Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2010 Aug;14(4):241-248. 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.4.241.
Inhibitory Effects of Olmesartan on Catecholamine Secretion from the Perfused Rat Adrenal Medulla
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 710-744, Korea.
- 2Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju 501-759, Korea.
- 3Department of Pharmacology, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju 501-759, Korea. dylim@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2285409
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.4.241
Abstract
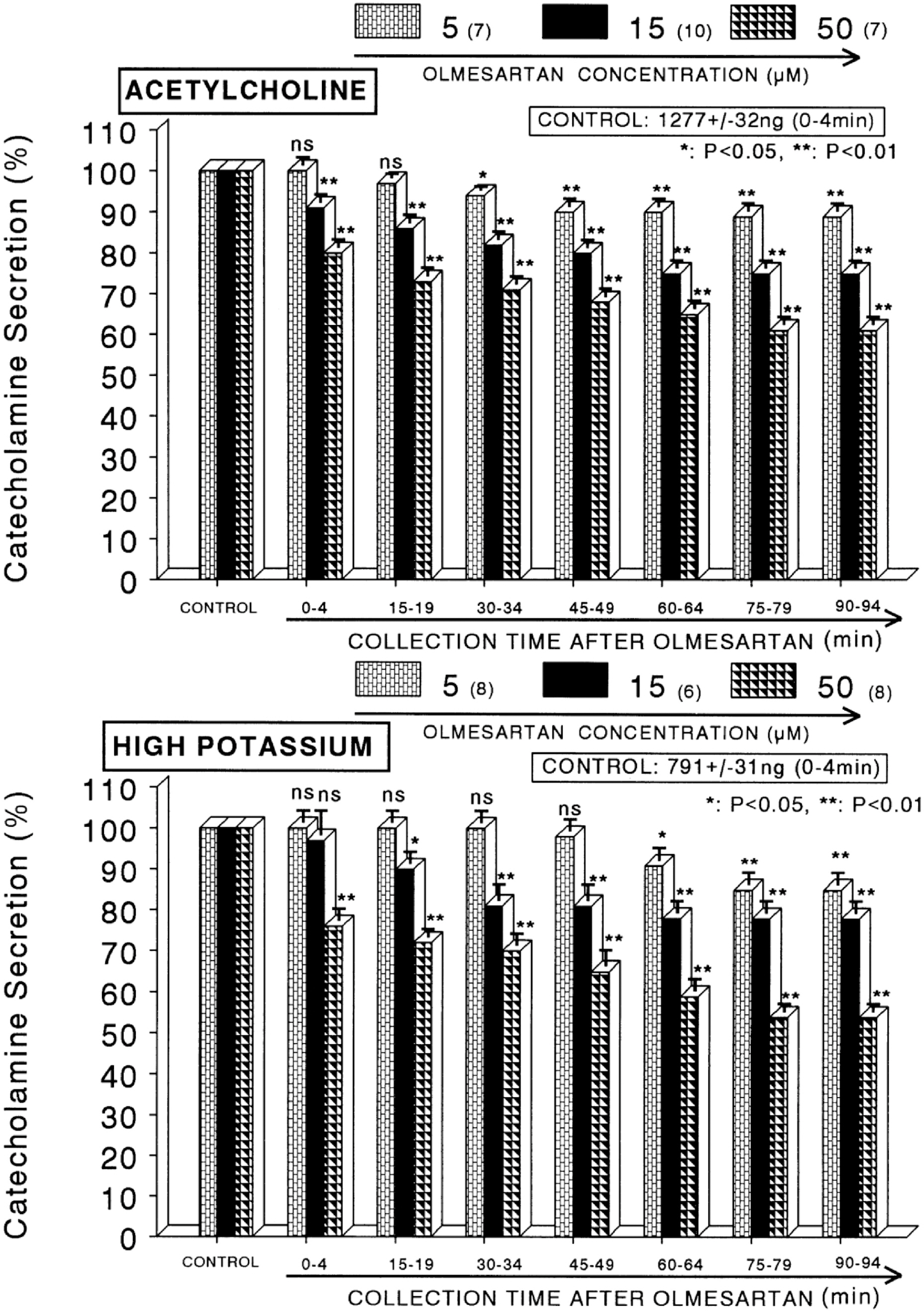
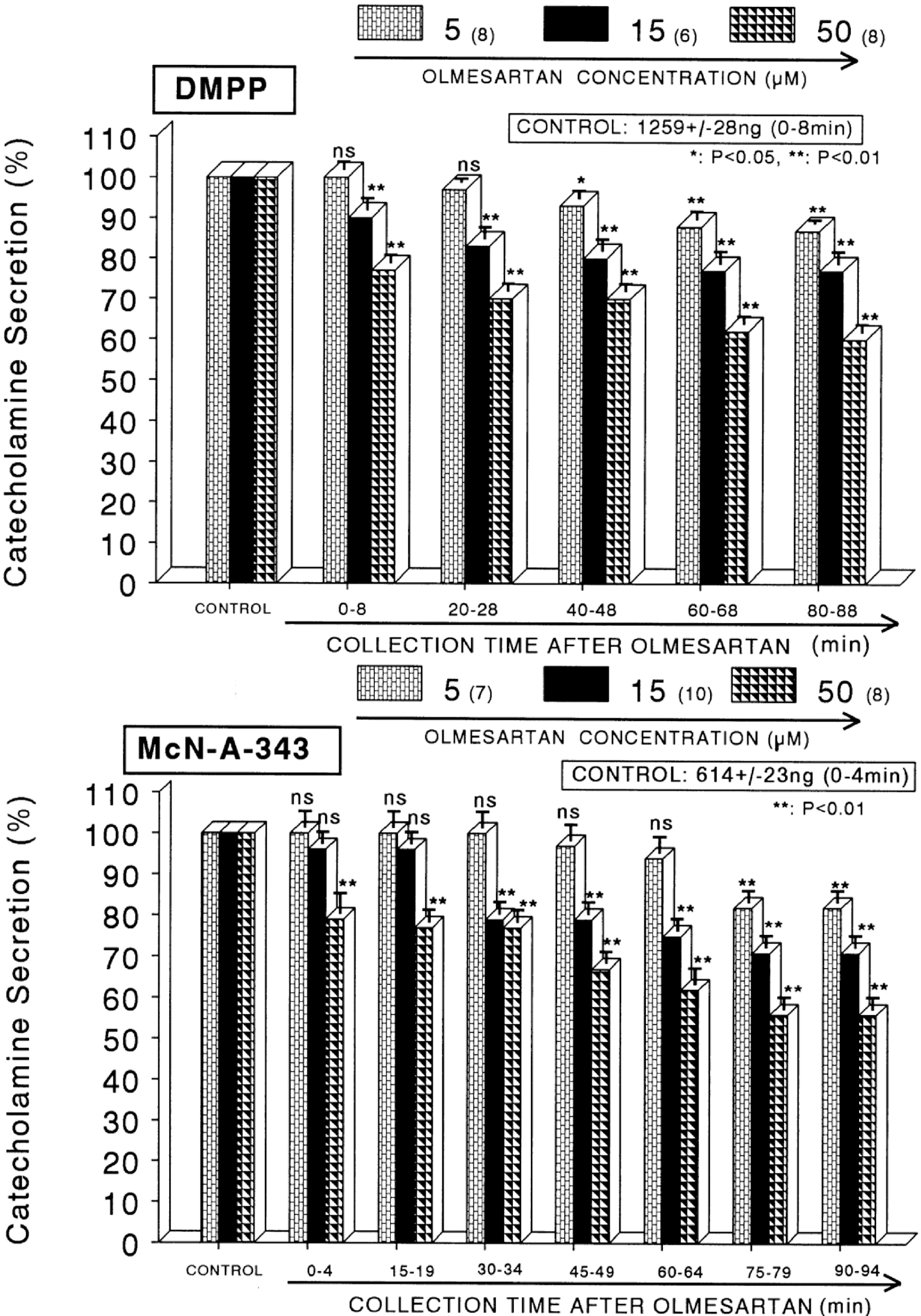
- The present sutdy aimed to determine whether olmesartan, an angiotensin II (Ang II) type 1 (AT1) receptor blocker, can influence the CA release from the isolated perfused model of the rat adrenal medulla. Olmesartan (5~50 micrometer) perfused into an adrenal vein for 90 min produced dose- and time-dependent inhibition of the CA secretory responses evoked by ACh (5.32 mM), high K+ (56 mM, a direct membrane-depolarizer), DMPP (100 micrometer) and McN-A-343 (100 micrometer). Olmesartan did not affect basal CA secretion. Also, in adrenal glands loaded with olmesartan (15 micrometer), the CA secretory responses evoked by Bay-K-8644 (10 micrometer, an activator of voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ channels), cyclopiazonic acid (10 micrometer, an inhibitor of cytoplasmic Ca2+ -ATPase), veratridine (100 micrometer, an activator of voltage-dependent Na+ channels), and Ang II (100 nM) were markedly inhibited. However, at high concentrations (150~300 micrometer), olmesartan rather enhanced the ACh-evoked CA secretion. Taken together, these results show that olmesartan at low concentrations inhibits the CA secretion evoked by cholinergic stimulation (both nicotininc and muscarinic receptors) as well as by direct membrane depolarization from the rat adrenal medulla, but at high concentrations it rather potentiates the ACh-evoked CA secretion. It seems that olmesartan has a dual action, acting as both agonist and antagonist at nicotinic receptors of the isolated perfused rat adrenal medulla, which might be dependent on the concentration. It is also thought that this inhibitory effect of olmesartan may be mediated by blocking the influx of both Na+ and Ca2+ into the rat adrenomedullary chromaffin cells as well as by inhibiting the Ca2+ release from the cytoplasmic calcium store, which is thought to be relevant to the AT1 receptor blockade, in addition to its enhancement on the CA secreton.
MeSH Terms
-
(4-(m-Chlorophenylcarbamoyloxy)-2-butynyl)trimethylammonium Chloride
3-Pyridinecarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-, Methyl ester
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal Medulla
Angiotensin II
Animals
Calcium
Chromaffin Cells
Cytoplasm
Dimethylphenylpiperazinium Iodide
Imidazoles
Indoles
Membranes
Rats
Receptors, Nicotinic
Tetrazoles
Veins
Veratridine
(4-(m-Chlorophenylcarbamoyloxy)-2-butynyl)trimethylammonium Chloride
3-Pyridinecarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-5-nitro-4-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-, Methyl ester
Angiotensin II
Calcium
Dimethylphenylpiperazinium Iodide
Imidazoles
Indoles
Receptors, Nicotinic
Tetrazoles
