J Bone Metab.
2014 Aug;21(3):223-226. 10.11005/jbm.2014.21.3.223.
Intravenous Zoledronate for a Patient with Paget's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dankook University School of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. puhoo73@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2286293
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2014.21.3.223
Abstract
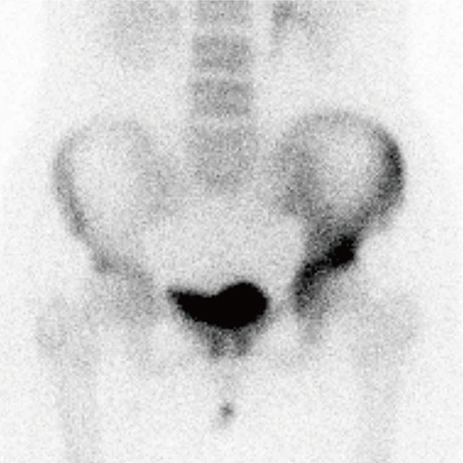
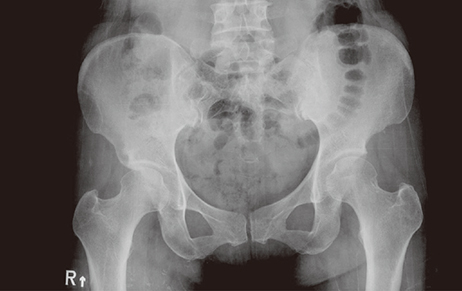
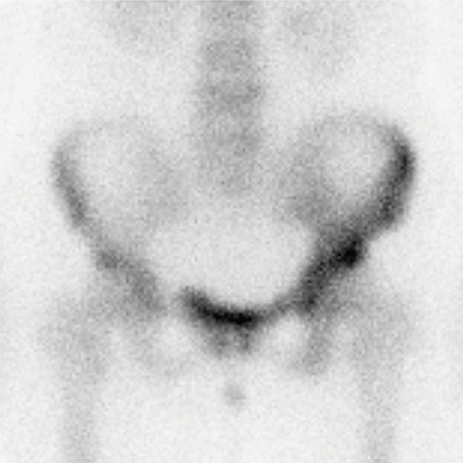
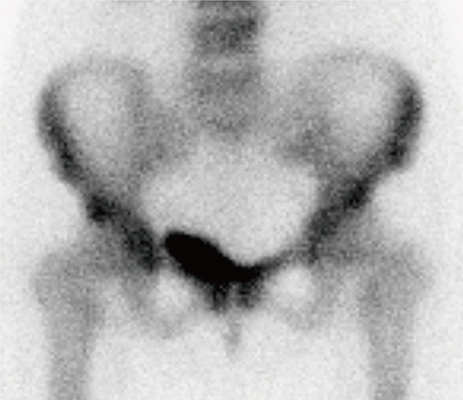
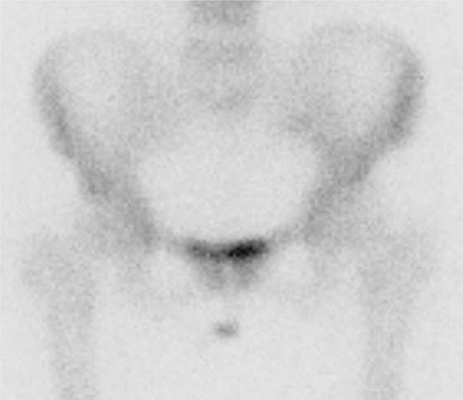
- Paget's disease (PD) of bone is characterized by increase of bone resorption by atypical osteoclasts, followed by rapid new bone formation resulting in a disorganized mosaic bone. Although the pathophysiology is not fully understood, bisphosphonate, which is a potent anti-resorptive agent for treatment of osteoporosis, have been the most effective agents available for the treatment of PD. We report a case of PD of bone in a 49-year-old woman patient, who was treated with intravenous zoledronate.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lyles KW, Siris ES, Singer FR, et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis and management of Paget's disease of bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2001; 16:1379–1387.
Article2. Cundy T, Reid IR. Paget's disease of bone. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45:43–48.
Article3. Ralston SH, Langston AL, Reid IR. Pathogenesis and management of Paget's disease of bone. Lancet. 2008; 372:155–163.
Article4. Galson DL, Roodman GD. Pathobiology of Paget's Disease of Bone. J Bone Metab. 2014; 21:85–98.
Article5. Black DM, Delmas PD, Eastell R, et al. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:1809–1822.
Article6. Lyles KW, Colón-Emeric CS, Magaziner JS, et al. Zoledronic acid and clinical fractures and mortality after hip fracture. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:1799–1809.
Article7. Reid IR, Brown JP, Burckhardt P, et al. Intravenous zoledronic acid in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:653–661.
Article8. Tucci JR. Therapy with zoledronic acid, 5 mg, for a patient with Paget disease of bone. Endocr Pract. 2008; 14:607–610.
Article9. Boonen S, Vanderschueren D, Venken K, et al. Recent developments in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis with bisphosphonates: enhanced efficacy by enhanced compliance. J Intern Med. 2008; 264:315–332.
Article10. Kamatari M, Koto S, Ozawa N, et al. Factors affecting long-term compliance of osteoporotic patients with bisphosphonate treatment and QOL assessment in actual practice: alendronate and risedronate. J Bone Miner Metab. 2007; 25:302–309.
Article11. Kertes J, Dushenat M, Vesterman JL, et al. Factors contributing to compliance with osteoporosis medication. Isr Med Assoc J. 2008; 10:207–213.12. Reid IR, Miller P, Lyles K, et al. Comparison of a single infusion of zoledronic acid with risedronate for Paget's disease. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:898–908.
Article13. Hosking D, Lyles K, Brown JP, et al. Long-term control of bone turnover in Paget's disease with zoledronic acid and risedronate. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22:142–148.
Article14. Lee YK, Nho JH, Ha YC, et al. Persistence with intravenous zoledronate in elderly patients with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2012; 23:2329–2333.
Article15. Lee YK, Kim KC, Choi HY, et al. Intravenous zolendronic acid for the patients treated operatively after hip fracture: a short-term safety prospective cohort study. J Korean Hip Soc. 2008; 20:305–310.
Article