Diabetes Metab J.
2013 Apr;37(2):117-124. 10.4093/dmj.2013.37.2.117.
Efficacy and Safety of Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30/70 in Type 2 Diabetes Suboptimally Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Therapy in Korea: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Center, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kskomd@paik.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2280713
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.2.117
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The purpose of this study was to evaluate change in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), side effects, and quality of life (QOL) after a 16-week treatment period with Biphasic insulin aspart 30/70 (BIasp30) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who had been suboptimally controlled with oral antidiabetic drugs (OADs).
METHODS
The study consisted of a 4-week titration period when concurrent OAD(s) were replaced with BIasp30 and followed by a 12-week maintenance period. All patients completed the Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire at the beginning and the end of the trial. Hypoglycemic episodes were recorded by the patient throughout the trial.
RESULTS
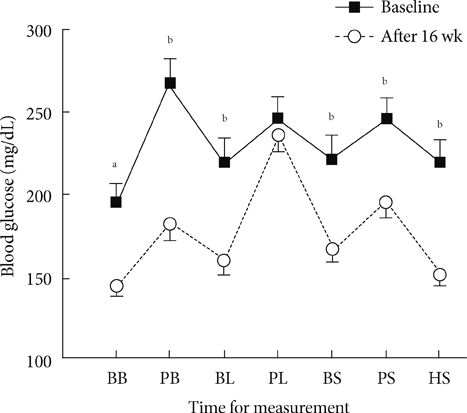
Sixty patients were included, of whom 55 patients (92%) completed the full 16-week treatment period. Seven-point blood glucose was significantly improved as compared with the baseline, except for the postlunch blood glucose level. HbA1c at the end of period was significantly improved from 9.2% to 8.2% (P<0.001). Eleven percent (n=6) of patients achieved HbA1c values < or =6.5% and 22% (n=12) of patients achieved <7.0%. There were 3.4 episodes/patients-year of minor hypoglycemia and 0.05 episodes/patients-year of major hypoglycemia. QOL showed significant changes only in the acceptability of high blood glucose category (P=0.003).
CONCLUSION
Treatment with once or twice daily BIasp30 may be an option for the patients with T2DM suboptimally controlled with OADs in Korea. However, considering the low number of patients achieving the HbA1c target and the high postlunch blood glucose levels, additional management with another modality may be required for optimal control.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim SG, Choi DS. The present state of diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2008. 51:791–798.2. Lim S, Kim DJ, Jeong IK, Son HS, Chung CH, Koh G, Lee DH, Won KC, Park JH, Park TS, Ahn J, Kim J, Park KG, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Lee I. A nationwide survey about the current status of glycemic control and complications in diabetic patients in 2006: the Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association on the epidemiology of diabetes mellitus. Korean Diabetes J. 2009. 33:48–57.3. Defronzo RA. Banting Lecture. From the triumvirate to the ominous octet: a new paradigm for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 2009. 58:773–795.4. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R, Zinman B. American Diabetes Association. European Association for Study of Diabetes. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:193–203.5. Rodbard HW, Jellinger PS, Davidson JA, Einhorn D, Garber AJ, Grunberger G, Handelsman Y, Horton ES, Lebovitz H, Levy P, Moghissi ES, Schwartz SS. Statement by an American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology consensus panel on type 2 diabetes mellitus: an algorithm for glycemic control. Endocr Pract. 2009. 15:540–559.6. Malone JK, Bai S, Campaigne BN, Reviriego J, Augendre-Ferrante B. Twice-daily pre-mixed insulin rather than basal insulin therapy alone results in better overall glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2005. 22:374–381.7. Holman RR, Thorne KI, Farmer AJ, Davies MJ, Keenan JF, Paul S, Levy JC. 4-T Study Group. Addition of biphasic, prandial, or basal insulin to oral therapy in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2007. 357:1716–1730.8. Raskin P, Allen E, Hollander P, Lewin A, Gabbay RA, Hu P, Bode B, Garber A. INITIATE Study Group. Initiating insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes: a comparison of biphasic and basal insulin analogs. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:260–265.9. Garber AJ. Premixed insulin analogues for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2006. 66:31–49.10. Qayyum R, Bolen S, Maruthur N, Feldman L, Wilson LM, Marinopoulos SS, Ranasinghe P, Amer M, Bass EB. Systematic review: comparative effectiveness and safety of premixed insulin analogues in type 2 diabetes. Ann Intern Med. 2008. 149:549–559.11. World Diabetes Foundation. International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes atlas. 2006. 3rd ed. Brussels: IDF Executive Office.12. Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009. 301:2129–2140.13. Liu KH, Chan YL, Chan WB, Chan JC, Chu CW. Mesenteric fat thickness is an independent determinant of metabolic syndrome and identifies subjects with increased carotid intimamedia thickness. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:379–384.14. Dickinson S, Colagiuri S, Faramus E, Petocz P, Brand-Miller JC. Postprandial hyperglycemia and insulin sensitivity differ among lean young adults of different ethnicities. J Nutr. 2002. 132:2574–2579.15. Bradley C, Lewis KS. Measures of psychological well-being and treatment satisfaction developed from the responses of people with tablet-treated diabetes. Diabet Med. 1990. 7:445–451.16. Pearson J, Powers MA. Systematically initiating insulin: the staged diabetes management approach. Diabetes Educ. 2006. 32:1 Suppl. 19S–28S.17. Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R, Zinman B. American Diabetes Association. European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Medical management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2009. 52:17–30.18. Holman RR, Farmer AJ, Davies MJ, Levy JC, Darbyshire JL, Keenan JF, Paul SK. 4-T Study Group. Three-year efficacy of complex insulin regimens in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009. 361:1736–1747.19. DECODE Study Group. European Diabetes Epidemiology Group. Is the current definition for diabetes relevant to mortality risk from all causes and cardiovascular and noncardiovascular diseases? Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:688–696.20. Meigs JB, Nathan DM, D'Agostino RB Sr, Wilson PW. Framingham Offspring Study. Fasting and postchallenge glycemia and cardiovascular disease risk: the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:1845–1850.21. Garber AJ, Wahlen J, Wahl T, Bressler P, Braceras R, Allen E, Jain R. Attainment of glycaemic goals in type 2 diabetes with once-, twice-, or thrice-daily dosing with biphasic insulin aspart 70/30 (The 1-2-3 study). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2006. 8:58–66.22. Rohlfing CL, Wiedmeyer HM, Little RR, England JD, Tennill A, Goldstein DE. Defining the relationship between plasma glucose and HbA(1c): analysis of glucose profiles and HbA(1c) in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:275–278.23. Yoshioka N, Kurihara Y, Manda N, Komori K, Kato M, Kijima H, Wada N, Yanagisawa K, Aoki S, Ono Y, Koike T. Step-up therapy with biphasic insulin aspart-70/30: Sapporo 1-2-3 study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009. 85:47–52.24. Lund SS, Tarnow L, Frandsen M, Nielsen BB, Hansen BV, Pedersen O, Parving HH, Vaag AA. Combining insulin with metformin or an insulin secretagogue in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes: 12 month, randomised, double blind trial. BMJ. 2009. 339:b4324.25. Ebato C, Shimizu T, Arakawa M, Mita T, Fujitani Y, Watada H, Kawamori R, Hirose T. Effect of sulfonylureas on switching to insulin therapy (twice-daily biphasic insulin aspart 30): comparison of twice-daily biphasic insulin aspart 30 with or without glimepiride in type 2 diabetic patients poorly controlled with sub-maximal glimepiride. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2009. 86:31–36.26. Swinnen SG, Hoekstra JB, DeVries JH. Insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:Suppl 2. S253–S259.27. Davies M, Storms F, Shutler S, Bianchi-Biscay M, Gomis R. ATLANTUS Study Group. Improvement of glycemic control in subjects with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes: comparison of two treatment algorithms using insulin glargine. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:1282–1288.28. Selam JL, Koenen C, Weng W, Meneghini L. Improving glycemic control with insulin detemir using the 303 Algorithm in insulin naive patients with type 2 diabetes: a subgroup analysis of the US PREDICTIVE 303 study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008. 24:11–20.29. Bretzel RG, Nuber U, Landgraf W, Owens DR, Bradley C, Linn T. Once-daily basal insulin glargine versus thrice-daily prandial insulin lispro in people with type 2 diabetes on oral hypoglycaemic agents (APOLLO): an open randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008. 371:1073–1084.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30/70 in Type 2 Diabetes Suboptimally Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Therapy in Korea: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study (Diabetes Metab J 2013;37:117-24)
- Response: Efficacy and Safety of Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30/70 in Type 2 Diabetes Suboptimally Controlled on Oral Antidiabetic Therapy in Korea: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study (Diabetes Metab J 2013;37:117-24)
- Switching to Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart from Basal Insulin Improves Postprandial Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Controlled Trial
- A 4-Week, Two-Center, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of EOPatch in Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Comparison of Antidiabetic Regimens in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Uncontrolled by Combination Therapy of Sulfonylurea and Metformin: Results of the MOHAS Disease Registry in Korea