Veratridine
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Influence of Fimasartan (a Novel AT1 Receptor Blocker) on Catecholamine Release in the Adrenal Medulla of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Hyo-Jeong Lim, Seog-Ki Lee, Dong-Yoon Lim
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;17(1):99-109. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.1.99.
Reference
-
References
1. Mire DE, Silfani TN, Pugsley MK. A review of the structural and functional features of olmesartan medoxomil, an angiotensin receptor blocker. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2005; 46:585–593.
Article2. Mizuno M, Sada T, Ikeda M, Fukuda N, Miyamoto M, Yanagisawa H, Koike H. Pharmacology of CS-866, a novel nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995; 285:181–188.
Article3. Burnier M. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers. Circulation. 2001; 103:904–912.
Article4. Goodfriend TL, Elliott ME, Catt KJ. Angiotensin receptors and their antagonists. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:1649–1654.
Article5. Kakuta H, Sudoh K, Sasamata M, Yamagishi S. Telmisartan has the strongest binding affinity to angiotensin II type 1 receptor: comparison with other angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 2005; 25:41–46.6. Le MT, Pugsley MK, Vauquelin G, Van Liefde I. Molecular characterisation of the interactions between olmesartan and telmisartan and the human angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2007; 151:952–962.7. Oparil S, Silfani TN, Walker JF. Role of angiotensin receptor blockers as monotherapy in reaching blood pressure goals. Am J Hypertens. 2005; 18:287–294.
Article8. Smith DHG. Strategies to meet lower blood pressure goals with a new standard in angiotensin II receptor blockade. Am J Hypertens. 2002; 15:108–114.
Article9. Teschemacher AG, Seward EP. Bidirectional modulation of exocytosis by angiotensin II involves multiple G-protein-regulated transduction pathways in chromaffin cells. The J Neurosci. 2000; 20:4776–4785.
Article10. Uresin Y, Erbas B, Ozek M, Ozkök E, Gürol AO. Losartan may prevent the elevation of plasma glucose, corticosterone and catecholamine levels induced by chronic stress. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2004; 5:93–96.11. Seltzer A, Bregonzio C, Armando I, Baiardi G, Saavedra JM. Oral administration of an AT1 receptor antagonist prevents the central effects of angiotensin II in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res. 2004; 1028:9–18.12. Critchley L, Ding B, Fok B, Wang D, Tomlinson B, James A, Thomas GN, Critchley J. The effects of candesartan and ramipril on adrenal catecholamine release in anaesthetized dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004; 489:67–75.
Article13. Takekoshi K, Ishii K, Kawakami Y, Isobe K, Nakai T. Activation of angiotensin II subtype 2 receptor induces catecholamine release in an extracellular Ca2+-dependent manner through a decrease of cyclic guanosine 3′,5′-monophosphate production in cultured porcine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. Endocrinol. 2001; 142:3075–3086.14. Martineau D, Lamouche S, Briand R, Yamaguchi N. Functional involvement of angiotensin AT2 receptor in adrenal catecholamine secretion in vivo. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999; 77:367–374.
Article15. Worck RH, Frandsen E, Ibsen H, Petersen JS. AT1 and AT2 receptor blockade and epinephrine release during insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Hyperten. 1998; 31:384–390.16. Wakade AR. Studies on secretion of catecholamines evoked by acetylcholine or transmural stimulation of the rat adrenal gland. J Physiol. 1981; 313:463–480.
Article17. Anton AH, Sayre DF. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxidetrihydroxy indole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962; 138:360–375.18. Tallarida RJ, Murray RB. Manual of pharmacologic calculation with computer programs. 2nd ed.New York: Speringer-Verlag;1987. p. 132.19. Hammer R, Giachetti A. Muscarinic receptor subtypes: M1 and M2 biochemical and functional characterization. Life Sci. 1982; 31:2992–2998.20. Garcia AG, Sala F, Reig JA, Viniegra S, Frias J, Fonteriz R, Gandia L. Dihydropyridine Bay-K-8644 activates chromaffin cell calcium channels. Nature. 1984; 309:69–71.21. Lim DY, Kim CD, Ahn KW. Influence of TMB-8 on secretion of catecholamines from the perfused rat adrenal glands. Arch Pharm Res. 1992; 15:115–125.
Article22. Goeger DE, Riley RT. Interaction of cyclopiazonic acid with rat skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Effect on Ca2+ binding and Ca2+ permeability. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989; 38:3995–4003.23. Seidler NW, Jona I, Vegh N, Martonosi A. Cyclopiazonic acid is a specific inhibitor of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasimc reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1989; 264:17816–17823.24. Catterall WA. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000; 26:13–25.25. Wada A, Takara H, Izumi F, Kobayashi H, Yanagihara N. Influx of 22Na through acetylcholine receptor-associated Na channels: relationship between 22Na influx, 45Ca influx and secretion of catecholamines in cultured bovine adrenal medulla cells. Neuroscience. 1985; 15:283–292.26. Hano T, Mizukoshi M, Baba A, Nakamura N, Nishio I. Angiotensin II subtype 1 receptor modulates epinephrine release from isolated rat adrenal gland. Blood Press. 1994; 5:S105–108.27. Livett BG, Marley PD. Non cholinergic control of adrenal catecholamine secretion. J Anat. 1993; 183:277–289.28. Plunkett LM, Correa FM, Saavedra JM. Quantitative auto-radiographic determination of angiotensin-converting enzyme binding in rat pituitary and adrenal glands with 124I–351A, a specific inhibitor. Regul Pept. 1985; 28:263–272.29. Phillips MI, Speakman EA, Kimura B. Levels of angiotensin and molecular biology of the tissue rennin angiotensin systems. Regul Pept. 1993; 43:1–20.30. Israel A, Strömberg C, Tsutsumi K, Garrido MR, Torres M, Saavedra JM. Angiotensin II receptor subtypes and phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat adrenal medulla. Brain Res Bull. 1995; 38:441–446.
