Diabetes Metab J.
2013 Feb;37(1):72-80. 10.4093/dmj.2013.37.1.72.
Predictive Clinical Parameters and Glycemic Efficacy of Vildagliptin Treatment in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drhopper@catholic.ac.kr, hys@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2280745
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.1.72
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The aims of this study are to investigate the glycemic efficacy and predictive parameters of vildagliptin therapy in Korean subjects with type 2 diabetes.
METHODS
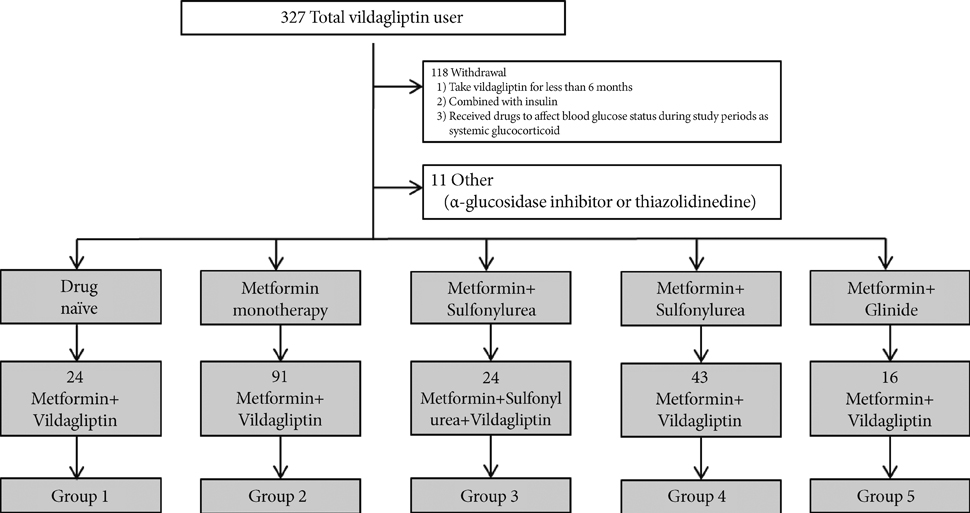
In this retrospective study, we retrieved data for subjects who were on twice-daily 50 mg vildagliptin for at least 6 months, and classified the subjects into five treatment groups. In three of the groups, we added vildagliptin to their existing medication regimen; in the other two groups, we replaced one of their existing medications with vildagliptin. We then analyzed the changes in glucose parameters and clinical characteristics.
RESULTS
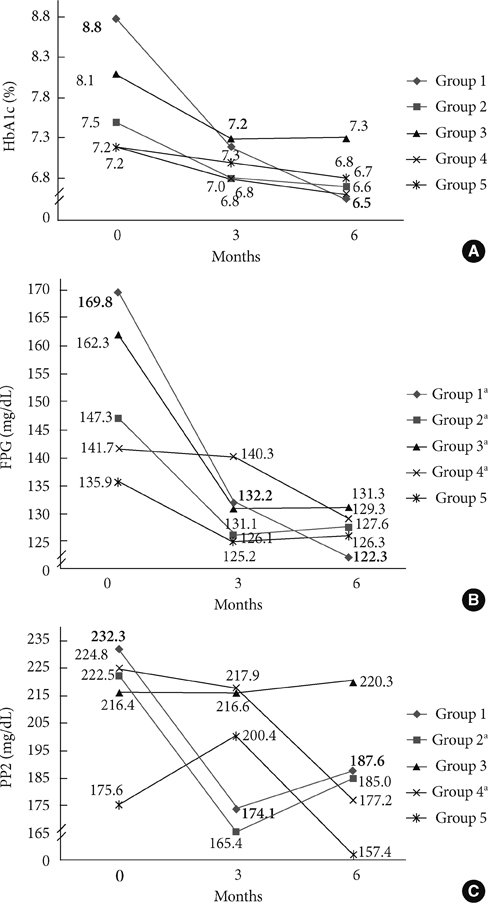
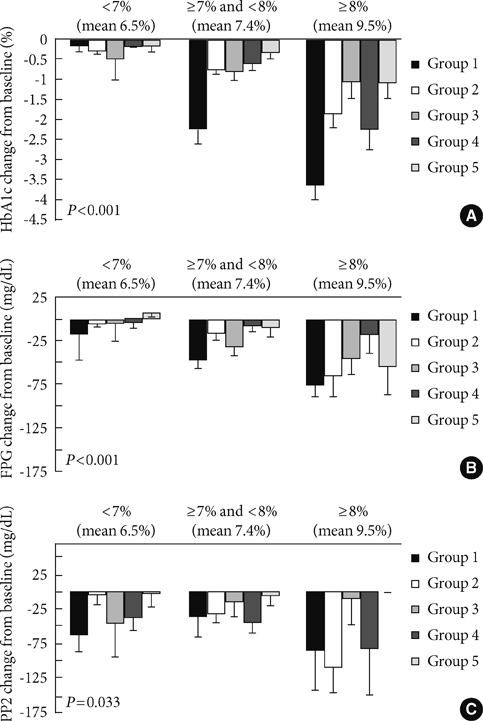
Ultimately, 327 subjects were analyzed in this study. Vildagliptin significantly improved hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels over 6 months. The changes in HbA1c levels (DeltaHbA1c) at month 6 were -2.24% (P=0.000), -0.77% (P=0.000), -0.80% (P=0.001), -0.61% (P=0.000), and -0.34% (P=0.025) for groups 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively, with significance. We also found significant decrements in fasting plasma glucose levels in groups 1, 2, 3, and 4 (P<0.05). Of the variables, initial HbA1c levels (P=0.032) and history of sulfonylurea use (P=0.026) were independently associated with responsiveness to vildagliptin treatment.
