36.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Mimicking Schwannoma of Lumbar Spine
- Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Mimicking Lacunar Infarction
- Relapse of Ocular Lymphoma following Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
- Non Hodgkin lymphoma in the maxillary sinus mimicking dental abscess: a case report
- Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma in a Patient with Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma