Healthc Inform Res.
2011 Jun;17(2):101-110. 10.4258/hir.2011.17.2.101.
Development of an Electronic Claim System Based on an Integrated Electronic Health Record Platform to Guarantee Interoperability
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Information Technology, Daegu Haany University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Medical Informatics, Kyungpook National University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. inkeunlee@gmail.com
- KMID: 1447787
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2011.17.2.101
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
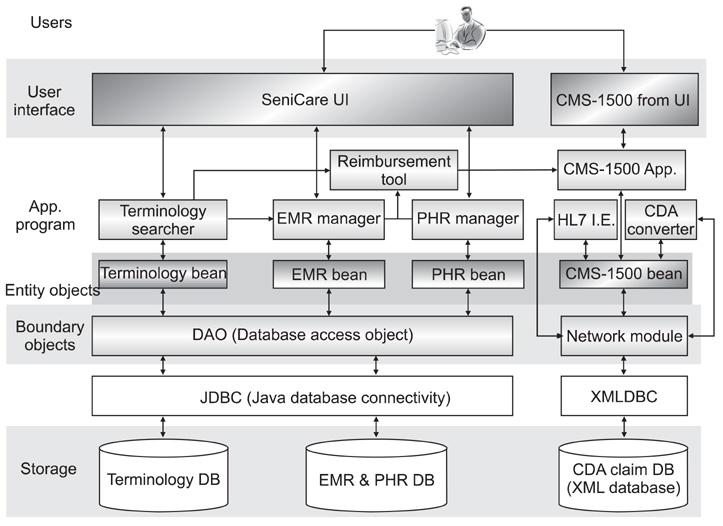
We design and develop an electronic claim system based on an integrated electronic health record (EHR) platform. This system is designed to be used for ambulatory care by office-based physicians in the United States. This is achieved by integrating various medical standard technologies for interoperability between heterogeneous information systems.
METHODS
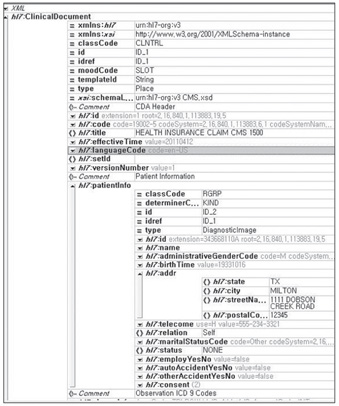
The developed system serves as a simple clinical data repository, it automatically fills out the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)-1500 form based on information regarding the patients and physicians' clinical activities. It supports electronic insurance claims by creating reimbursement charges. It also contains an HL7 interface engine to exchange clinical messages between heterogeneous devices.
RESULTS
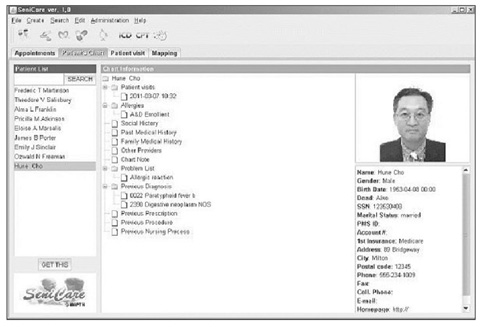
The system partially prevents physician malpractice by suggesting proper treatments according to patient diagnoses and supports physicians by easily preparing documents for reimbursement and submitting claim documents to insurance organizations electronically, without additional effort by the user. To show the usability of the developed system, we performed an experiment that compares the time spent filling out the CMS-1500 form directly and time required create electronic claim data using the developed system. From the experimental results, we conclude that the system could save considerable time for physicians in making claim documents.
CONCLUSIONS
The developed system might be particularly useful for those who need a reimbursement-specialized EHR system, even though the proposed system does not completely satisfy all criteria requested by the CMS and Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC). This is because the criteria are not sufficient but necessary condition for the implementation of EHR systems. The system will be upgraded continuously to implement the criteria and to offer more stable and transparent transmission of electronic claim data.