CONCLUSION
Vildagliptin was effective when it was used in subjects with poor glycemic control. It controlled fasting plasma glucose levels as well as sulfonylurea treatment in Korean type 2 diabetic subjects.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 359:1577–1589.2. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Harrap S, Heller S, Liu L, Mancia G, Mogensen CE, Pan C, Poulter N, Rodgers A, Williams B, Bompoint S, de Galan BE, Joshi R, Travert F. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:2560–2572.3. Rosenstock J, Foley JE, Rendell M, Landin-Olsson M, Holst JJ, Deacon CF, Rochotte E, Baron MA. Effects of the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitor vildagliptin on incretin hormones, islet function, and postprandial glycemia in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:30–35.4. Azuma K, Radikova Z, Mancino J, Toledo FG, Thomas E, Kangani C, Dalla Man C, Cobelli C, Holst JJ, Deacon CF, He Y, Ligueros-Saylan M, Serra D, Foley JE, Kelley DE. Measurements of islet function and glucose metabolism with the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008. 93:459–464.5. D'Alessio DA, Denney AM, Hermiller LM, Prigeon RL, Martin JM, Tharp WG, Saylan ML, He Y, Dunning BE, Foley JE, Pratley RE. Treatment with the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor vildagliptin improves fasting islet-cell function in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009. 94:81–88.6. Ahren B, Schweizer A, Dejager S, Dunning BE, Nilsson PM, Persson M, Foley JE. Vildagliptin enhances islet responsiveness to both hyper- and hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009. 94:1236–1243.7. He YL, Serra D, Wang Y, Campestrini J, Riviere GJ, Deacon CF, Holst JJ, Schwartz S, Nielsen JC, Ligueros-Saylan M. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007. 46:577–588.8. Dejager S, Razac S, Foley JE, Schweizer A. Vildagliptin in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose study. Horm Metab Res. 2007. 39:218–223.9. Pi-Sunyer FX, Schweizer A, Mills D, Dejager S. Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin monotherapy in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 76:132–138.10. Schweizer A, Couturier A, Foley JE, Dejager S. Comparison between vildagliptin and metformin to sustain reductions in HbA(1c) over 1 year in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2007. 24:955–961.11. Bosi E, Camisasca RP, Collober C, Rochotte E, Garber AJ. Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control over 24 weeks in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin. Diabetes Care. 2007. 30:890–895.12. Blonde L, Dagogo-Jack S, Banerji MA, Pratley RE, Marcellari A, Braceras R, Purkayastha D, Baron M. Comparison of vildagliptin and thiazolidinedione as add-on therapy in patients inadequately controlled with metformin: results of the GALIANT trial: a primary care, type 2 diabetes study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009. 11:978–986.13. Bolli G, Dotta F, Rochotte E, Cohen SE. Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin vs. pioglitazone when added to metformin: a 24-week, randomized, double-blind study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. 10:82–90.14. Garber AJ, Schweizer A, Baron MA, Rochotte E, Dejager S. Vildagliptin in combination with pioglitazone improves glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes failing thiazolidinedione monotherapy: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007. 9:166–174.15. Rosenstock J, Kim SW, Baron MA, Camisasca RP, Cressier F, Couturier A, Dejager S. Efficacy and tolerability of initial combination therapy with vildagliptin and pioglitazone compared with component monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007. 9:175–185.16. Garber AJ, Foley JE, Banerji MA, Ebeling P, Gudbjornsdottir S, Camisasca RP, Couturier A, Baron MA. Effects of vildagliptin on glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with a sulphonylurea. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. 10:1047–1056.17. Fonseca V, Schweizer A, Albrecht D, Baron MA, Chang I, Dejager S. Addition of vildagliptin to insulin improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2007. 50:1148–1155.18. Fonseca V, Baron M, Shao Q, Dejager S. Sustained efficacy and reduced hypoglycemia during one year of treatment with vildagliptin added to insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res. 2008. 