J Adv Prosthodont.
2014 Oct;6(5):423-426. 10.4047/jap.2014.6.5.423.
Restorative management using hybrid ceramic of a patient with severe tooth erosion from swimming: a clinical report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Prince of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand. mongkon.5c@gmail.com
- KMID: 2284743
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2014.6.5.423
Abstract
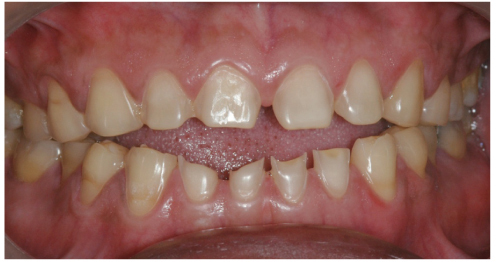
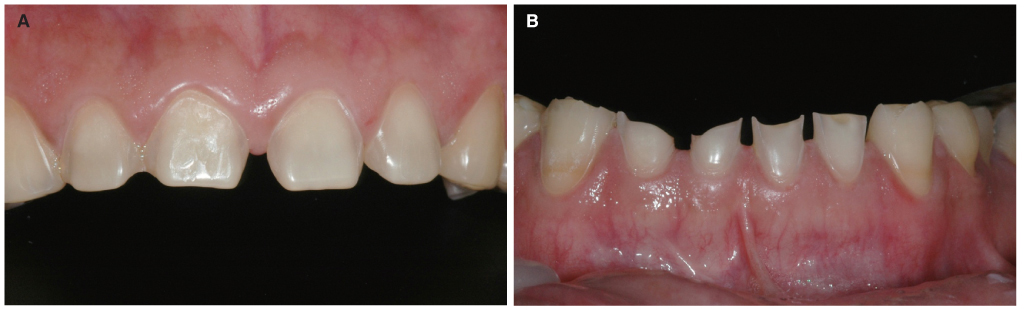
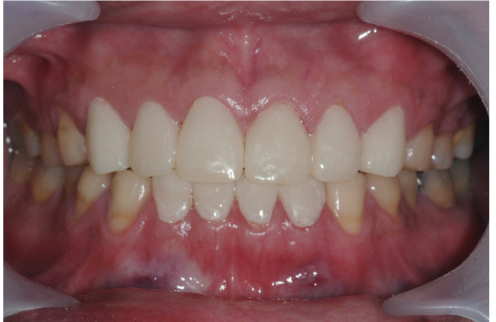
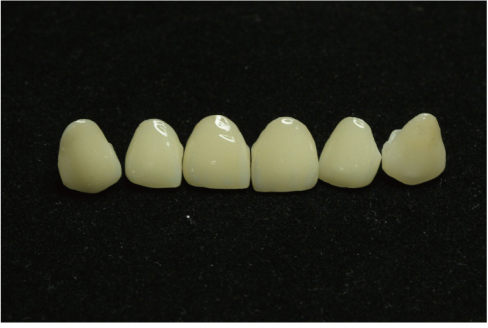
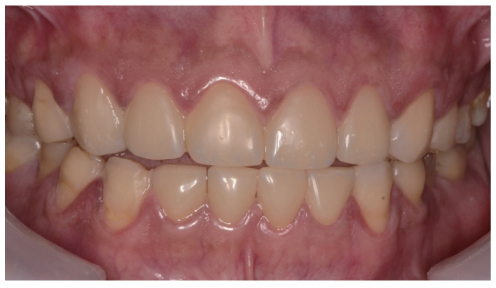
- This clinical report presents the clinical appearance and treatment approach in a case of excessive anterior teeth erosion resulted from swimming in a poorly-chlorinated swimming pool. Clinical findings revealed tooth sensitivity, severe enamel erosion resembling veneer preparations, and the presence of anterior open bite. A novel hybrid ceramic (Vita Enamic) was chosen for fabricating full-coverage crowns for this patient. After 6-months follow-up, the tooth sensitivity disappeared and the patient was satisfied with esthetic outcome. The hybrid ceramic restorations can be recommended with no complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wiegand A, Attin T. Occupational dental erosion from exposure to acids: a review. Occup Med (Lond). 2007; 57:169–176.2. Bartlett DW, Evans DF, Smith BG. The relationship between gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and dental erosion. J Oral Rehabil. 1996; 23:289–297.3. Scheutzel P. Etiology of dental erosion--intrinsic factors. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996; 104:178–190.4. Chuajedong P, Kedjarune-Leggat U, Kertpon V, Chongsuvivatwong V, Benjakul P. Associated factors of tooth wear in southern Thailand. J Oral Rehabil. 2002; 29:997–1002.5. Dawes C, Boroditsky CL. Rapid and severe tooth erosion from swimming in an improperly chlorinated pool: case report. J Can Dent Assoc. 2008; 74:359–361.6. Jahangiri L, Pigliacelli S, Kerr AR. Severe and rapid erosion of dental enamel from swimming: a clinical report. J Prosthet Dent. 2011; 106:219–223.7. Hayashi M, Shimizu K, Takeshige F, Ebisu S. Restoration of erosion associated with gastroesophageal reflux caused by anorexia nervosa using ceramic laminate veneers: a case report. Oper Dent. 2007; 32:306–310.8. Chuenarrom C, Daosodsai P, Benjakul P. Erosive potential of low pH swimming pool water on dental enamel. J Health Res. 2010; 24:91–94.9. Coldea A, Swain MV, Thiel N. Mechanical properties of polymer-infiltrated-ceramic-network materials. Dent Mater. 2013; 29:419–426.10. Dirxen C, Blunck U, Preissner S. Clinical performance of a new biomimetic double network material. Open Dent J. 2013; 7:118–122.11. Bindl A, Lüthy H, Mörmann WH. Strength and fracture pattern of monolithic CAD/CAM-generated posterior crowns. Dent Mater. 2006; 22:29–36.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A 48-month clinical performance of hybrid ceramic fragment restorations manufactured in CAD/CAM in noncarious cervical lesions: case report
- Management of dental erosion induced by gastro-esophageal reflux disorder with direct composite veneering aided by a flexible splint matrix
- Comparison of fracture strength between hybrid-ceramic crown and metal-ceramic crown
- Volume difference in upper central incisor preparation according to the changes of restorative design and marginal location
- Non-destructive management of white spot lesions by using tooth jewelry