J Breast Cancer.
2012 Mar;15(1):57-64. 10.4048/jbc.2012.15.1.57.
Imaging Findings of Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Breast
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. med20@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pathology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2286474
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2012.15.1.57
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to evaluate imaging and histopathologic findings including the immunohistochemical characteristics of invasive micropapillary carcinoma (IMPC) of the breast.
METHODS
Twenty-nine patients diagnosed with IMPC were included in the present study. Mammographic, sonographic, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings were analyzed retrospectively according to the American College of Radiology Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System lexicon. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) findings were also evaluated. Microscopic slides of surgical specimens were reviewed in consensus by two pathologists with a specialty in breast pathology.
RESULTS
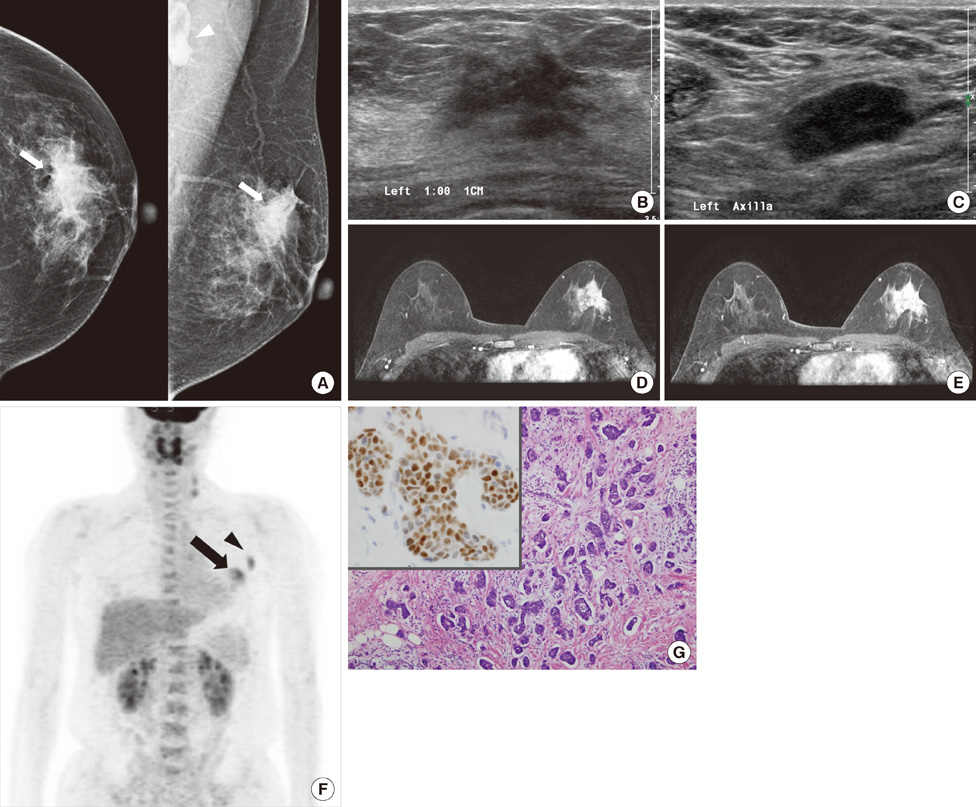
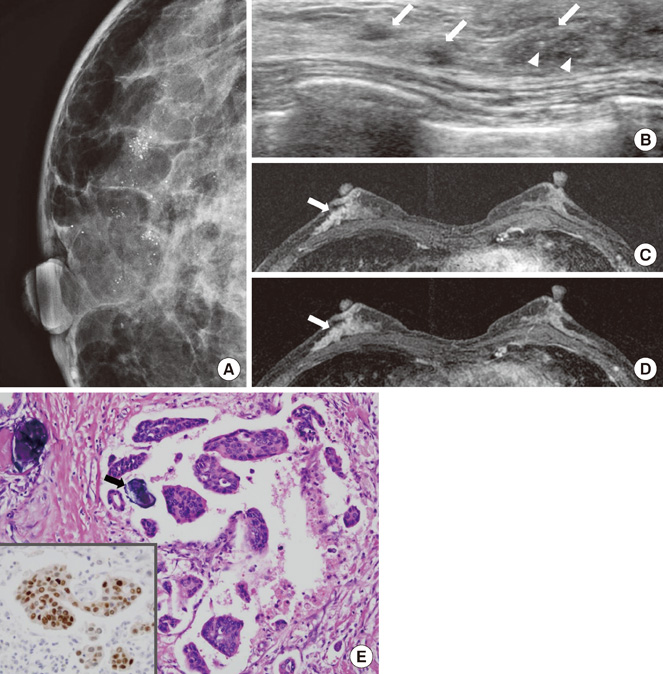
Most IMPCs presented as a high density irregular mass with a non-circumscribed margin associated with microcalcifications on mammography, as an irregular hypoechoic mass with a spiculated margin on ultrasound, and as irregular spiculated masses with washout patterns on MRI. PET-CT showed a high maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) (mean, 11.2). Axillary nodal metastases were identified in 65.5% of the patients. Immunohistochemical studies showed high positivities for estrogen receptor and c-erbB-2 (93.1% and 51.7micro, respectively).
CONCLUSION
Even though the imaging characteristics of IMPCs are not distinguishable from typical invasive ductal carcinomas, this tumor type frequently results in nodal metastases and high positivities for both estrogen receptor and c-erbB-2. The high SUVmax value that is apparent on PET-CT might be helpful in the diagnosis of IMPC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma in Axillary Ectopic Breast and Synchronous Ductal Carcinoma In Situ in the Contralateral Breast
Seung Won Oh, Hyo Soon Lim, Ji Shin Lee, Sung Min Moon, Min Ho Park
J Breast Cancer. 2017;20(3):314-318. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2017.20.3.314.
Reference
-
1. Petersen JL. Breast carcinomas with an unexpected inside-out growth pattern: rotation of polarization associated with angioinvasion. Pathol Res Pract. 1993. 189:A780.2. Adrada B, Arribas E, Gilcrease M, Yang WT. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: mammographic, sonographic, and MRI features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009. 193:W58–W63.
Article3. Siriaunkgul S, Tavassoli FA. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. Mod Pathol. 1993. 6:660–662.4. Zekioglu O, Erhan Y, Ciris M, Bayramoglu H, Ozdemir N. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: high incidence of lymph node metastasis with extranodal extension and its immunohistochemical profile compared with invasive ductal carcinoma. Histopathology. 2004. 44:18–23.
Article5. Gunhan-Bilgen I, Zekioglu O, Ustün EE, Memis A, Erhan Y. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: clinical, mammographic, and sonographic findings with histopathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:927–931.6. Kim DS, Cho N, Ko ES, Kim DY, Yang SK, Kim SJ, et al. Imaging and the clinical-pathologic features of invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2007. 56:497–503.
Article7. Yang WT, Chang J, Metreweli C. Patients with breast cancer: differences in color Doppler flow and gray-scale US features of benign and malignant axillary lymph nodes. Radiology. 2000. 215:568–573.
Article8. Tavassoli FA, Devilee P. International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Breast and Female Genital Organs. 2003. Lyon: IAPS Press;35–36.9. Guo X, Chen L, Lang R, Fan Y, Zhang X, Fu L. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: association of pathologic features with lymph node metastasis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006. 126:740–746.10. Wong SI, Cheung H, Tse GM. Fine needle aspiration cytology of invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. A case report. Acta Cytol. 2000. 44:1085–1089.
Article11. Gil-Rendo A, Martínez-Regueira F, Zornoza G, García-Velloso MJ, Beorlegui C, Rodriguez-Spiteri N. Association between [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and prognostic parameters in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2009. 96:166–170.
Article12. Ueda S, Tsuda H, Asakawa H, Shigekawa T, Fukatsu K, Kondo N, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic relevance of uptake level using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography fusion imaging (18F-FDG PET/CT) in primary breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008. 38:250–258.
Article13. Cermik TF, Mavi A, Basu S, Alavi A. Impact of FDG PET on the preoperative staging of newly diagnosed breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008. 35:475–483.
Article14. Choi WH, Kim SH, Yoo LR, Park YH, Lee SY, Sohn HS, et al. Pre-operative FDG PET/CT findings related to early tumor recurrence in breast cancer patients. 2007. In : The Society of Nuclear Medicine 54th Annual Meeting; Abstract #47.15. Kim MJ, Gong G, Joo HJ, Ahn SH, Ro JY. Immunohistochemical and clinicopathologic characteristics of invasive ductal carcinoma of breast with micropapillary carcinoma component. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2005. 129:1277–1282.
Article16. Luna-Moré S, delosSantos F, Bretón JJ, Cañadas MA. Estrogen and progesterone receptors, c-erbB-2, p53, and Bcl-2 in thirty-three invasive micropapillary breast carcinomas. Pathol Res Pract. 1996. 192:27–32.
Article17. Nassar H, Wallis T, Andea A, Dey J, Adsay V, Visscher D. Clinicopathologic analysis of invasive micropapillary differentiation in breast carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2001. 14:836–841.
Article18. Paterakos M, Watkin WG, Edgerton SM, Moore DH 2nd, Thor AD. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: a prognostic study. Hum Pathol. 1999. 30:1459–1463.19. Walsh MM, Bleiweiss IJ. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast: eighty cases of an underrecognized entity. Hum Pathol. 2001. 32:583–589.
Article20. Yu JH, Kim SW, Han WS, Kim SW, Park IA, Youn YK, et al. Micropapillary carcinoma of breast. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2004. 7:132–135.
Article21. Tresserra F, Grases PJ, Fábregas R, Férnandez-Cid A, Dexeus S. Invasive micropapillary carcinoma. Distinct features of a poorly recognized variant of breast carcinoma. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 1999. 20:205–208.22. Kim JK, Song YJ, Cho SI, Ryu DH, Yun HY, Sung RH. Clinicopathologic significance of p53 and c-erbB-2 protein expression in breast carcinoma. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2002. 5:59–64.
Article23. Barbati A, Cosmi EV, Sidoni A, Collini P, Porpora MG, Ferri I, et al. Value of c-erbB-2 and p53 oncoprotein co-overexpression in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 1997. 17:401–405.24. Bebenek M, Bar JK, Harlozinska A, Sedlaczek P. Prospective studies of p53 and c-erbB-2 expression in relation to clinicopathological parameters of human ductal breast cancer in the second stage of clinical advancement. Anticancer Res. 1998. 18(1B):619–623.25. Bertheau P, Steinberg SM, Merino MJ. C-erbB-2, p53, and nm23 gene product expression in breast cancer in young women: immunohistochemical analysis and clinicopathologic correlation. Hum Pathol. 1998. 29:323–329.
Article26. Ross JS, Fletcher JA. The HER-2/neu oncogene: prognostic factor, predictive factor and target for therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 1999. 9:125–138.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma in Breast Presented as Hyperechoic Mass with Coarse Macrocalcifications: A Case Report
- Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Breast: A clinicopathologic study of 16 cases
- Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic, Sonographic and MR Imaging Findings
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Breast
- Prognostic Significance of a Micropapillary Pattern in Pure Mucinous Carcinoma of the Breast: Comparative Analysis with Micropapillary Carcinoma