Clin Nutr Res.
2012 Jul;1(1):66-77. 10.7762/cnr.2012.1.1.66.
Accuracy of Predictive Equations for Resting Metabolic Rates and Daily Energy Expenditures of Police Officials Doing Shift Work by Type of Work
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Gangneung 210-702, Korea. ekkim@gwnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2279754
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2012.1.1.66
Abstract
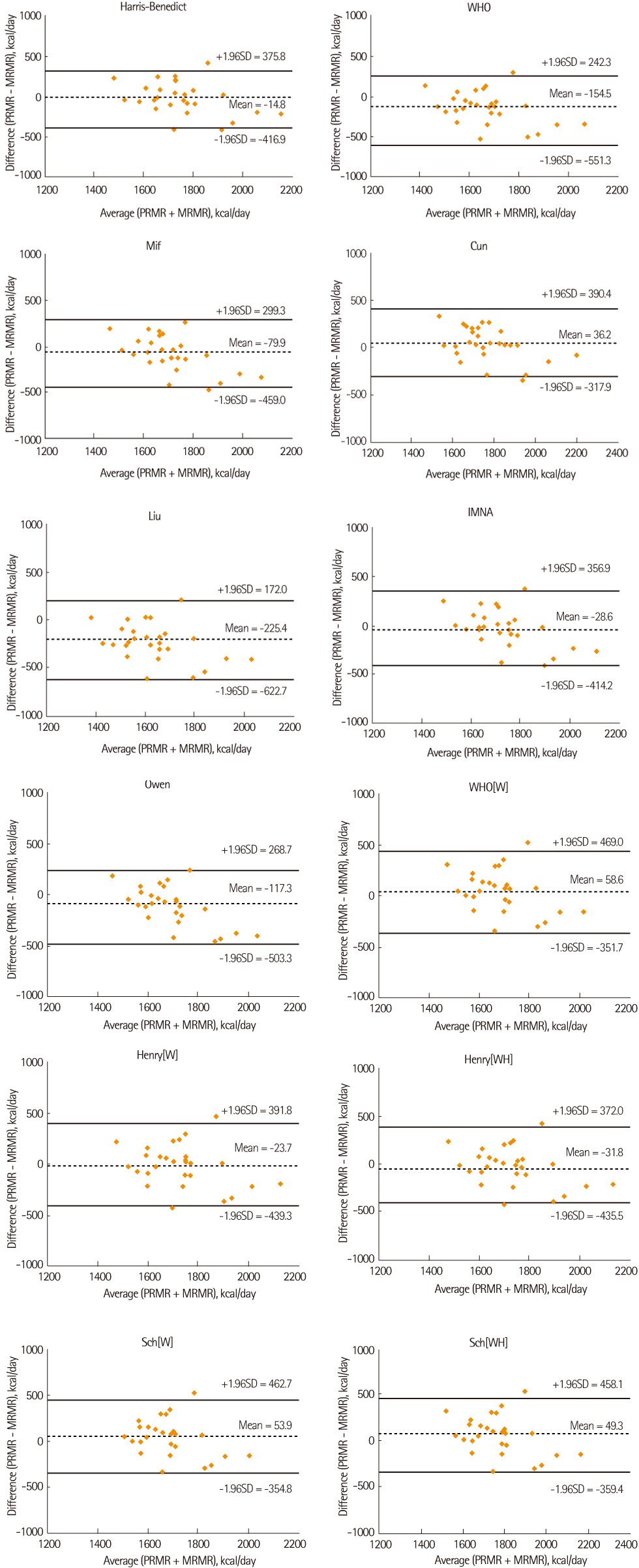
- The purpose of this study was to analyze the accuracy of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate (RMR) and daily energy expenditure in policemen on a rotating shift. Subjects were 28 healthy policemen on a rotating shift (males) age of 23-46 years. The participants' RMR was measured by using indirect calorimetry (TrueOne2400) and also calculated from various predicted equations of RMR (Harris-Benedict, Schofield(W)/(WH), FAO/WHO/UNU(W)/(W/H), Cunningham, Mifflin, Liu, Owen, IMNA and Henry(W)/(WH)). The accuracy of these equations were evaluated on basis of accurate prediction (the percentage of subjects whose RMR was predicted within 90% to 110% of the RMR measured), mean difference, root mean squared prediction error, mean % difference, limits of agreement of Bland-Altman method between predicted and measured RMR. The measured RMR value of subjects was 1748 +/- 205.9 kcal. Of the predictive equations tested, the Harris-Benedict equation (mean difference: -14.8 kcal/day, RMSPE: 195.8 kcal/day, mean % difference: 0.1%) was the most accurate and precise, but accuracy in prediction of the equation were only 35.7%. The daily energy expenditure at night-duty was 3062 kcal calculated as multiplying RMR by its physical activity level. Subsequently, daily energy expenditure of day-duty was 2647 kcal and the lowest daily energy expenditure was, 2310 kcal at holiday duty. Daily energy intake of all study participants was 2351 kcal at day-duty, 1959 kcal at night-duty and 1796 kcal at holiday-duty in order. The estimated energy requirements for policemen on a rotating shift on day shift, night shift and holiday came to 2743.6 kcal/day, 2998.6 kcal/day and 2576.9 kcal/day, respectively. These results suggest that estimated energy requirements (EER) of policemen on a rotating shift should be differently proposed by a proper equation which can closely reflect their metabolic status at each time shift.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Validity of predictive equations for resting energy expenditure in Korean non-obese adults
Didace Ndahimana, Yeon-Jung Choi, Jung-Hye Park, Mun-Jeong Ju, Eun-Kyung Kim
Nutr Res Pract. 2018;12(4):283-290. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2018.12.4.283.
