Infect Chemother.
2014 Jun;46(2):120-124. 10.3947/ic.2014.46.2.120.
A Case of Ventriculitis Associated with Renal Abscess Caused by Serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. muze1004@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2284990
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2014.46.2.120
Abstract
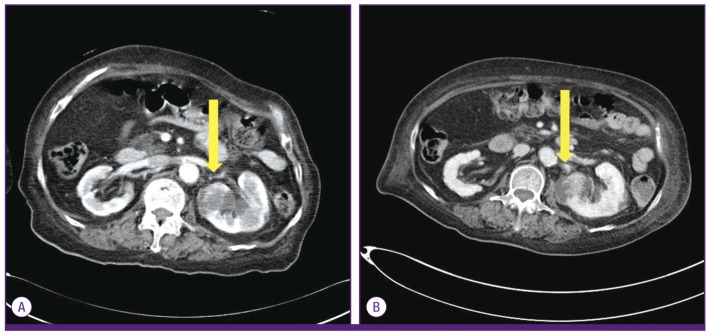
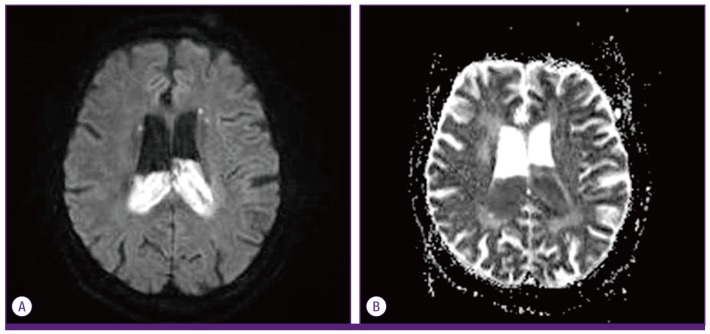
- Recently, serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae has been a major agent of an invasive syndrome characterized by liver abscess and its metastatic infection. Extrahepatic infection and its characteristics in patients with renal abscess caused by K. pneumoniae are poorly understood, and few cases of central nervous system infection have been reported. This is a report of 80-year-old woman with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus with renal abscess caused by serotype K1 K. pneumoniae, complicated with ventriculitis despite of appropriate use of antibiotics. Physicians need to be aware of possibility of metastatic infection in patients with serotype K1 K. pneumoniae infection, if they develop neurologic symptom and focus of infection is still present.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Shon AS, Bajwa RP, Russo TA. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) klebsiella pneumoniae: a new and dangerous breed. Virulence. 2013; 4:107–118. PMID: 23302790.2. Saccente M. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess, endophthalmitis, and meningitis in a man with newly recognized diabetes mellitus. Clin Infect Dis. 1999; 29:1570–1571. PMID: 10585817.3. Cheng DL, Liu YC, Yen MY, Liu CY, Wang RS. Septic metastatic lesions of pyogenic liver abscess: association with Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia in diabetic patients. Arch Intern Med. 1991; 151:1557–1559. PMID: 1872659.4. Lin WH, Wang MC, Tseng CC, Ko WC, Wu AB, Zheng PX, Wu JJ. Clinical and microbiologic characteristics of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates causing community-acquired urinary tract infections. Infection. 2010; 38:459–464. PMID: 20734217.5. Brisse S, Fevre C, Passet V, Issenhuth-Jeanjean S, Tournebize R, Diancourt L, Grimont P. Virulent clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae: identification and evolutionary scenario based on genomic and phenotypic characterization. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e4982. PMID: 19319196.6. Kasper DL, Baron MJ. Intraabdominal infections and abscesses. In : Kasper DL, Braunwald E, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson JL, Fauci AS, editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 18th ed. New York: McGraw Hill;2011. p. 1077–1083.7. Lin JC, Siu LK, Fung CP, Tsou HH, Wang JJ, Chen CT, Wamg SC, Chang FY. Impaired phagocytosis of capsular serotypes K1 or K2 Klebsiella pneumoniae in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with poor glycemic control. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 91:3084–3087. PMID: 16720670.8. Podschun R, Ullmann U. Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1998; 11:589–603. PMID: 9767057.9. Jung J, Jang Y, Choi G, Min K, Han K, Park J. A Case of renal abscess associated with endogeneous endophthalmitis and septic pulmonary embolism by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect Chemother. 2011; 43:485–489.10. Liliang PC, Lin YC, Su TM, Rau CS, Lu CH, Chang WN, Lee TC, Chen HJ. Klebsiella brain abscess in adults. Infection. 2001; 29:81–86. PMID: 11339480.11. Lee TH, Chang WN, Su TM, Chang HW, Lui CC, Ho JT, Wang HC, Lu CH. Clinical features and predictive factors of intraventricular rupture in patients who have bacterial brain abscesses. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007; 78:303–309. PMID: 17012340.
Article12. Ziai WC, Lewin JJ 3rd. Update in the diagnosis and management of central nervous system infections. Neurol Clin. 2008; 26:427–468. PMID: 18514821.
Article13. Chang WN, Huang CR, Lu CH, Chien CC. Adult Klebsiella pneumoniae meningitis in Taiwan: an overview. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2012; 21:87–96. PMID: 22879119.14. Fang CT, Chuang YP, Shun CT, Chang SC, Wang JT. A novel virulence gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains causing primary liver abscess and septic metastatic complications. J Exp Med. 2004; 199:697–705. PMID: 14993253.15. Lin JC, Chang FY, Fung CP, Xu JZ, Cheng HP, Wang JJ, Huang LY, Siu LK. High prevalence of phagocytic resistant capsular serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in liver abscess. Microbes Infect. 2004; 6:1191–1198. PMID: 15488738.16. Maruno T, Ooiwa Y, Takahashi K, Kodama Y, Takakura S, Ichiyama S, Chiba T. A liver abscess deprived a healthy adult of eyesight: endogenous endophthalmitis associated with a pyogenic liver abscess caused by serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae. Intern Med. 2013; 52:919–922. PMID: 23583997.17. Fang CT, Lai SY, Yi WC, Hsueh PR, Liu KL, Chang SC. Klebsiella pneumonia genotype K1: an emerging pathogen that causes septic ocular or central nervous system complications from pyogenic liver abscess. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45:284–293. PMID: 17599305.18. Yu WL, Ko WC, Cheng KC, Lee HC, Ke DS, Lee CC, Fung CP, Chuang YC. Association between rmpA and magA genes and clinical syndromes caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae in Taiwan. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 42:1351–1358. PMID: 16619144.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ventriculitis Associated with Liver Abscess Caused by Klebsiella Pneumoniae
- Klebsiella pneumoniae Meningoencephalitis and Ventriculitis Originated from Renal Abscess in an Immunocompetent Patient
- Spondylodiscitis with Epidural Abscess Caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Ventriculitis Associated with Invasive
Klebsiella Pneumoniae Syndrome: A Case Report - Klebsiella pneumoniae Liver Abscess