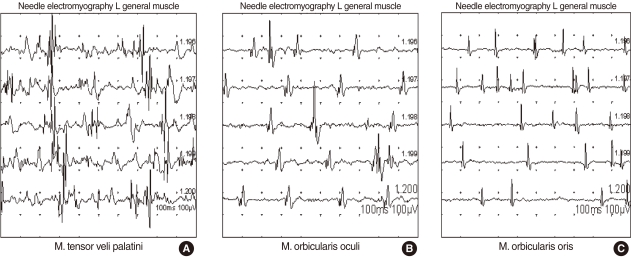
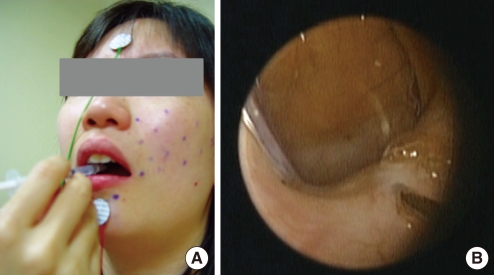
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Mar;5(1):44-48.
Palatal Myoclonus Associated with Orofacial Buccal Dystonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. snparkmd@catholic.ac.kr
Abstract
- Palatal myoclonus is a rare condition in which there are rhythmic jerky movements of the soft palate and sometimes of the other muscles innervated by the brainstem A particularly annoying symptom is a rhythmic clicking sound in the ear due to the opening and closing of the Eustachian tube. Orofacial buccal dystonia is a focal dystonia with sustained spasms of the masticatory, facial or lingual muscles. The frequent symptoms of this disease have mainly been reported to be involuntary and possibly painful jaw opening, closing, deflecting and retruding, or a combination of the above. However, the subtle and unnoticeable involuntary movement of multiple facial muscles, which might be an infrequent symptom of orofacial buccal dystonia, makes this disease hard to diagnose. Understanding the functional orofacial anatomy that is responsible for the clinical signs and symptoms is necessary for making a proper diagnosis. Here we report on a rare case of palatal myoclonus that was associated with orofacial buccal dystonia, and such a case has not been previously reported. We describe the diagnostic approach and excellent treatment results after Botulinum toxin A (Dysport) injection and proper counseling.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Deuschl G, Mischke G, Schenck E, Schulte-Monting J, Lucking CH. Symptomatic and essential rhythmic palatal myoclonus. Brain. 1990; 12. 113(Pt 6):1645–1672. PMID: 2276039.
Article2. Clark GT, Koyano K, Browne PA. Oral motor disorders in humans. J Calif Dent Assoc. 1993; 1. 21(1):19–30. PMID: 7682605.3. Tolosa E, Marti MJ. Blepharospasm-oromandibular dystonia syndrome (Meige's syndrome): clinical aspects. Adv Neurol. 1988; 49:73–84. PMID: 3278555.4. Badia L, Parikh A, Brookes GB. Management of middle ear myoclonus. J Laryngol Otol. 1994; 5. 108(5):380–382. PMID: 8035114.
Article5. Balasubramaniam R, Rasmussen J, Carlson LW, Van Sickels JE, Okeson JP. Oromandibular dystonia revisited: a review and a unique case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 2. 66(2):379–386. PMID: 18201628.
Article6. Tan EK, Jankovic J. Botulinum toxin A in patients with oromandibular dystonia: long-term follow-up. Neurology. 1999; 12. 10. 53(9):2102–2107. PMID: 10599789.
Article7. Bakke M, Werdelin LM, Dalager T, Fuglsang-Frederiksen A, Prytz S, Moller E. Reduced jaw opening from paradoxical activity of mandibular elevator muscles treated with botulinum toxin. Eur J Neurol. 2003; 11. 10(6):695–699. PMID: 14641515.
Article8. Jankovic J, Fahn S. Jankovic J, Tolosa E, editors. Dystonic syndromes. Parkinson's disease and movement disorders. 1993. 2nd ed. Baltimore (MD): Williams & Wilkins;p. 337–374.9. Sankhla C, Lai EC, Jankovic J. Peripherally induced oromandibular dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998; 11. 65(5):722–728. PMID: 9810945.
Article10. Sutcher HD, Underwood RB, Beatty RA, Sugar O. Orofacial dyskinesia: a dental dimension. JAMA. 1971; 5. 31. 216(9):1459–1463. PMID: 4931312.
Article12. Kwee HL, Struben WH. Tinnitus and myoclonus. J Laryngol Otol. 1972; 3. 86(3):237–241. PMID: 5014915.
Article13. Jamieson DR, Mann C, O'Reilly B, Thomas AM. Ear clicks in palatal tremor caused by activity of the levator veli palatini. Neurology. 1996; 4. 46(4):1168–1169. PMID: 8780116.
Article14. Park SN, Park KH, Lee DH, Yeo SW. A case of palatal myoclonus tinnitus treated with botulinm toxin injection. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2005; 9. 48(9):1177–1180.15. Krause E, Leunig A, Klopstock T, Gurkov R. Treatment of essential palatal myoclonus in a 10-year-old girl with botulinum neurotoxin. Otol Neurotol. 2006; 8. 27(5):672–675. PMID: 16868515.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Propriospinal Myoclonus and Cervical Dystonia Developed by Compressive Cervical Myelopathy
- A Familial Case of Myoclonus-Dystonia
- A Patient with Genetically Confirmed Myoclonus-Dystonia Responded to Anticholinergic Treatment and Improved Spontaneously
- A Case of Palatal Myoclonus Tinnitus Treated with Botolinum Toxin Injection
- A Case of Lingual Myoclonus