Article31. Wong PC, Hart SD, Zaspel AM, Chiu AT, Ardecky RJ, Smith RD, Timmermans PB. Functional studies of nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor subtype-specific ligands: DuP 753 (AII-1) and PD123177 (AII-2). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990; 255:584–592.32. Armando I, Carranza A, Nishimura Y, Hoe KL, Barontini M, Terron JA, Falcon-Neri A, Ito T, Jourio AV, Saavedra JM. Peripheral administration of and angiotensin II AT1 receptor antagonist decreases the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal response to isolation stress. Endocrinology. 2001; 142:3880–3889.33. Yang G, Xi Z, Wan Y, Wang H, Bi G. Changes in circulating and tissue angiotensin II during acute and chronic stress. Biol Signals. 1993; 2:166–172.
Article34. McGehee DS, Role LW. Physiological diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed by vertebrate neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995; 57:521–546.
Article35. Cheek TR, O'Sullivan AJ, Moreton RB, Berridge MJ, Burgoyne RD. Spatial localization of the stimulus-induced rise in cyrosolic Ca2+ in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: Distinct nicotinic and muscarinic patterns. FEBS Lett. 1989; 247:429–434.36. Ghosh A, Greenberg ME. Calcium signaling in neurons: molecular mechanisms and cellular consequences. Science. 1995; 268:239–247.
Article37. Holz RW, Senter RA, Frye RA. Relationship between Ca2+ uptake and catecholamine secretion in primary dissociated cultures of adrenal modulla. J Neurochem. 1982; 39:635–640.38. Suzuki M, Muraki K, Imaizumi Y, Watanabe M. Cyclopiazonic acid, an inhibitor of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-pump, reduces Ca2+-dependent K+ currents in guinea-pig smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992; 107:134–140.39. Challiss RA, Jones JA, Owen PJ, Boarder MR. Changes in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate mass accumulations in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells in response to bradykinin and histamine. J Neurochem. 1991; 56:1083–1086.
Article40. Dendorfer A, Raasch W, Tempel K, Dominiak P. Interactions between the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and the sympathetic system. Basic Res Cardiol. 1998; 93:S24–29.
Article41. Stoehr SJ, Smolen JE, Holz RW, Agranoff BW. Inositol trisphosphate mobilizes intracellular calcium in permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1986; 46:637–640.
Article42. Dunn LA, Holz RW. Catecholamine secretion from digitonintreated adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1983; 258:4989–4993.
Article43. Vijayapandi P, Nagappa AN. Biphasic effects of losartan potassium on immobility in mice. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2005; 125:653–657.
Article44. Nahmod VE, Finkielman S, Benarroch EE, Pirola CJ. Angiotensin regulates release and synthesis of serotonin in brain. Science. 1978; 202:1091–1093.
Article45. Han HJ, Park SH, Koh HJ, Taub M. Mechanism of regulation of Na+ transport by angiotensin II in primary renal cells. Kidney Int. 2000; 57:2457–2467.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Influence of SKF81297 on Catecholamine Release from the Perfused Rat Adrenal Medulla
- Influence of Ketamine on Catecholamine Secretion in the Perfused Rat Adrenal Medulla
- Suppressive Impact of Ginsenoside-Rg2 on Catecholamine Secretion from the Rat Adrenal Medulla
- Comparison of Inhibitory Effects between Enalapril and Losartan on Adrenal Catecholamine Secretion
- R-(-)-TNPA, a Dopaminergic D2 Receptor Agonist, Inhibits Catecholamine Release from the Rat Adrenal Medulla