Reference
-
1. Kogi K. Introduction to the problems of shift work in hours of works temporal factors in work schduling. 1985. New York: John Wiley and Sons.2. LaDou J. Occupational and environmental medicine. 1997. 2nd ed. Stamford: Appleton & Lange.3. Statistics Korea. Socio-Statistical Survey. 2010. cited 2012 July 4. Available from http://kosis.kr/abroad/abroad_01List.jsp?parentId=A.4. National police agency. Improving and efficient police force operating basic planning positions. 2008.5. Lee SA. New criminal justice. 2001. Seoul: Publishing Company Daemyoung.6. Akerstedt T. Psychophysiological effects of shift work. Scand J Work Environment Health. 1990. 16:67–73.7. Lee SH, Park JS, Kim EK. Assessment of daily steps, physical activities and activity coefficient of policemen who do shift-work. Korean J Nutr. 2007. 40:576–583.8. Matarese LE. Indirect calorimetry: Technical aspect. J Am Diet Assoc. 1997. 97:S154–S160.9. Stewart CL, Goody CM, Branson R. Comparison of two systems of measuring energy expenditure. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2005. 29:212–217.
Article10. Harris JA, Benedict FG. A biometric study of basal metabolism in man. 1919. Washington DC: Carnegie Ins..11. FAO/WHO/UNU Expert consultation. Energy and protein requirements. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1985. 724:71–112.12. The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans. 2010. Seoul: Hanarum Publishers.13. Trumbo P, Schlicker S, Yates AA, Poos M. The National Academies. Dietary reference intakes for energy, carbohydrate, fiber, fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, protein and amino acids. J Am Diet Assoc. 2002. 102:1621–1630.
Article14. Du Bois D, Du Bois EF. A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. 1916. Nutrition. 1989. 5:303–311.15. Weir JB. New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol. 1949. 109:1–9.
Article16. Taaffe DR, Thompson J, Butterfield G, Marcus R. Accuracy of equations to predict basal metabolic rate in older women. J Am Diet Assoc. 1995. 95:1387–1392.
Article17. Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986. 1:307–310.
Article18. Nelson KM, Weinsier RL, Long CL, Schutz Y. Prediction of resting energy expenditure from fat-free mass and fat mass. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992. 56:848–856.
Article19. Heymsfield SB, Gallagher D, Wang Z. Body composition modeling. Application to exploration of the resting energy expenditure fat-free mass relationship. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2000. 904:290–297.
Article20. Webb P. Energy expenditure and fat-free mass in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981. 34:1816–1826.21. Park JA, Kim KJ, Yoon JS, Koo JO, Yoon JS. A Comparison of the resting energy expenditure of Korean adults using indirect calorimetry. Korean J Community Nutr. 2003. 8:993–1000.22. Lee GH, Kim MH, Kim EK. Accuracy of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate in Korean college students. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009. 14:462–473.23. Owen OE, Kavle E, Owen RS, Polansky M, Caprio S, Mzzoli MA, Kendrick ZV, Bushman MC, Boden G. A reappraisal of caloric requirements in healthy women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1986. 44:1–19.
Article24. Owen OE, Holup JL, D'Alessio DA. A reappraisal of caloric requirements of men. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987. 46:875–885.25. Mifflin MD, St Jeor ST, Hill LA, Scott BJ, Daugherty SA, Koh YO. A new predictive equation for resting energy expenditure in healthy individuals. Am J Clin Nutr. 1990. 51:241–247.
