Healthc Inform Res.
2013 Dec;19(4):307-313. 10.4258/hir.2013.19.4.307.
Development of Mobile Electronic Health Records Application in a Secondary General Hospital in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. korean.er.md@gmail.com
- 2Management Information System, School of Business, Ewha Woman University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Computational Team, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2229507
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2013.19.4.307
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The recent evolution of mobile devices has opened new possibilities of providing strongly integrated mobile services in healthcare. The objective of this paper is to describe the decision driver, development, and implementation of an integrated mobile Electronic Health Record (EHR) application at Ulsan University Hospital. This application helps healthcare providers view patients' medical records and information without a stationary computer workstation.
METHODS
We developed an integrated mobile application prototype that aimed to improve the mobility and usability of healthcare providers during their daily medical activities. The Android and iOS platform was used to create the mobile EHR application. The first working version was completed in 5 months and required 1,080 development hours.
RESULTS
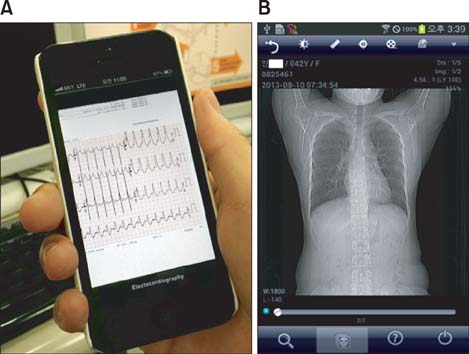
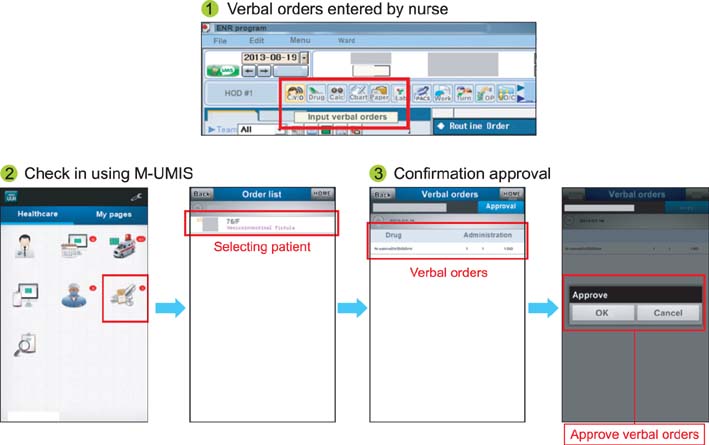
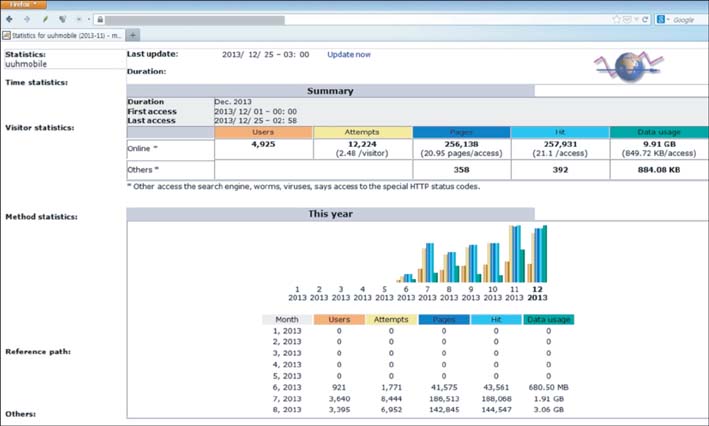
The mobile EHR application provides patient vital signs, patient data, text communication, and integrated EHR. The application allows our healthcare providers to know the status of patients within and outside the hospital environment. The application provides a consistent user environment on several compatible Android and iOS devices. A group of 10 beta testers has consistently used and maintained our copy of the application, suggesting user acceptance.
CONCLUSIONS
We are developing the integrated mobile EHR application with the goals of implementing an environment that is user-friendly, implementing a patient-centered system, and increasing the hospital's competitiveness.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Early Experiences with Mobile Electronic Health Records Application in a Tertiary Hospital in Korea
Wookjin Choi, Minah Park, Eunseok Hong, Sunhyu Kim, Ryeok Ahn, Jungseok Hong, Seungyeol Song, Tak Kim, Jeongkeun Kim, Seongwoon Yeo
Healthc Inform Res. 2015;21(4):292-298. doi: 10.4258/hir.2015.21.4.292.
Reference
-
1. Walker JM, Carayon P, Leveson N, Paulus RA, Tooker J, Chin H, et al. EHR safety: the way forward to safe and effective systems. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2008; 15(3):272–277.
Article2. Zhao QA, Stasko JT. Evaluating image filtering based techniques in media space applications. In : Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work; 1998 Nov 14-18; Seattle, WA. p. 11–18.3. Ehrler F, Wipfli R, Teodoro D, Sarrey E, Walesa M, Lovis C. Challenges in the implementation of a mobile application in clinical practice: case study in the context of an application that manages the daily interventions of nurses. JMIR mHealth uHealth. 2013; 1(1):e7.
Article4. Destailleur L. AWStats logfile analyzer documentation [Internet]. Boulogne Billancourt, France: NLTechno;2005. cited at 2013 Oct 1. Available from: http://awstats.sourceforge.net/docs/.5. Nolan T. A smarter way to practise. BMJ. 2011; 342:d1124.
Article6. Lee OF, Meuter ML. The adoption of technology orientation in healthcare delivery: case study of a large-scale hospital and healthcare system's electronic health record. Int J Pharm Healthc Mark. 2010; 4(4):355–374.7. Choi JS, Yi B, Park JH, Choi K, Jung J, Park SW, et al. The uses of the smartphone for doctors: an empirical study from Samsung Medical Center. Healthc Inform Res. 2011; 17(2):131–138.
Article8. Choi J, Kim JW, Seo JW, Chung CK, Kim KH, Kim JH, et al. Implementation of consolidated HIS: improving quality and efficiency of healthcare. Healthc Inform Res. 2010; 16(4):299–304.
Article9. Srivastava J, Cooley R, Deshpande M, Tan PN. Web usage mining: discovery and applications of usage patterns from Web data. ACM SIGKDD Explor. 2000; 1(2):12–23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Mobile Platform Integrated with Existing Electronic Medical Records
- Early Experiences with Mobile Electronic Health Records Application in a Tertiary Hospital in Korea
- Use of clinical terminology for semantic interoperability of electronic health records
- Development of a mobile application focusing on developmental support care for Korean infants born prematurely: a methodological study
- Usability of Academic Electronic Medical Record Application for Nursing Students' Clinical Practicum