J Clin Neurol.
2013 Jul;9(3):176-185. 10.3988/jcn.2013.9.3.176.
Complementarity between 18F-FDG PET/CT and Ultrasonography or Angiography in Carotid Plaque Characterization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. kdongeog@duih.org
- 2Department of Neurology, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Laboratory of Veterinary Dermatology and Neurology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungbuk National University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 4Laboratory of Genome to Drug Medicine, Joint Center for Biosciences, Incheon, Korea.
- 5Department of Radiology and Experimental Diagnostic Imaging, University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas, USA.
- 6Department of Nuclear Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 7Molecular Imaging and Neurovascular Research (MINER) Laboratory, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2287556
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2013.9.3.176
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
To estimate clinical roles of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) versus angiography and ultrasonography in carotid plaque characterization.
METHODS
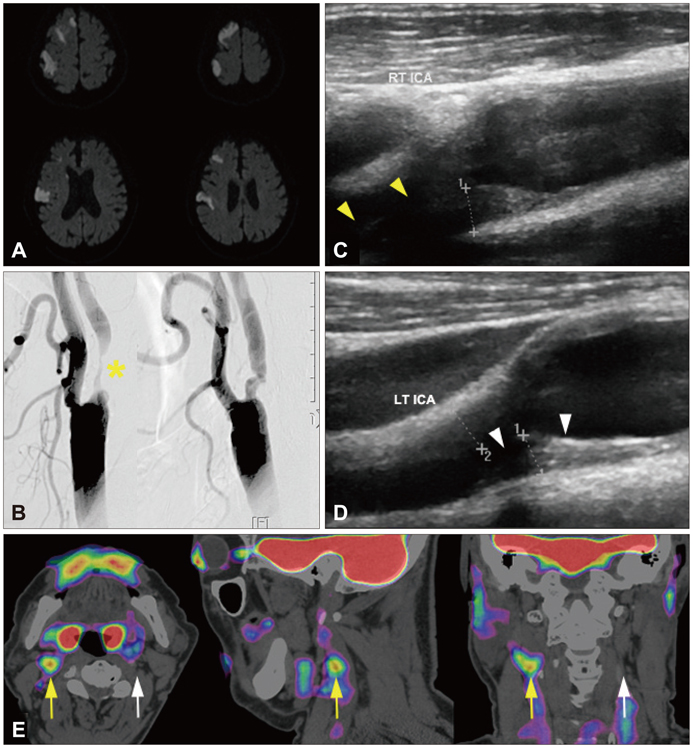
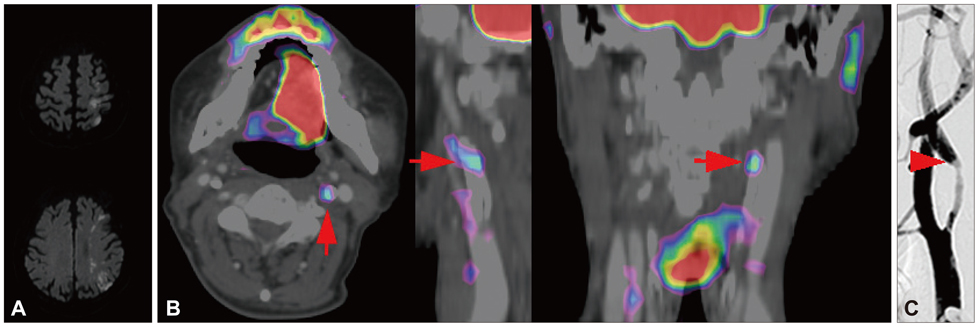
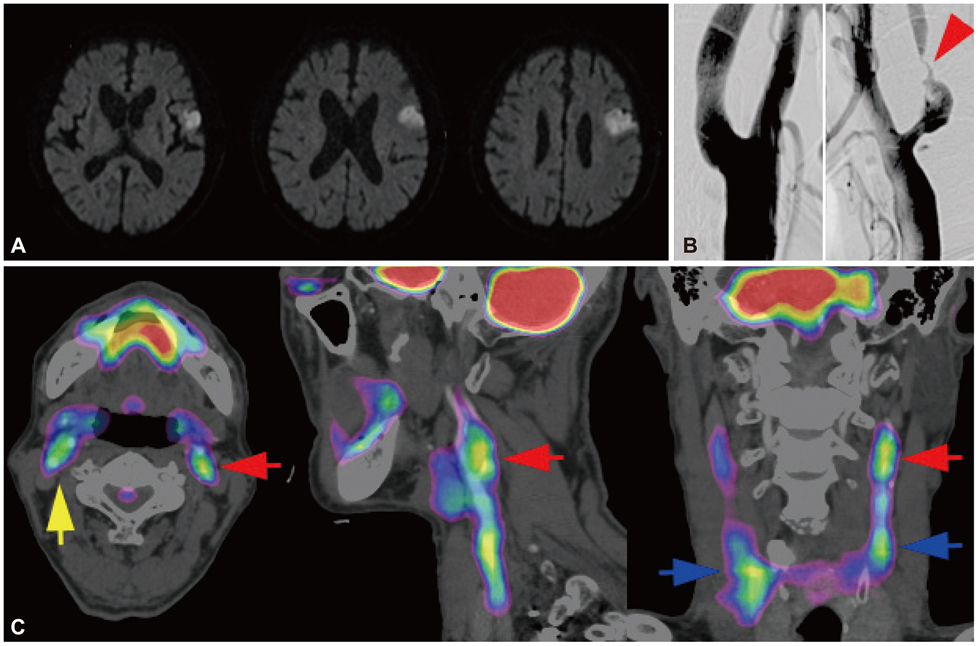
