Diabetes Metab J.
2015 Jun;39(3):240-246. 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.3.240.
The Relationship between Anemia and the Initiation of Dialysis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Chonbuk National University Hospital, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. pts@jbnu.ac.
- KMID: 2281537
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.3.240
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Anemia is associated with various poor clinical outcomes in chronic kidney disease patients. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between anemia and the initiation degree and time of dialysis in type 2 diabetic nephropathy patients.
METHODS
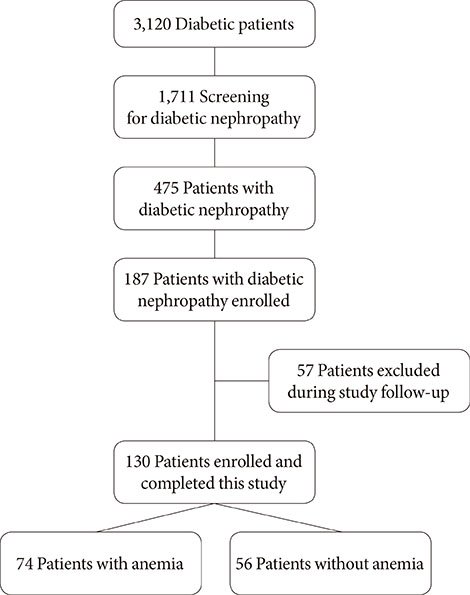
This observational retrospective study included 130 type 2 diabetic nephropathy patients in Korea. The existence of anemia, the degree and time of dialysis initiation were reviewed. Clinical characteristics and variables were also compared.
RESULTS
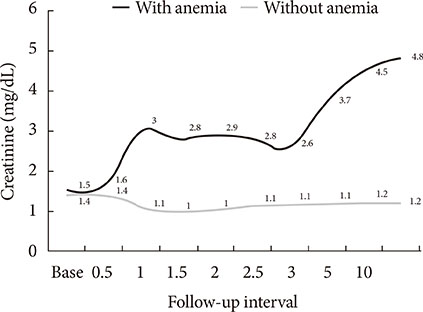
The levels of hemoglobin and serum creatinine were significantly correlated with the dialysis initiation (P<0.05) during the 10-year follow-up period. Patients with anemia showed rapid decline of renal function, causing significantly more dialysis initiation (54.1% vs. 5.4%, P<0.05) compare to the patients without anemia. Average time to initiate dialysis in patients with anemia was 45.1 months (range, 8.0 to 115.8 months), which was significantly faster than that (68.3 months [range, 23.3 to 108.8 months]) in patients without anemia (P<0.01). The risk to dialysis initiation was significantly increased in patients with anemia compared to the patients without anemia (adjusted hazard ratio, 8.1; 95% confidence interval, 2.4 to 27.0; P<0.05).
CONCLUSION
Anemia is associated with rapid decline of renal dysfunction and faster initiation of dialysis in diabetic nephropathy patients. Therefore, clinicians should pay an earlier attention to anemia during the management of diabetes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984; 310:356–360.2. USRDS: the United States Renal Data System. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 42:6 Suppl 5. 1–230.3. Valmadrid CT, Klein R, Moss SE, Klein BE. The risk of cardiovascular disease mortality associated with microalbuminuria and gross proteinuria in persons with older-onset diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 2000; 160:1093–1100.4. Peterson JC, Adler S, Burkart JM, Greene T, Hebert LA, Hunsicker LG, King AJ, Klahr S, Massry SG, Seifter JL. Blood pressure control, proteinuria, and the progression of renal disease. The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Ann Intern Med. 1995; 123:754–762.5. Jones RL, Peterson CM. Hematologic alterations in diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 1981; 70:339–352.6. Jones SC, Smith D, Nag S, Bilous MT, Winship S, Wood A, Bilous RW. Prevalence and nature of anaemia in a prospective, population-based sample of people with diabetes: Teesside anaemia in diabetes (TAD) study. Diabet Med. 2010; 27:655–659.7. Keane WF, Brenner BM, de Zeeuw D, Grunfeld JP, McGill J, Mitch WE, Ribeiro AB, Shahinfar S, Simpson RL, Snapinn SM, Toto R. RENAAL Study Investigators. The risk of developing end-stage renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy: the RENAAL study. Kidney Int. 2003; 63:1499–1507.8. Stevens PE, O'Donoghue DJ, Lameire NR. Anaemia in patients with diabetes: unrecognised, undetected and untreated? Curr Med Res Opin. 2003; 19:395–401.9. Portoles J, Gorriz JL, Rubio E, de Alvaro F, Garcia F, Alvarez-Chivas V, Aranda P, Martinez-Castelao A. NADIR-3 Study Group. The development of anemia is associated to poor prognosis in NKF/KDOQI stage 3 chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2013; 14:2.10. National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes and CKD: 2012 update. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012; 60:850–886.11. Ma JZ, Ebben J, Xia H, Collins AJ. Hematocrit level and associated mortality in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:610–619.12. Unsal A, Koc Y, Basturk T, Akgun AO, Sakaci T, Ahbap E. Risk factors for progression of renal disease in patient with diabetic nephropathy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012; 16:878–883.13. Mohanram A, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S, Keane WF, Brenner BM, Toto RD. Anemia and end-stage renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2004; 66:1131–1138.14. Valdivia J, Gutierrez C, Treto J, Delgado E, Mendez D, Fernandez I, Abdo A, Perez L, Forte M, Rodriguez Y. Prognostic factors in hemodialysis patients: experience of a Havana hospital. MEDICC Rev. 2013; 15:11–15.15. Fine LG, Bandyopadhay D, Norman JT. Is there a common mechanism for the progression of different types of renal diseases other than proteinuria? Towards the unifying theme of chronic hypoxia. Kidney Int Suppl. 2000; 75:S22–S26.16. Rosenberger C, Mandriota S, Jurgensen JS, Wiesener MS, Horstrup JH, Frei U, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH, Bachmann S, Eckardt KU. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha in hypoxic and ischemic rat kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:1721–1732.17. Silverberg DS, Wexler D, Blum M, Keren G, Sheps D, Leibovitch E, Brosh D, Laniado S, Schwartz D, Yachnin T, Shapira I, Gavish D, Baruch R, Koifman B, Kaplan C, Steinbruch S, Iaina A. The use of subcutaneous erythropoietin and intravenous iron for the treatment of the anemia of severe, resistant congestive heart failure improves cardiac and renal function and functional cardiac class, and markedly reduces hospitalizations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000; 35:1737–1744.18. Ritz E. Anemia and diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2006; 6:469–472.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Reduced Erythropoietin Responsiveness to Anemia in Diabetic Patients before Advanced Diabetic Nephropathy
- Changes of Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Antioxidant Enzymes in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
- The Clinical Results of Vitrectomy in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy with Diabetic Nephropathy
- A Case of Diabetic Nephropathy without Microalbuminuria in Type 1 Diabetes
- Angiotensin-I converting enzyme gene polymorphism in Turkish type 2 diabetic patients