MeSH Terms
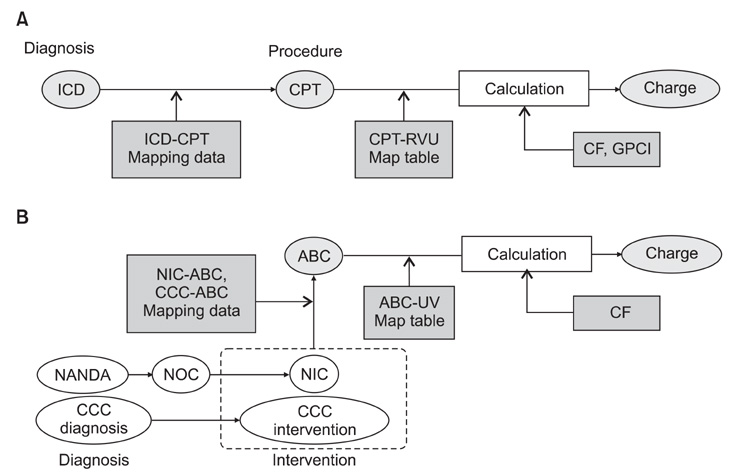
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Development of a Graphical User Interface Engine for the Convenient Use of the HL7 Version 2.x Interface Engine
Hwa Sun Kim, Hune Cho, In Keun Lee
Healthc Inform Res. 2011;17(4):214-223. doi: 10.4258/hir.2011.17.4.214.
Reference
-
1. Walker JM, Bieber EJ, Richards F. Implementing an electronic health record system. 2004. New York: Springer;3–43.2. SeniCare [Internet]. Medical Informatics Platform for Telehealth Development Center. cited at 2011 May 13. Daegue: Medical Informatics Platform for Telehealth Development Center;Available from: http://medinfo.knu.ac.kr/senicare.3. Henricks WH. "Meaningful use" of electronic health records and its relevance to laboratories and pathologists. J Pathol Inform. 2011. 2:7.
Article4. American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 [Internet]. American Medical Association. cited at 2011 May 20. Available from: http://www.ama-assn.org/resources/doc/washington/arra-hit-provisions.pdf.5. CMS EHR meaningful use overview [Internet]. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. cited at 2011 May 20. Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services;Available from: https://www.cms.gov/EHRIncentivePrograms/30_Meaningful_Use.asp#TopOfPage.6. Establishment of the permanent certification program for health information technology [Internet]. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. 2011. cited at 2011 May 20. Washington: The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology;Available from: http://origin.www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2011-01-07/pdf/2010-33174.pdf.7. Medicare and medicaid programs: electronic health record incentive program [Internet]. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 2010. cited at 2011 May 20. Washington: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services;Available from: http://edocket.access.gpo.gov/2010/pdf/2010-17207.pdf.8. Certified health IT product list [Internet]. The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. 2010. cited at 2011 May 20. Washington: The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology;Available from: http://onc-chpl.force.com/ehrcert/EHRProductSearch.9. 22nd Annual HIMSS Leadership Survey [Internet]. Health Information Management Systems Society. 2011. cited at 2011 May 9. Chicago: Health Information Management Systems Society;Available from: http://www.himss.org/2011survey/healthcareCIO_final.asp.10. Hsiao CJ, Hing E, Socey TC, Cai B. NCHS Health E-Stat [Internet]. Electronic medical record/electronic health record use by office-based physicians: United States, 2009 and preliminary 2010 state estimates. 2010. cited at 2011 May 9. Hyattsville: National Center for Health Statistics;Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hestat/emr_ehr_09/emr_ehr_09.htm.11. Practice management system [Internet]. Wikipedia. 2011. cited at 2011 May 9. Wikipedia;Available from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Practice_management_software.12. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act [Internet]. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 2011. cited at 2011 May 9. Baltimore: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services;Available from: http://www.cms.gov/HIPAAGenInfo.13. CMS-1500 [Internet]. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. 2011. cited at 2011 May 9. Baltimore: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services;Available from: http://www.cms.gov/ElectronicBillingEDITrans/16_1500.asp.14. Coding tools for medical coding professionals [Internet]. InstaCode. c2011. cited at 2011 Jun 20. InstaCode Inc.;Available from: http://www.instacode.com.15. MPM Soft [Internet]. cited at 2011 Jun 20. Available from: http://www.mpmsoft.com.16. Tran T, Kim HS, Cho H. A development of HL7 middleware for medical device communication. Proceedings of SERA'2007. 2007. Busan, KR: 485–492.
