Korean J Perinatol.
2015 Sep;26(3):183-189. 10.14734/kjp.2015.26.3.183.
Clinical Consideration of Surveillance Cultures for Out-born Neonates Transferred to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. oyk5412@wonkwang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2281221
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2015.26.3.183
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To identify trends in bacterial organisms and antimicrobial susceptibilities for transmission by outborn neonates, it is important to perform surveillance cultures. The aim of this study was to investigate major organisms and any other clinical factors through surveillance cultures of out-born neonates who transferred to neonatal intensive care units (NICU).
METHODS
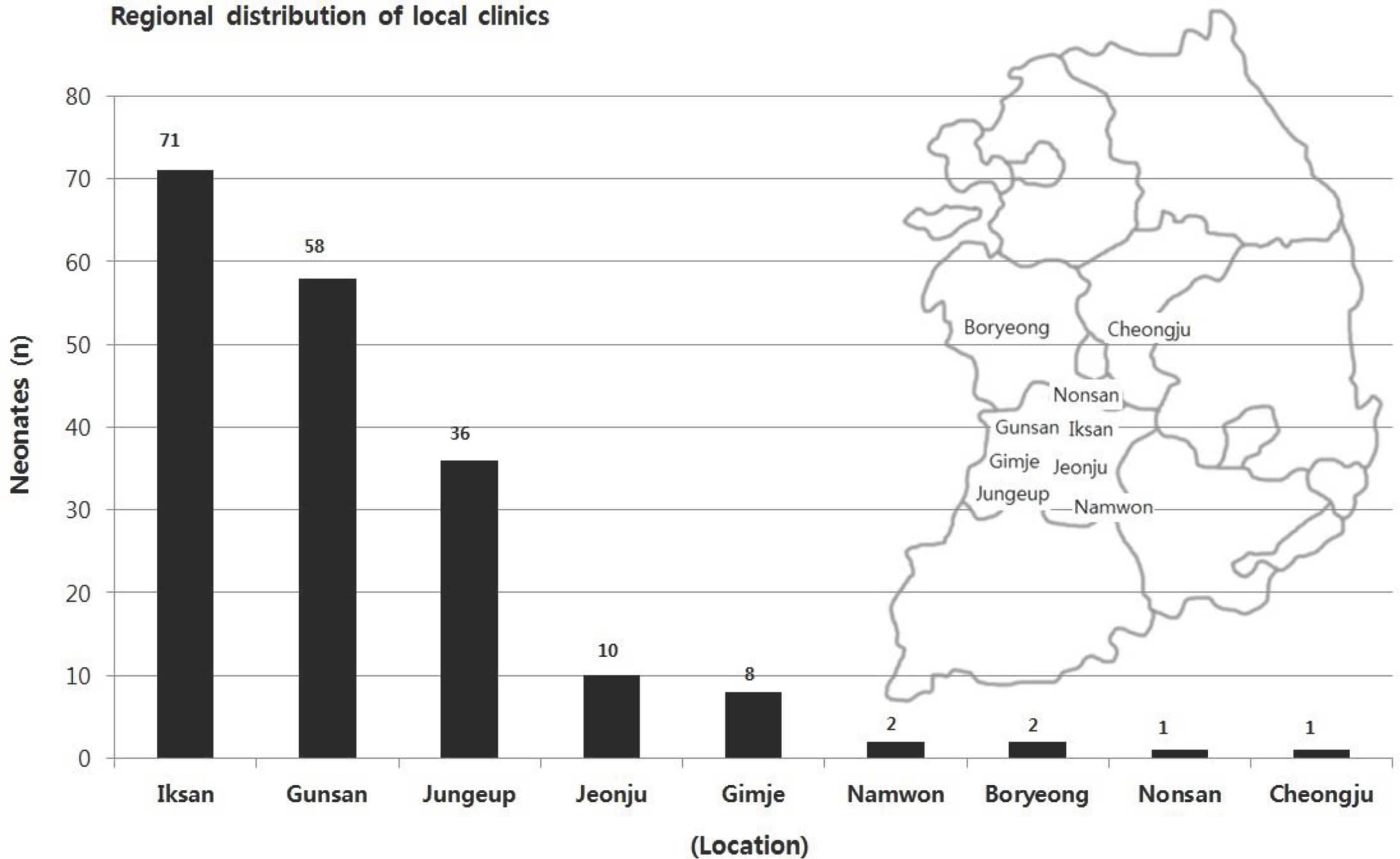
This study is a retrospective collected data among 189 out-born neonates admitted to NICU from Mar. 2012, to Feb. 2014. Surveillance cultures were obtained routinely from both nasal and axillary region and inoculated CHROM agar(TM) MRSA immediately. Bacterial culture identification and antibiotic susceptibility were carried out using Vitek II ID-GPI card.