We characterized two groups of patients with recently (<1 month) symptomatic (n=14; age=71.8+/-8.6 years, mean+/-SD) or chronic (n=13, age=68.9+/-9.0 years) carotid stenosis using a battery of imaging tests: diffusion magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, MR or transfemoral angiography, duplex ultrasonography (DUS), and carotid FDG-PET/computed tomography.
RESULTS
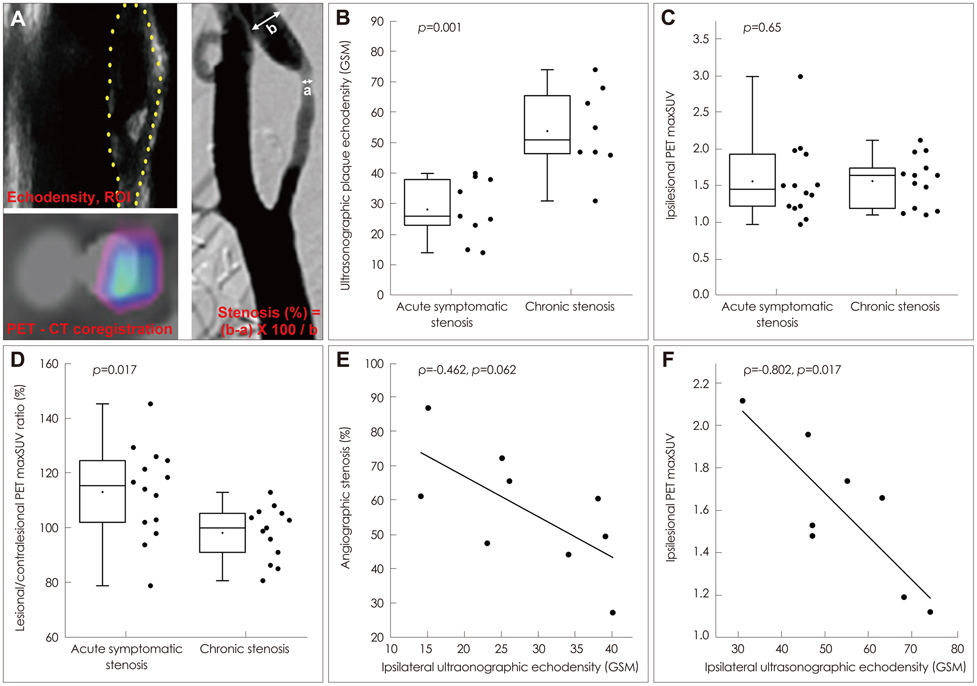
The degree of angiographic stenosis was greater in patients with recently symptomatic carotid plaques (67.5+/-21.5%) than in patients with chronic carotid plaques (32.4+/-26.8%, p=0.001). Despite the significant difference in the degree of stenosis, lesional maximum standardized uptake values (maxSUVs) on the carotid FDG-PET did not differ between the recently symptomatic (1.56+/-0.53) and chronic (1.56+/-0.34, p=0.65) stenosis groups. However, lesional-to-contralesional maxSUV ratios were higher in the recently symptomatic stenosis group (113+/-17%) than in the chronic stenosis group (98+/-10%, p=0.017). The grayscale median value of the lesional DUS echodensities was lower in the recently symptomatic stenosis group (28.2+/-10.0, n=9) than in the chronic stenosis group (53.9+/-14.0, n=8; p=0.001). Overall, there were no significant correlations between angiographic stenosis, DUS echodensity, and FDG-PET maxSUV. Case/subgroup analyses suggested complementarity between imaging modalities.