Article26. Frankenfield D, Roth-Yousey L, Compher C. Comparison of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate in healthy nonobese and obese adults: a systematic review. J Am Diet Assoc. 2005. 105:775–789.
Article27. Daly JM, Heymsfield SB, Head CA, Harvey LP, Nixon DW, Katzeff H, Grossman GD. Human energy requirements: overestimation by widely used prediction equation. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985. 42:1170–1174.
Article28. Bouchard C, Trembly A, Leblanc C, Lortie G, Savard R, Theriault G. A method to assess energy expenditure in children and adult. Am J Clin Nutr. 1983. 37:461–467.29. Ravussin E, Lillioja S, Anderson TE, Christin L, Bogardus C. Determinants of 24-hour energy expenditure in man. Methods and results using a respiratory chamber. J Clin Invest. 1986. 78:1568–1578.
Article30. Benedict FG. The racial elements in human metabolism. Am J Physiol Anthropol. 1932. 16:463–473.31. Schofield C. An annotated bibliography of source material for basal meabolic rate data. Hum Nutr Clin Nutr. 1985. 39:Suppl 1. 42–91.32. FAO/WHO/UNU. Energy and protein requirements: Report of a joint FAO/WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1985. 724:1–206.33. Liu HY, Lu YF, Chen WJ. Predictive equations for basal metabolic rate in chinese adults. A Cross-Validation Study. J Am Diet Assoc. 1995. 95:1403–1408.34. Henry CJ, Rees DG. New predictive equations for the estimation of basal metabolic rate in tropical peoples. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1991. 45:177–185.35. Patwarthan VN. Indian Research Fund Association Special Report No. 12. Studies on basal metabolism in Indians. 1944. Bombay:36. Banerjee S. ICMR Special Report No. 43. Studies in energy metabolism. 1962. New Delhi:37. Shetty PS, Soares M. Basal metabolic rate in South Indian males. 1986. Bangalore, India: FAO.38. Durnin JV. Low energy expenditures in free-living populations. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1990. 44:Suppl. 95–102.39. Chang UJ, Lee KR, Chang UJ. Correlation between measured resting energy expenditure and predicted basal energy expenditure in female college students. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2005. 34:196–201.
Article40. Bandini LG, Schoeller DA, Dietz WH. Energy expenditure in obese and nonobese adolescents. Pediatr Res. 1990. 27:198–203.
Article41. Cunningham JJ. A Reanalysis of the factors influencing basal metabolic rate in normal adults. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980. 33:2372–2374.
Article42. Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2010 National Health and Nutritional Survey Report in Korean. 2010. cited 2012 July 4. Available from http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.43. Park JA, Kim KJ, Yoon JS. A Comparison of energy intake and energy expenditure in normal-weight and over-weight Korean adults. Korean J Community Nutr. 2004. 9:285–291.44. Lim WJ, Yoon JS. A longitudinal study on seasonal variation of physicl activity and body composition of rural women. Korean J Nutr. 1995. 28:893–903.45. Johan L, Solvoll K, Bjomeboe GE, Drevon CA. Under-and over reporting of energy intake related to weight ststus and lifestyle in a nationwide sample. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998. 68:266–274.46. Johanson RK, Goran MI, Poehlman ET. Correlations of over-and underrporting of energy intake in healthy older men and women. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994. 50:1286–1290.47. Lissner L, Habicht JP, Strupp BJ, Levitsky DA, Haas JD, Roe DA. Body composition and energy intake : do overweight women overeat and underreport? Am J Clin Nutr. 1989. 49:320–325.
Article48. Myers RJ, Klesges RC, Eck LH, Hanson CL, Klem ML. Accuracy of self-reports of food intake in obese and normal-weight individuals: effects of obesity on self-reports of dietary intake in adults females. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988. 48:1248–1251.
Article49. Hong SK. Energy balance and obesity. J Korean Soc Study Obes. 2000. 9:1–5.50. Heymsfield SB, McManus CB, Smith J, Stevens V, Nixon DW. Anthropometric measurement of muscle mass, revised equations for calculating bone-free arm muscle area. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982. 36:680–690.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Accuracy of Predictive Equations for Resting Metabolic Rate in Korean College Students
- Accuracy of predictive equations for resting energy expenditure (REE) in non-obese and obese Korean children and adolescents
- Association between split shift work and work-related injury and disease absence
- The Association between Shift Work and the Metabolic Syndrome in Female Workers
- Validity of predictive equations for resting energy expenditure in Korean non-obese adults