RESULTS
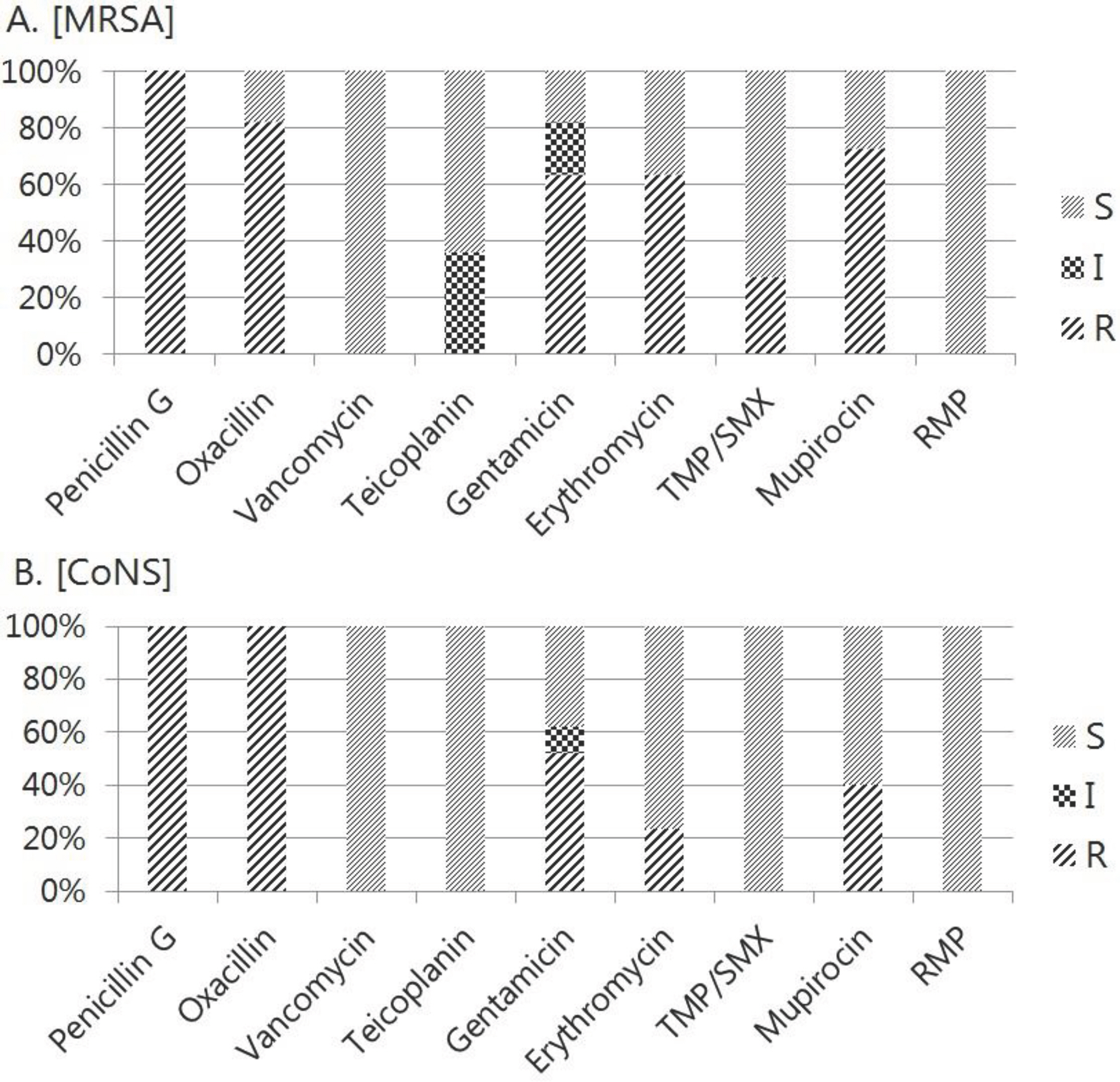
The most prevalent organisms isolated from the nasal surveillance cultures were methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and coagulase negative Staphylococcus (CoNS) (each 17 cases vs. 11 cases); both vancomycin and rifampin were susceptible. Only 1 case of S. epidermidis has same result in blood and surveillance culture. Demographic, clinical and healthcare related parameters according to surveillance culture results were compared, but no obvious association was apparent on above parameters. Nevertheless, positive surveillance culture group showed lower birth weight and longer duration until transferred to NICU.