Article17. Lee IK, Kim HS, Cho H. Design and development of a system for mapping of medical standard terminologies. J Intell Inf Syst. 2011. 21:237–243.
Article18. Clinical Document Architecture [Internet]. cited at 2011 May 13. Available from: http://hl7book.net/index.php?title=CDA.19. Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine-Clinical Terms [Internet]. International Health Terminology Standards Development Organization. cited at 2011 May 13. Copenhagen: International Health Terminology Standards Development Organization;Available from: http://www.ihtsdo.org.20. International Classification of Diseases [Internet]. World Health Organization. c2011. cited at 2011 May 13. Geneva: World Health Organization;Available from: http://www.who.int/classifications/icd/en.21. Current Procedural Terminology [Internet]. American Medical Association. c2011. cited at 2011 May 13. Chicago: American Medical Association;Available from: http://www.ama-assn.org/ama/pub/physicianresources/solutions-managing-your-practice/codingbilling-insurance/cpt.page.22. ABC [Internet]. ABC Coding Solutions Alternative Link. cited at 2010 Nov 5. Albuquerque, NM: ABC Coding Solutions Alternative Link;Available from: http://www.abccodes.com/ali/products_services/pro_description.asp.23. North American Nursing Diagnosis Association [Internet]. cited at 2010 Nov 5. Kaukauna, WI: NANDA International;Available from: http://www.nanda.org.24. Nursing Outcomes Classification [Internet]. The University of Iowa College of Nursing. cited at 2010 Nov 5. Iowa City: The University of Iowa College of Nursing;Available from: http://www.nursing.uiowa.edu/excellence/nursing_knowledge/clinical_effectiveness/noc.htm.25. Nursing Interventions Classification [Internet]. The University of Iowa College of Nursing. cited at 2010 Nov 5. Iowa City: The University of Iowa College of Nursing;Available from: http://www.nursing.uiowa.edu/excellence/nursing_knowledge/clinical_effectiveness/nic.htm.26. Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes [Internet]. cited at 2010 Nov 5. Available from: http://loinc.org.27. Johnson M, Bulechek G, Butcher H, Dochterman JM, Maas M, Moorhead S, Swanson E. NANDA, NOC, and NIC linkages. 2006. St. Louis: Mosby.28. Cross Coder [Internet]. Wasserman Medical Publishers. c2011. cited at 2010 Dec 3. Wasserman Medical Publishers;Available from: http://www.crosscoder.com.29. The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System [Internet]. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. cited at 2011 May 9. Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services;Available from: https://www.cms.gov/medhcpcsgeninfo.30. CY 2011 physician fee schedule final rule with comment period [Internet]. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. cited at 2011 May 9. Baltimore, MD: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services;Available from: http://www.cms.gov/PhysicianFeeSched.31. Introduction to relative value units and how medicare reimbursement in calculated [Internet]. cited at 2011 May 11. Available from: http://www.acro.org/washington/RVU.pdf.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Terminologies: A Solution for Semantic Interoperability
- Use of clinical terminology for semantic interoperability of electronic health records
- Adoption of Electronic Health Records: A Roadmap for India
- Comparison of Open-Source Electronic Health Record Systems Based on Functional and User Performance Criteria
- Comparison of Nursing Records of Open Heart Surgery Patients before and after Implementation of Electronic Nursing Record