CONCLUSIONS
There were both correspondences and discrepancies between the carotid FDG-PET images and DUS or angiography data. Further studies are required to determine whether FDG-PET could improve the clinical management of carotid stenosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Writing Group Members. Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2010; 121:e46–e215.2. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993; 24:35–41.
Article3. Hermus L, van Dam GM, Zeebregts CJ. Advanced carotid plaque imaging. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010; 39:125–133.
Article4. Li ZY, Tang T, U-King-Im J, Graves M, Sutcliffe M, Gillard JH. Assessment of carotid plaque vulnerability using structural and geometrical determinants. Circ J. 2008; 72:1092–1099.
Article5. Lee DK, Nahrendorf M, Schellingerhout D, Kim DE. Will molecular optical imaging have clinically important roles in stroke management, and how? J Clin Neurol. 2010; 6:10–18.
Article6. Kolodgie FD, Nakazawa G, Sangiorgi G, Ladich E, Burke AP, Virmani R. Pathology of atherosclerosis and stenting. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2007; 17:285–301. vii
Article7. Libby P, Aikawa M. Stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques: new mechanisms and clinical targets. Nat Med. 2002; 8:1257–1262.
Article8. Tahara N, Imaizumi T, Virmani R, Narula J. Clinical feasibility of molecular imaging of plaque inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Nucl Med. 2009; 50:331–334.
Article9. Waki H, Masuyama T, Mori H, Maeda T, Kitade K, Moriyasu K, et al. Ultrasonic tissue characterization of the atherosclerotic carotid artery: histological correlates or carotid integrated backscatter. Circ J. 2003; 67:1013–1016.
Article10. Aikawa M, Manabe I, Chester A, Aikawa E. Cardiovascular inflammation. Int J Inflam. 2012; 2012:904608.
Article11. Morishige K, Kacher DF, Libby P, Josephson L, Ganz P, Weissleder R, et al. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging enhanced with superparamagnetic nanoparticles measures macrophage burden in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2010; 122:1707–1715.
Article12. Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002; 105:1135–1143.
Article13. Deguchi JO, Aikawa M, Tung CH, Aikawa E, Kim DE, Ntziachristos V, et al. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: visualizing matrix metalloproteinase action in macrophages in vivo. Circulation. 2006; 114:55–62.14. Sheikine Y, Akram K. FDG-PET imaging of atherosclerosis: do we know what we see? Atherosclerosis. 2010; 211:371–380.
Article15. Davies JR, Izquierdo-Garcia D, Rudd JH, Figg N, Richards HK, Bird JL, et al. FDG-PET can distinguish inflamed from non-inflamed plaque in an animal model of atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010; 26:41–48.
Article16. Rudd JH, Warburton EA, Fryer TD, Jones HA, Clark JC, Antoun N, et al. Imaging atherosclerotic plaque inflammation with [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Circulation. 2002; 105:2708–2711.
Article17. Marnane M, Merwick A, Sheehan OC, Hannon N, Foran P, Grant T, et al. Carotid plaque inflammation on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography predicts early stroke recurrence. Ann Neurol. 2012; 71:709–718.
Article18. Ben-Haim S, Kupzov E, Tamir A, Frenkel A, Israel O. Changing patterns of abnormal vascular wall F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on follow-up PET/CT studies. J Nucl Cardiol. 2006; 13:791–800.
Article19. Spagnoli LG, Bonanno E, Sangiorgi G, Mauriello A. Role of inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Nucl Med. 2007; 48:1800–1815.
Article20. Menezes LJ, Kayani I, Ben-Haim S, Hutton B, Ell PJ, Groves AM. What is the natural history of 18F-FDG uptake in arterial atheroma on PET/CT? Implications for imaging the vulnerable plaque. Atherosclerosis. 2010; 211:136–140.
Article21. Laurberg JM, Olsen AK, Hansen SB, Bottcher M, Morrison M, Ricketts SA, et al. Imaging of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques with FDG-microPET: no FDG accumulation. Atherosclerosis. 2007; 192:275–282.
Article22. Okane K, Ibaraki M, Toyoshima H, Sugawara S, Takahashi K, Miura S, et al. 18F-FDG accumulation in atherosclerosis: use of CT and MR co-registration of thoracic and carotid arteries. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006; 33:589–594.