CONCLUSION
In our surveillance culture study showed that MRSA and CoNS were the most common organisms in out-born neonates; both were penicillin- and oxacillin-resistant on antibiotic susceptibility testing. Although there is no statistical meaning, positive surveillance culture group showed relatively lower birth weight and longer duration from birth to NICU arrival. These findings were contributed to obtain a reliable policy of the transmission in NICU.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim YS, Kim JK, Yoo HS, Ahn SY, Seo HJ, Choi SH, et al. Pathogens and prognotic factors for early onset sepsis in very low birth weight infants. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2009; 16:163–71.2. Park HW, Lim G, Koo SE, Lee BS, Kim KS, Pi SY, et al. Causative agents and antimicrobial sensitivity of neonatal sepsis: ten-year experience in one neonatal intensive care unit. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2009; 16:172–81.3. Cimolai N. Staphylococcus aureus outbreaks among newborns: new frontiers in an old dilemma. Am J Perinatol. 2003; 20:125–36.4. Bizzarro MJ, Gallagher PG. Antibiotic-resistant organisms in the neonatal intensive care unit. Semin Perinatol. 2007; 31:26–32.
Article5. Carey AJ, Saiman L, Polin RA. Hospital-acquired infections in the NICU: epidemiology for the new millennium. Clin Perinatol. 2008; 35:223–49.
Article6. Eveillard M, Martin Y, Hidri N, Boussougant Y, Joly-Guillou ML. Carriage of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among hospital employees: prevalence, duration, and transmission to households. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiol. 2004; 25:114–20.7. Geva A, Wright SB, Baldini LM, Smallcomb JA, Safran C, Gray JE. Spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a large tertiary NICU: network analysis. Pediatrics. 2011; 128:e1173–80.
Article8. Andersen BM, Lindemann R, Bergh K, Nesheim BI, Syversen G, Solheim N, et al. Spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a neonatal intensive unit associated with understaffing, overcrowding and mixing of patients. J Hosp Infect. 2002; 50:18–24.
Article9. Shiojima T, Ohki Y, Nako Y, Morikawa A, Okubo T, Iyobe S. Immediate control of a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus outbreak in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Infect Chemother. 2003; 9:243–7.
Article10. Carey AJ, Long SS. Staphylococcus aureus: a continuously evolving and formidable pathogen in the neonatal intensive care unit. Clin Perinatol. 2010; 37:535–46.
Article11. Kim EA. Antimicrobial management of neonatal sepsis. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2012; 19:53–64.
Article12. Lee J, Kim EK, Lee JA, Choi CW, Kim HS, Kim BI, et al. Effective ways of performing surveillance surface cultures in extremely low birth weight infants. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2011; 18:240–7.
Article13. Goldmann DA, Durbin WA, Jr. , Freeman J. Nosocomial infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Infect Dis. 1981; 144:449–59.
Article14. Hoogkamp-Korstanje JA, Cats B, Senders RC, van Ertbrug-gen I. Analysis of bacterial infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. J Hosp Infect. 1982; 3:275–84.
Article15. Song X, Perencevich E, Campos J, Short BL, Singh N. Clinical and economic impact of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization or infection on neonates in intensive care units. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010; 31:177–82.
Article16. Huang YC, Chou YH, Su LH, Lien RI, Lin TY. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization and its association with infection among infants hospitalized in neonatal intensive care units. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:469–74.
Article17. Giuffre M, Bonura C, Cipolla D, Mammina C. MRSA infection in the neonatal intensive care unit. Expert Rrev Anti-Infect Ther. 2013; 11:499–509.18. Park SH, Kim SY, Lee JH, Park C, Lee DG. Community-genotype strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with high-level mupirocin resistance in a neonatal intensive care unit. Early Hum Dev. 2013; 89:661–5.
Article19. Kim HJ, Kang SJ, Park HK, Kim CR, Choi TY, Oh SH. The effect of eradication of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from neonatal intensive care unit by aggressive infection control measures: isolation program and the use of chlorhexidine. Korean J Perinatol. 2010; 21:248–57.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Preterm Delivery between 32(+0)-33(+6) Weeks of Gestation
- Incidence and Clinical Manifestations of Rotaviral Infections in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Causes of Transfer of Neonates (Born after ≥34 Weeks of Gestation) to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Owing to Respiratory Distress and their Clinical Features
- Carriage Rates of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Neonates with Neonatal Jaundice
- Amplitude Integrated Electroencephalography in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit for Diagnosis of Neonatal Seizure