Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2012 Apr;5(Suppl 1):S43-S47.
Improving the Accuracy of Baha(R) Fittings through Measures of Direct Bone Conduction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cochlear Bone Anchored Solutions, Gothenburg, Sweden. mflynn@cochlear.com
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Variability in Baha(R) sound processor fittings may arise from the nature of the implant-to-bone transmission as well as transcranial attenuation for patients with single-sided sensorineural deafness (SSD). One method of improving the predictability of Baha fittings is to measure the individual patient's actual bone conduction thresholds, thereby removing the influences of skin thickness and/or the implant location site.
METHODS
Twenty adult wearers of the Baha bone conduction implant system participated in the study. Direct bone conduction thresholds were obtained through the BC Direct function of the Baha Fitting Software combined with the Cochlear Baha BP100 sound processor. For comparison, the masked and unmasked bone conduction responses of the patients were collected through standard audiometric testing techniques. Test-retest reliability measurement was performed for all participants. Data for each frequency and frequency range were analyzed separately.
RESULTS
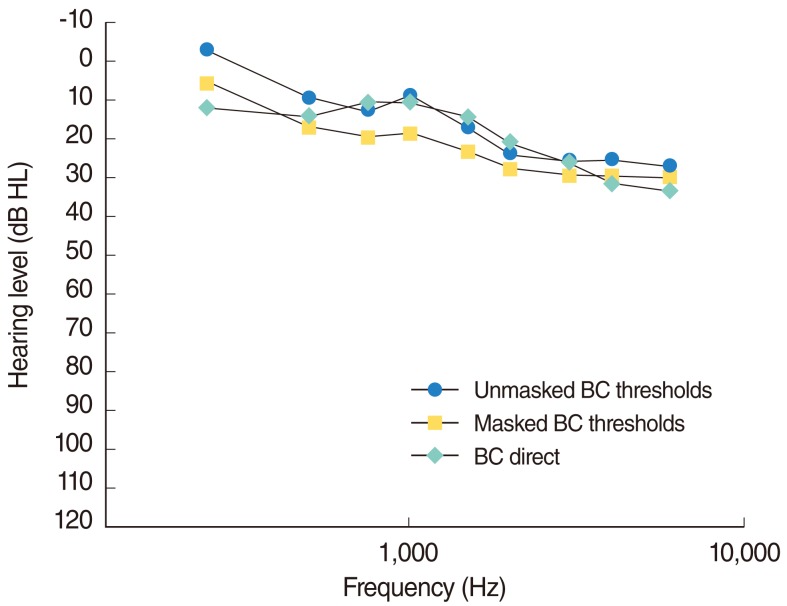
The results confirm the improved transmission of sound through the implant rather than transcutaneously through the skin. On average, the BC Direct thresholds were closer to the patient's unmasked thresholds than the masked values. In subjects with SSD, BC Direct results were poorer than contra-lateral bone conduction thresholds, most likely due to transcranial attenuation. The test-retest reliability for the BC Direct measurements was within +/-5 dB. The comparison of preferred amplification, based on direct bone conduction or bone conduction audiometry, found higher agreement for fittings based on direct bone conduction measurements.
CONCLUSION
While the transfer function between the implant and the skin can be predicted on average, there are a number of patients for whom measurement is essential to determine the required amplification. These were patients with: 1) SSD, 2) asymmetrical hearing loss, 3) unusual implant location or skull formation, and 4) users of Testband or Softband. The result for the clinician is that a fitting can take place with less fine-tuning and a greater understanding of the variability of bone conducted sound transmission.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nolan M, Lyon DJ. Transcranial attenuation in bone conduction audiometry. J Laryngol Otol. 1981; 6. 95(6):597–608. PMID: 7252337.
Article2. Stenfelt S, Goode RL. Transmission properties of bone conducted sound: measurements in cadaver heads. J Acoust Soc Am. 2005; 10. 118(4):2373–2391. PMID: 16266160.
Article3. Stenfelt S, Hakansson B, Tjellstrom A. Vibration characteristics of bone conducted sound in vitro. J Acoust Soc Am. 2000; 1. 107(1):422–431. PMID: 10641651.4. Stenfelt SP, Hakansson BE. Sensitivity to bone-conducted sound: excitation of the mastoid vs the teeth. Scand Audiol. 1999; 28(3):190–198. PMID: 10489868.
Article5. von Bekesy G, Wever EG. Experiments in hearing. 1960. Woodbury: Acoustical Society of America.6. Studebaker GA. Placement of vibrator in bone-conduction testing. J Speech Hear Res. 1962; 12. 5(4):321–331. PMID: 13993268.
Article7. Eeg-Olofsson M, