Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis.
2013 Aug;20(2):63-70.
Increasing Rates of Community Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Children with Muscular-Skeletal Infections in Korea: A Single Center Experience from 2000 to 2012
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. bjlover@lycos.co.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to explore how prevalent the community-related methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) was in children with muscular-skeletal infections.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients of 18 years or under who were diagnosed with suppurative arthritis or osteomyelitis and S. aureus from September 2000 through August 2012 at the CHA Bundang Medical center.
RESULTS
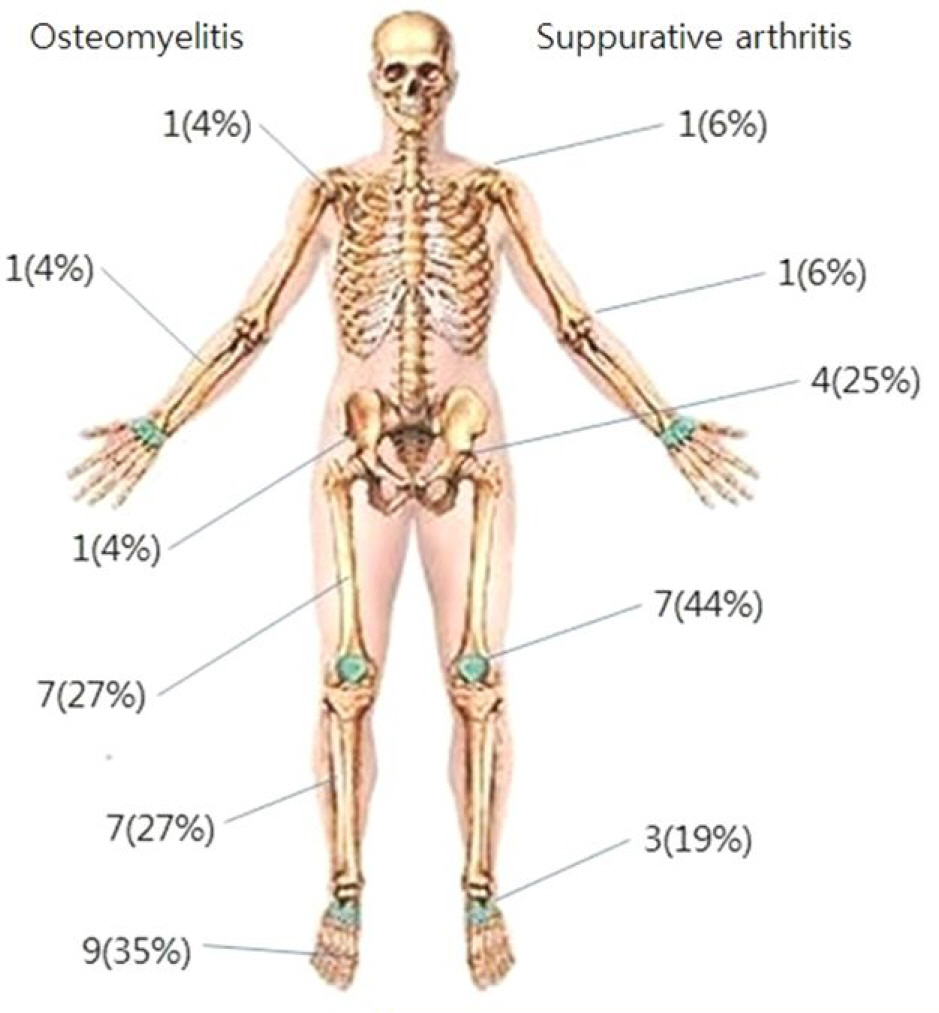
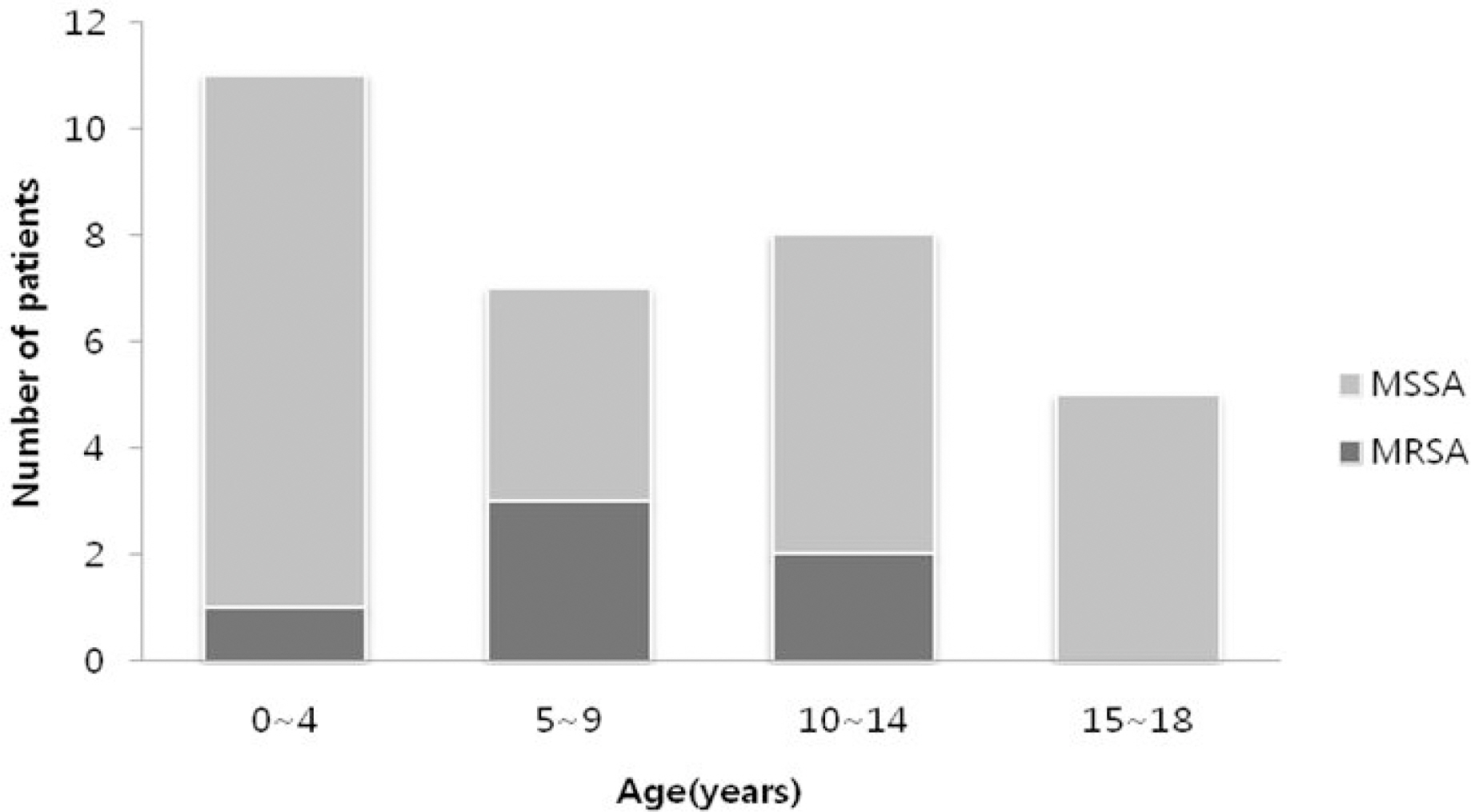
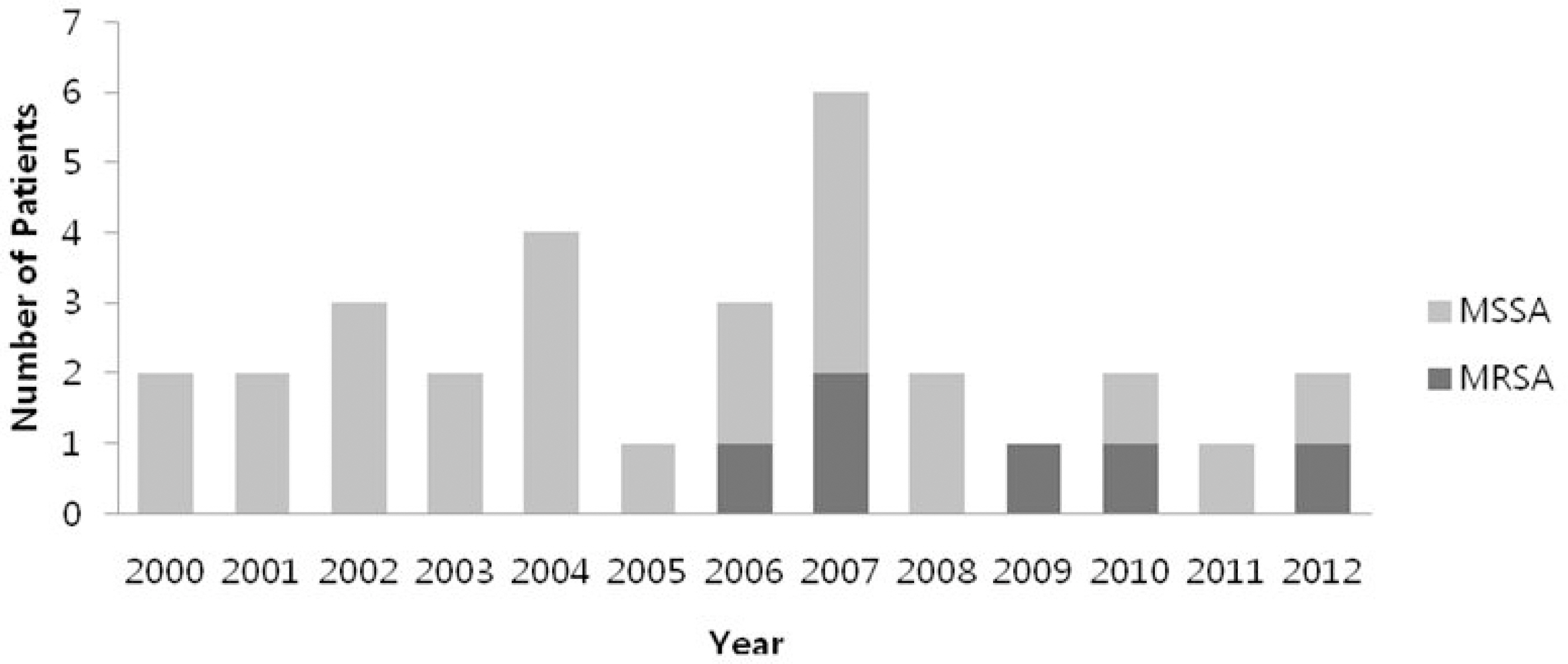
Thirty-one cases of suppurative arthritis or osteomyelitis were identified. The patients were between 17 days old and 18 years old with an average age of 7. Eleven cases (33.5%) of