Korean J Perinatol.
2014 Dec;25(4):284-291. 10.14734/kjp.2014.25.4.284.
Serum Enzymes in Predicting Transient Tachypnea of Newborn and Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Ilsan, Korea. kimhs@dumc.or.kr
- KMID: 2281146
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2014.25.4.284
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Perinatal asphyxia is a major factor correlated with diseases that cause respiratory distress in a neonate. So we aimed to investigate the relationship between respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and transient tachypnea of newborn (TTN) with plasma biological markers of perinatal asphyxia in full-term neonates.
METHODS
Full-term neonates with transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) and respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) who were admitted within 24 hours after birth were enrolled in a study group. And control group are infants with premature rupture of amniotic membrane without significant findings. Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), creatine kinase (CK) and myoglobin were measured at admission.
RESULTS
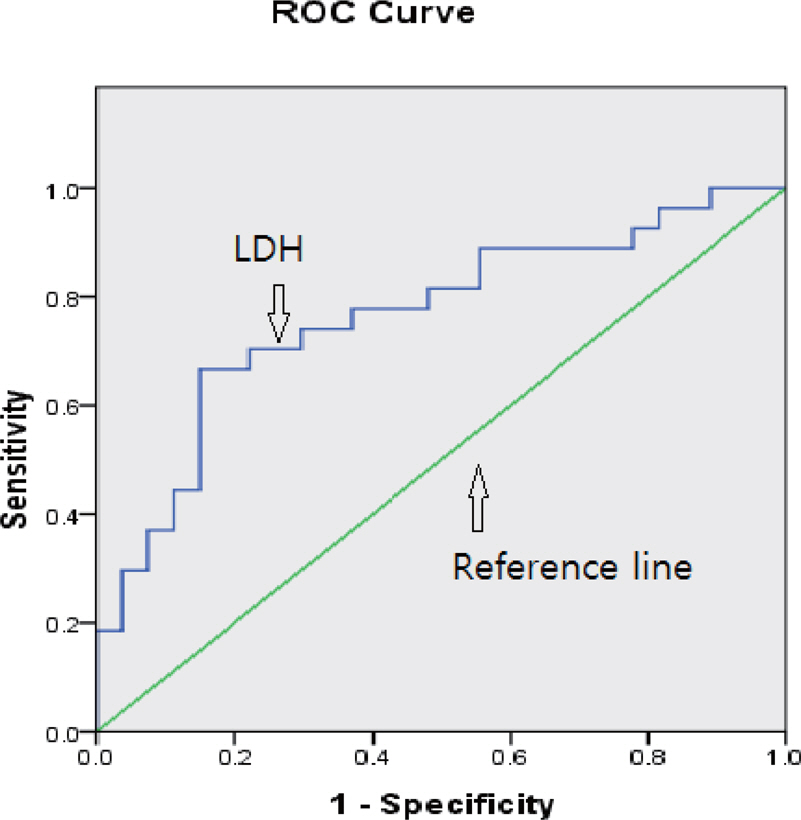
Of the total 80 infants, 54 were of the study group and 26 were of the control group. The numbers of RDS and TTN groups were 27 and 27, and the numbers of RDS with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and RDS without HIE were 6 and 21 retrospectively. Serum AST, ALT, LDH and CK were significantly higher in the study group than the control group (P<0.05). When RDS group and TTN group were compared AST and LDH were significantly higher in RDS group than TTN group (P<0.05). Serum AST, ALT and LDH were significantly higher in RDS with HIE group than RDS without HIE group (P<0.05). A prediction of RDS by LDH analysis showed good correlation by receiver operating characteristic curve (P<0.05). A cut off level of 720 IU/L for LDH was the best predictor of RDS (sensitivity 63% and specificity 86%).
CONCLUSION
LDH is an excellent predictor to differentiate RDS from TTN soon after birth in full-term neonates with respiratory distress.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Alanine Transaminase
Amnion
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Asphyxia
Biomarkers
Creatine Kinase
Humans
Hypoxia-Ischemia, Brain
Infant
Infant, Newborn
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase
Myoglobin
Parturition
Plasma
Retrospective Studies
ROC Curve
Rupture
Sensitivity and Specificity
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn*
Alanine Transaminase
Aspartate Aminotransferases
Creatine Kinase
L-Lactate Dehydrogenase
Myoglobin
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Serum Enzymes in Predicting the Severity of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome in Newborn
Mu-Yeol Yang, In-Uk Kim, Hye-Ryeong Jeong, Soo-Hyun Kim, Do-Hyun Kim, Hee-Sup Kim M.D.
Korean J Perinatol. 2015;26(3):215-221. doi: 10.14734/kjp.2015.26.3.215.
Reference
-
1.Lee JM., Kim DK., Lee SJ. Probable prognostic factors among the revealing clinical manifestations at admission in neonates with tachypnea. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2006. 13:32–9.2.Ozkiraz S., Gokmen Z., Boke SB., Kilicdag H., Ozel D., Sert A. Lactate and lactate dehydrogenase in predicting the severity of transient tachypnea of the newborn. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013. 26:1245–8.
Article3.Chang JY., Kim CR., Kim EA., Kim KS. Predictable risk factors and clinical courses for prolonged transient tachypnea of the newborn. Korean J Pediatr. 2010. 53:349–57.
Article4.Jackson JC. Respiratory distress syndrome. Gleason CA, Devaskar SU, editors. editors.Avery's disease of the newborn. 9th ed.Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders Co;2012. p. 633–46.5.Sykes GS., Molloy PM., Johnson P., Gu W., Ashworth F., Stirrat GM, et al. Do Apgar scores indicate asphyxia? Lancet. 1982. 1:494–6.
Article6.Lackmann GM. Influence of neonatal idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome on serum enzyme activities in premature healthy and asphyxiated newborns. Am J Perinatol. 1996. 13:329–34.
Article7.Kim DH., Shim SY., Kim JR., Shin SH., Kim ES., Joung KE, et al. Recent outcome of extremely low birth weight infants: The use of CRIB (clinical risk index for babies) II score for analyzing the survival rate. Korean J Pediatr. 2006. 49:952–8.8.Levene MI., Sands C., Grindulis H., Moore JR. Comparison of two methods of predicting outcome in perinatal asphyxia. Lancet. 1986. 1:67–9.
Article9.Barberi I., Calabro MP., Cordaro S., Gitto E., Sottile A., Pru-dente D, et al. Myocardial ischaemia in neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Electrocardiographic, echocardiographic and enzymatic correlations. Eur J Pediatr. 1999. 158:742–7.10.Karlsson M., Blennow M., Nemeth A., Winbladh B. Dynamics of hepatic enzyme activity following birth asphyxia. Acta Paediatr. 2006. 95:1405–11.
Article11.Karlsson M., Dung KT., Thi TL., Borgstrom E., Jonstam K., Kasstrom L, et al. Lactate dehydrogenase as an indicator of severe illness in neonatal intensive care patients: a longitudinal cohort study. Acta Paediatr. 2012. 101:1225–31.
Article12.Karlsson M., Wiberg-Itzel E., Chakkarapani E., Blennow M., Winbladh B., Thoresen M. Lactate dehydrogenase predicts hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy in newborn infants: a preliminary study. Acta Paediatr. 2010. 99:1139–44.
Article13.Lackmann GM., Tollner U., Mader R. Serum enzyme activities in full-term asphyxiated and healthy newborns: enzyme kinetics during the first 144 hours of life. Enzyme Protein. 1993. 47:160–72.
Article14.Son MK., Kang ES., Jung SH., Choeh K. Significance of creatine kinase isoenzymes for neurologic outcome in perinatal asphyxia. Korean J Pediatr Soc. 1996. 39:924–33.15.Kasik JW., Leuschen MP., Bolam DL., Nelson RM. Rhabdomyolysis and myoglobinemia in neonates. Pediatrics. 1985. 76:255–8.
Article16.Kojima T., Kobayashi T., Matsuzaki S., Iwase S., Kobayashi Y. Effects of perinatal asphyxia and myoglobinuria on development of acute, neonatal renal failure. Archives Dis Child. 1985. 60:908–12.
Article17.Lackmann GM., Tollner U. The predictive value of elevation in specific serum enzymes for subsequent development of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy or intraventricular hemorrhage in full-term and premature asphyxiated newborns. Neuropediatrics. 1995. 26:192–8.
Article18.Burtis CA., Ashwood ER., Bruns DE. editors.Tietz tesxtbook of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics. 4th ed.St. Louis: Elsevier Saunders Co;2006. p. 657–60.19.Shah P., Riphagen S., Beyene J., Perlman M. Multiorgan dysfunction in infants with post-asphyxial hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2004. 89:152–5.
Article20.Henrion J., Schapira M., Luwaert R., Colin L., Delannoy A., Heller FR. Hypoxic hepatitis: clinical and hemodynamic study in 142 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 2003. 82:392–406.21.Gibson PR., Dudley FJ. Ischemic hepatitis: clinical features, diagnosis and prognosis. Aust N Z J Med. 1984. 14:822–5.
Article22.Nelson DL., Cox MM. Lehninger principles of biochemistry. 3rd ed.Newyork: Worth Publishers;2000. p. 206.23.Reddy S., Dutta S., Narang A. Evaluation of lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase and hepatic enzymes for the retrospective diagnosis of perinatal asphyxia among sick neonates. Indian pediatr. 2008. 45:144–7.24.Warburton D., Singer DB., Oh W. Effects of acidosis on the activity of creatine phosphokinase and its isoenzymes in the serum of newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1981. 68:195–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neonatal respiratory distress: recent progress in understanding pathogenesis and treatment outcomes
- Clinical Study of Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
- Clinical courses and diagnoses of neonates who are transferred due to mild respiratory distress soon after birth in a university hospital
- Probable Prognostic Factors among the Revealing Clinical Manifestations at Admission in Neonates with Tachypnea
- Predictable risk factors and clinical courses for prolonged transient tachypnea of the newborn