Healthc Inform Res.
2014 Jul;20(3):231-235. 10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.231.
Development of Mobile Platform Integrated with Existing Electronic Medical Records
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Medical Information and Technology, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. SEMEKIM@yuhs.ac
- 3HOOH Healthcare Inc., Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2284587
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.231
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This paper describes a mobile Electronic Medical Record (EMR) platform designed to manage and utilize the existing EMR and mobile application with optimized resources.
METHODS
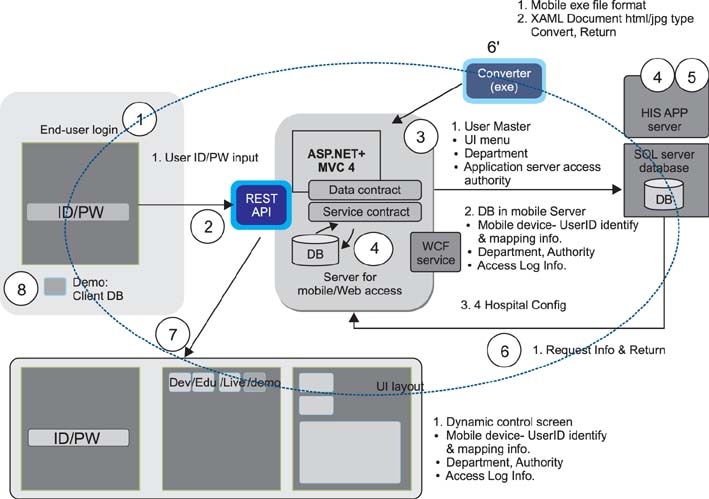
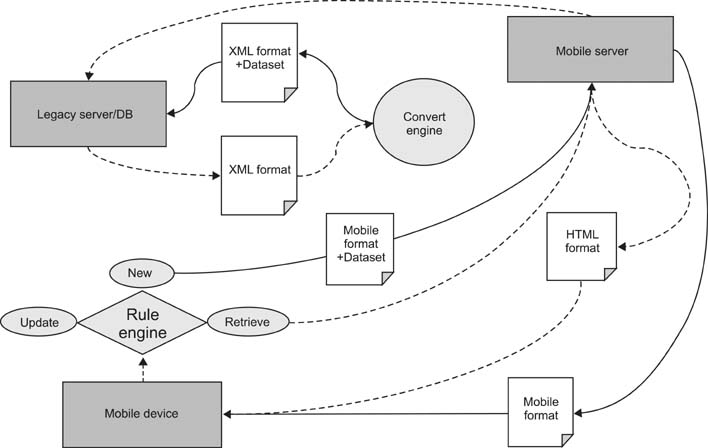
We structured the mEMR to reuse services of retrieval and storage in mobile app environments that have already proven to have no problem working with EMRs. A new mobile architecture-based mobile solution was developed in four steps: the construction of a server and its architecture; screen layout and storyboard making; screen user interface design and development; and a pilot test and step-by-step deployment. This mobile architecture consists of two parts, the server-side area and the client-side area. In the server-side area, it performs the roles of service management for EMR and documents and for information exchange. Furthermore, it performs menu allocation depending on user permission and automatic clinical document architecture document conversion.
RESULTS
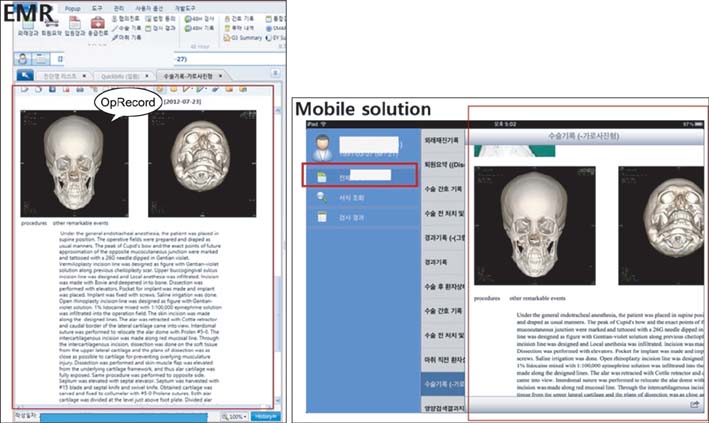
Currently, Severance Hospital operates an iOS-compatible mobile solution based on this mobile architecture and provides stable service without additional resources, dealing with dynamic changes of EMR templates.
CONCLUSIONS
The proposed mobile solution should go hand in hand with the existing EMR system, and it can be a cost-effective solution if a quality EMR system is operated steadily with this solution. Thus, we expect this example to be shared with hospitals that currently plan to deploy mobile solutions.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Usability of Academic Electronic Medical Record Application for Nursing Students' Clinical Practicum
Mona Choi, Hyeong Suk Lee, Joon Ho Park
Healthc Inform Res. 2015;21(3):191-195. doi: 10.4258/hir.2015.21.3.191.
Reference
-
1. Abraham C, Watson RT, Boudreau MC. Ubiquitous access: on the front lines of patient care and safety. Commun ACM. 2008; 51(6):95–99.2. Health Level Seven International. CDA Release 2 [Internet]. Ann Arbor (MI): Health Level Seven International;c2013. cited at 2013 Nov 12. Available from: http://www.hl7.org/implement/standards/product_brief.cfm?product_id=7.3. Muller M, Frankewitsch T, Ganslandt T, Burkle T, Prokosch HU. The Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) enables electronic medical records to wireless mobile computing. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2004; 107(Pt 2):1448–1452.4. Woo H, Lee HJ, Kim HC, Kang KJ, Seo SS. Hospital wireless local area network-based tracking system. Healthc Inform Res. 2011; 17(1):18–23.
Article5. Yeo K, Lee K, Kim JM, Kim TH, Choi YH, Jeong WJ, et al. Pitfalls and security measures for the mobile EMR system in medical facilities. Healthc Inform Res. 2012; 18(2):125–135.
Article6. Wu F, Wang H, Li X, Wu Y, Liu H. A mobile clinical information system based on iPad. In : Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Future Information and Communication Technologies for Ubiquitous HealthCare; 2013 Jul 1-3; Jinhua, China. p. 1–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Mobile Electronic Health Records Application in a Secondary General Hospital in Korea
- Development of Child-Teen Obesity Treatment Service Platform
- Early Experiences with Mobile Electronic Health Records Application in a Tertiary Hospital in Korea
- Development of an Electronic Claim System Based on an Integrated Electronic Health Record Platform to Guarantee Interoperability
- Analysis of Platforms and Functions of Mobile-Based Personal Health Record Systems