suppurative arthritis and 16 cases (51.6%) of osteomyelitis were observed. Five cases were accompanied by the two diseases. Methicillin sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) was isolated in 25 cases (80.6%) and methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) was isolated in 6 cases (19.4%). Multidrug resistant strains were not observed. MRSA was not found from 2000 through 2005. All patients were treated with antibiotics and the duration of antibiotics treatment was 26.4+/-12.7 days. Vancomycin was used as the initial antibiotic treatment in 4 cases (12.9%) and vancomycin was used as the definitive antibiotics in the 10 cases (32.3%).
CONCLUSIONS
The result of this study showed that methicillin resistance rate of S. aureus from muscular-skeletal infections was concentrated in the latter half of the 12 year period.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Krogstad P. Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis. Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 5th ed.W.B Saunders, Philadelphia;2004. p. 713–36.2. Gillespie WJ. Epidemiology in bone and joint infection. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1990; 4:361–76.
Article3. Park JS, Yeom JS, Hwang SC, Park ES, Seo JH, Lim JY, et al. Clinical study of acute pyogenic osteomyelitis in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48:731–6.4. Dormans JP, Drummond DS. Pediatric hematogenous osteomyelitis: New trends in presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1994; 2:333–41.
Article5. Manzotti A, Rovetta L, Pullen C, Catagni MA. Treatment of the late sequelae of septic arthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; 410:203–12.
Article6. Shirtliff ME, Mader JT. Acute septic arthritis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2002; 15:527–44.
Article7. Scott RJ, Christofersen MR, Robertson WW Jr, Davidson RS, Rankin L, Drummond DS. Acute osteomyelitis in children: a review of 116 cases. J Pediatr Orthop. 1990; 10:649–52.8. Goergens ED, McEvoy A, Watson M, Barrett IR. Acute osteomyelitis and septic arthritis in children. J Paediatr Child Health. 2005; 41:59–62.
Article9. Choi EH. Clinical manifestation and treatment of me-thicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureus infections in children. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2009; 16:1–5.10. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Nine-teenth informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S19; Philadelphia, CLSI. 2009.11. Yi J, Kim EC. Microbiological characteristics of methi-cillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 13:1–6.
Article12. Chong Y, Lee K. Present situation of antimicrobial resistance in Korea. J Infect Chemother. 2000; 6:189–95.
Article13. Kim HB, Jang HC, Nam HJ, Lee YS, Kim BS, Park WB, et al. In vitro activities of 28 antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus isolates from tertiary-care hospitals in Korea: a nationwide survey. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004; 48:1124–7.14. Otter JA, French GL. Molecular epidemiology of com-munity-associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Europe. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010; 10:227–39.15. Bukharie HA. Increasing threat of communityacquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Med Sci. 2010; 340:378–81.
Article16. Adam HJ, Allen VG, Currie A, McGeer AJ, Simor AE, Richardson SE, et al. Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: prevalence in skin and soft tissue infections at emergency departments in the Greater Toronto Area and associated risk factors. CJEM. 2009; 11:439–46.
Article17. Diederen BM, Kluytmans JA. The emergence of infections with community-associated methicillin resistant Staphy-lococcus aureus. J Infect. 2006; 52:157–68.
Article18. Kwak YH, Park SE, Hong JY, Jung HS, Park JY, Choi JH, et al. Etiologic agents and clinical features of acute pyogenic osteoarthritis in children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2000; 43:506–13.19. Como-Sabetti K, Jernigan JA, Harriman K, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Farley MM. Methicillin-resistant Sta-phylococcus aureus disease in three communities. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1436–44.20. Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, Ray S, et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylo-coccus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA. 2007; 298:1763–71.21. Gutman L. Osteomyelitis and suppurative arthritis. In:. Katz SL, Gershon AA, Hotez PJ., editorseditors.Infectious diseases of children. 10th ed.St Luis: Mosby;1998. p. 290–301.22. Song JS, Choe PG, Song KH, Cho JH, Kim SH, Bang JH, et al. Multicenter study for frequency and clinical features of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Korea. Infect Chemother. 2006; 38:325–33.23. Pr z-Roth E, Claverie-Martin F, Villar J, Mndezlvarez é S. Multiplex PCR for simultaneous identification of Staphylococcus aureus and detection of methicillin and mupirocin resistance. J Clin Microbiol. 2001; 39:4037–41.24. Bae IG, Kim JS, Kim S, Heo ST, Chang C, Lee EY. Genetic correlation of community-associated nethicillin-resi-stant Staphylococcus aureus strains from carriers and from patients with clinical infection in one region of Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:197–202.25. Diederen BM, Kluytmans JA. The emergence of infections with community-associated methicillin resistant Staphy-lococcus aureus. J Infect. 2006; 52:157–68.
Article26. Lee SO, Kim ES, Kim HY, Park ES, Jin HY, Ki HK, et al. Korean nosocomial infections surveillance system, intensive care unit module report: data summary from July 2007 through June 2008. Korean J Nosocomial Infect Control. 2008; 13:69–82. .S.27. Jeong HY, Jang SJ, Lee SD, Park SH, Chang JY, Min CS, et al. Antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from community in Korea. [SL-09] In: Program and abstract of the 4th International Symposium on Antimicrobial Agent and Resistance (Seoul). Republic of Korea: Asian-Pacific Research Foundation for Infectious Diseases. 2003.28. Naimi TS, LeDell KH, Como-Sabetti K, Borchardt SM, Boxrud DJ, Etienne J, et al. Comparison of community and health care-associated methicillin-resistant Staphy-lococcus aureus infection. JAMA. 2003; 290:2976–84.29. Salgado CD, Farr BM, Calfee DP. Community acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a metaanalysis of prevalence and risk factors. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 36:131–9.30. Boucher H, Miller LG, Razonable RR. Serious infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis. 2010; 51:183–97.31. Choe YJ, Lee SY, Sung JY, Yang MA, Lee JH, Oh CE, et al. A review of Staphylococcus aureus infections in children with an emphasis on community-associated methicillin-resistant S. aureus infections. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2009; 16:150–61.
Article32. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, 2002. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twelfth informational supplement (M100-S12), Wayne, PA.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA)
- Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Nosocomial Infections
- A statistical analysis of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
- A Review of Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Children with an Emphasis on Community-associated Methicillin-resistant S. aureus Infections