Article23. Davies JR, Rudd JH, Fryer TD, Graves MJ, Clark JC, Kirkpatrick PJ, et al. Identification of culprit lesions after transient ischemic attack by combined 18F fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography and high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke. 2005; 36:2642–2647.
Article24. Kim DE, Kim JY, Schellingerhout D, Kim EJ, Kim HK, Lee S, et al. Protease imaging of human atheromata captures molecular information of atherosclerosis, complementing anatomic imaging. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010; 30:449–456.
Article25. Sitzer M, Puac D, Buehler A, Steckel DA, von Kegler S, Markus HS, et al. Internal carotid artery angle of origin: a novel risk factor for early carotid atherosclerosis. Stroke. 2003; 34:950–955.26. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial. Methods, patient characteristics, and progress. Stroke. 1991; 22:711–720.27. Ferguson GG, Eliasziw M, Barr HW, Clagett GP, Barnes RW, Wallace MC, et al. The North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial: surgical results in 1415 patients. Stroke. 1999; 30:1751–1758.
Article28. Rudd JH, Myers KS, Bansilal S, Machac J, Rafique A, Farkouh M, et al. (18)Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging of atherosclerotic plaque inflammation is highly reproducible: implications for atherosclerosis therapy trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 50:892–896.
Article29. Rudd JH, Myers KS, Bansilal S, Machac J, Pinto CA, Tong C, et al. Atherosclerosis inflammation imaging with 18F-FDG PET: carotid, iliac, and femoral uptake reproducibility, quantification methods, and recommendations. J Nucl Med. 2008; 49:871–878.
Article30. AbuRahma AF, Wulu JT Jr, Crotty B. Carotid plaque ultrasonic heterogeneity and severity of stenosis. Stroke. 2002; 33:1772–1775.
Article31. Spagnoli LG, Mauriello A, Sangiorgi G, Fratoni S, Bonanno E, Schwartz RS, et al. Extracranial thrombotically active carotid plaque as a risk factor for ischemic stroke. JAMA. 2004; 292:1845–1852.
Article32. Graebe M, Pedersen SF, Højgaard L, Kjaer A, Sillesen H. 18FDG PET and ultrasound echolucency in carotid artery plaques. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010; 3:289–295.
Article33. Wassélius J, Larsson S, Jacobsson H. Time-to-time correlation of high-risk atherosclerotic lesions identified with [(18)F]-FDG-PET/CT. Ann Nucl Med. 2009; 23:59–64.
Article34. Tahara N, Kai H, Nakaura H, Mizoguchi M, Ishibashi M, Kaida H, et al. The prevalence of inflammation in carotid atherosclerosis: analysis with fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography. Eur Heart J. 2007; 28:2243–2248.
Article35. van der Wal AC, Becker AE. Atherosclerotic plaque rupture--pathologic basis of plaque stability and instability. Cardiovasc Res. 1999; 41:334–344.
Article36. van Gils MJ, Homburg PJ, Rozie S, de Weert TT, Dippel DW, van der Lugt A. Evolution of atherosclerotic carotid plaque morphology: do ulcerated plaques heal? A serial multidetector CT angiography study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011; 31:263–270.
Article37. Cohade C, Mourtzikos KA, Wahl RL. "USA-Fat": prevalence is related to ambient outdoor temperature-evaluation with 18F-FDG PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 2003; 44:1267–1270.38. Zhou SM, Wong TZ, Marks LB. Using FDG-PET activity as a surrogate for tumor cell density and its effect on equivalent uniform dose calculation. Med Phys. 2004; 31:2577–2583.
Article39. Kwee RM, Teule GJ, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Mess WH, Prins MH, van der Geest RJ, et al. Multimodality imaging of carotid artery plaques: 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke. 2009; 40:3718–3724.40. Bassiouny HS, Davis H, Massawa N, Gewertz BL, Glagov S, Zarins CK. Critical carotid stenoses: morphologic and chemical similarity between symptomatic and asymptomatic plaques. J Vasc Surg. 1989; 9:202–212.
Article41. Rothwell PM, Gibson R, Warlow CP. Interrelation between plaque surface morphology and degree of stenosis on carotid angiograms and the risk of ischemic stroke in patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis. On behalf of the European Carotid Surgery Trialists' Collaborative Group. Stroke. 2000; 31:615–621.
Article42. Prabhakaran S, Rundek T, Ramas R, Elkind MS, Paik MC, Boden-Albala B, et al. Carotid plaque surface irregularity predicts ischemic stroke: the northern Manhattan study. Stroke. 2006; 37:2696–2701.
Article