J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2016 Jun;32(2):130-134. 10.14368/jdras.2016.32.2.130.
Non Hodgkin lymphoma in the maxillary sinus mimicking dental abscess: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, Republic of Korea. 2460song@naver.com
- KMID: 2328895
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2016.32.2.130
Abstract
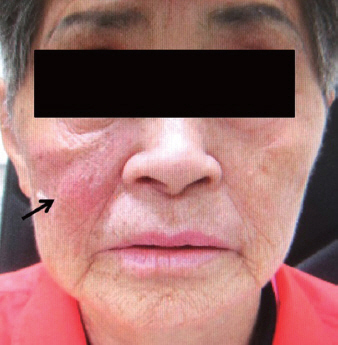
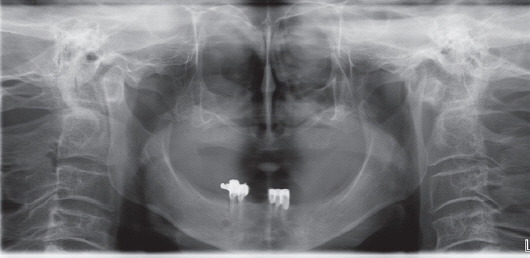
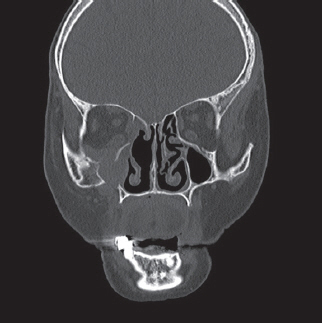
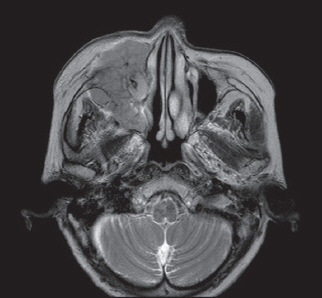
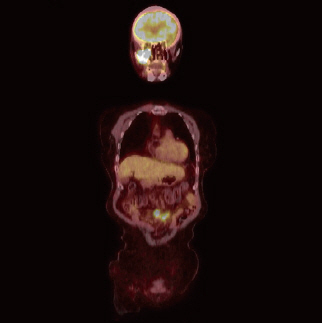
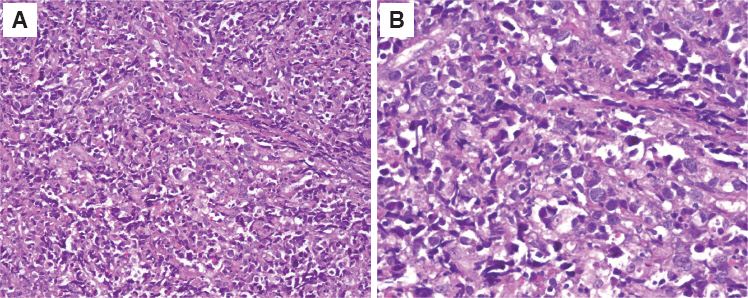
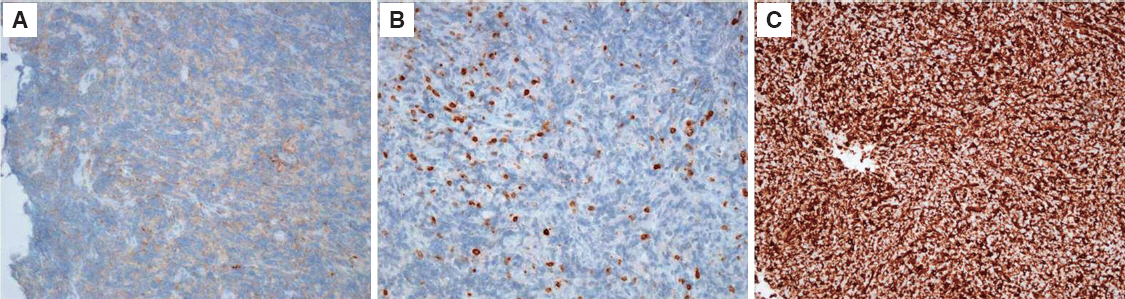
- Malignant lymphomas are neoplasms with diffuse proliferation of neoplastic lymphocytes and their precursor cells. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, which is a subtype of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, rarely occurs in the head and neck area and is especially rare in the maxillary sinus. We report a case of a 76-year-old female patient who was referred to the oral and maxillofacial surgery office for evaluation of a dental abscess as a clinical diagnosis. Laboratory tests revealed no signs of inflammation or infection; therefore, incisional biopsy was performed. The final diagnosis was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the maxillary sinus. Here we describe this case with a review of relevant literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bhattacharyya I, Chehal HK, Cohen DM, Al-Quran SZ. Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the oral cavity: germinal center classification. Head Neck Pathol. 2010; 4:181–91. DOI: 10.1007/s12105-010-0184-4. PMID: 20533006. PMCID: PMC2923304.2. Aral CA, Ağlarcı OS, Yılmaz HH, Taşlı F, Karaarslan S, Hatipoğlu F, Sanal MS. Diagnosis, PET/CT imaging, and treatment of extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma in keratinized gingiva: a case report. J Oral Sci. 2015; 57:59–62. DOI: 10.2334/josnusd.57.59. PMID: 25807910.3. Chalastras T, Elefteriadou A, Giotakis J, Soulandikas K, Korres S, Ferekidis E, Kandiloros D. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2007; 27:6–9. PMID: 17601204. PMCID: PMC2640014.4. Angiero F, Stegani M, Crippa R. Primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the mandibular gingiva with maxillary gingival recurrence. Oral Oncol Ext. 2006; 42:123–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ooe.2005.10.008.5. Adwani DG, Arora RS, Bhattacharya A, Bhagat B. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of maxillary sinus: an unusual presentation. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 3:95–7. DOI: 10.4103/2231-0746.110079. PMID: 23662270. PMCID: PMC3645622.6. Alacacioglu I, Ozcan MA, Ozkal S, Piskin O, Turgut N, Demirkan F, Ozsan GH, Kargi A, Undar B. Prognostic significance of immunohistochemical classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematology. 2009; 14:84–9. DOI: 10.1179/102453309X385205. PMID: 19298719.7. Kolokotronis A, Konstantinou N, Christakis I, Papadimitriou P, Matiakis A, Zaraboukas T, Antoniades D. Localized B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of oral cavity and maxillofacial region: a clinical study. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005; 99:303–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.03.028. PMID: 15716836.8. Coiffier B. State-of-the-art therapeutics: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:6387–93. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.015. PMID: 16155024.9. Tinoco P, Pereira JC, Ferreira FR, Carrara VL, Tinoco MB. B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma of the ethmoid sinus. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2013; 79:259. DOI: 10.5935/1808-8694.20130046. PMID: 23670337.10. Neves MC, Lessa MM, Voegels RL, Butugan O. Primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the frontal sinus: case report and review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J. 2005; 84:47–51. PMID: 15742775.11. Ferry JA, Sklar J, Zukerberg LR, Harris NL. Nasal lymphoma. A clinicopathologic study with immunophenotypic and genotypic analysis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991; 15:268–79. DOI: 10.1097/00000478-199103000-00007. PMID: 1996731.12. Yasumoto M, Taura S, Shibuya H, Honda M. Primary malignant lymphoma of the maxillary sinus: CT and MRI. Neuroradiology. 2000; 42:285–9. DOI: 10.1007/s002340050887. PMID: 10872174.13. Kumar G, Hingad N, Singh N, Sidhu GK. Diffuse large B - Cell lymphoma involving the maxilla in a minor. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8:ZD26–8. DOI: 10.7860/jcdr/2014/11446.5350.14. Drénou B, Lamy T, Amiot L, Fardel O, Caulet-Maugendre S, Sasportes M, Diebold J, Le Prisé PY, Fauchet R. CD3-CD56+non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas with an aggressive behavior related to multidrug resistance. Blood. 1997; 89:2966–74. PMID: 9108417.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Imaging characteristics of diffuse large cell extra nodal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma involving the palate and maxillary sinus: a case report
- Skeletal Muscle Lymphoma Mimicking Abscess
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Occurred in Psoas Muscle
- A Case of Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Mixed With Invasive Fungal Sinusitis of Maxillary Sinus
- Disappearance of a dental implant after migration into the maxillary sinus: an unusual case