40:427–430.19. Kikuchi M, Abe N, Kato M, Terao S, Mimori N, Tachibana H. Vildagliptin dose-dependently improves glycemic control in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009. 83:233–240.20. Iwamoto Y, Kashiwagi A, Yamada N, Terao S, Mimori N, Suzuki M, Tachibana H. Efficacy and safety of vildagliptin and voglibose in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2010. 12:700–708.21. Kikuchi M, Haneda M, Koya D, Tobe K, Onishi Y, Couturier A, Mimori N, Inaba Y, Goodman M. Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin as an add-on to glimepiride in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010. 89:216–223.22. Pan C, Xing X, Han P, Zheng S, Ma J, Liu J, Lv X, Lu J, Bader G. Institution Investigators. Efficacy and tolerability of vildagliptin as add-on therapy to metformin in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012. 14:737–744.23. Jeon HJ, Oh TK. Comparison of vildagliptin-metformin and glimepiride-metformin treatments in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab J. 2011. 35:529–535.24. Cai L, Cai Y, Lu ZJ, Zhang Y, Liu P. The efficacy and safety of vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2012. 37:386–398.25. He YL, Valencia J, Zhang Y, Schwartz SL, Ligueros-Saylan M, Foley J, Dole WP. Hormonal and metabolic effects of morning or evening dosing of the dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor vildagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010. 70:34–42.26. Marfella R, Barbieri M, Grella R, Rizzo MR, Nicoletti GF, Paolisso G. Effects of vildagliptin twice daily vs. sitagliptin once daily on 24-hour acute glucose fluctuations. J Diabetes Complications. 2010. 24:79–83.27. Balas B, Baig MR, Watson C, Dunning BE, Ligueros-Saylan M, Wang Y, He YL, Darland C, Holst JJ, Deacon CF, Cusi K, Mari A, Foley JE, DeFronzo RA. The dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor vildagliptin suppresses endogenous glucose production and enhances islet function after single-dose administration in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007. 92:1249–1255.28. Lee YH, Lee BW, Kwon HJ, Kang ES, Cha BS, Lee HC. Higher morning to evening ratio in total dose of twice-daily biphasic insulin analog might be effective in achieving glucose control in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012. 14:508–514.29. Perfetti R, Hui H. The role of GLP-1 in the life and death of pancreatic beta cells. Horm Metab Res. 2004. 36:804–810.30. Duttaroy A, Voelker F, Merriam K, Zhang X, Ren X, Subramanian K, Hughes TE, Burkey BF. The DPP-4 inhibitor vildagliptin increases pancreatic beta cell mass in neonatal rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. 650:703–707.31. Lukashevich V, Schweizer A, Shao Q, Groop PH, Kothny W. Safety and efficacy of vildagliptin versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate or severe renal impairment: a prospective 24-week randomized placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. 13:947–954.32. Dejager S, Schweizer A. Incretin therapies in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal impairment. Hosp Pract (Minneap). 2012. 40:7–21.33. Schweizer A, Dejager S, Foley JE. Impact of insulin resistance, body mass index, disease duration, and duration of metformin use on the efficacy of vildagliptin. Diabetes Ther. 2012. 3:8.34. Menzies DG, Campbell IW, McBain A, Brown IR. Metformin efficacy and tolerance in obese non-insulin dependent diabetics: a comparison of two dosage schedules. Curr Med Res Opin. 1989. 11:273–278.35. Ito H, Ohno Y, Yamauchi T, Kawabata Y, Ikegami H. Efficacy and safety of metformin for treatment of type 2 diabetes in elderly Japanese patients. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2011. 11:55–62.36. Boschmann M, Engeli S, Dobberstein K, Budziarek P, Strauss A, Boehnke J, Sweep FC, Luft FC, He Y, Foley JE, Jordan J. Dipeptidyl-peptidase-IV inhibition augments postprandial lipid mobilization and oxidation in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009. 94:846–852.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Vildagliptin-Metformin and Glimepiride-Metformin Treatments in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Effects of Vildagliptin or Pioglitazone on Glycemic Variability and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with Metformin Monotherapy: A 16-Week, Randomised, Open Label, Pilot Study
- The Effect of DPP-4 Inhibitors on Metabolic Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Glycemic Variability and Diabetes Mellitus
- The Efficacy of Vildagliptin in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes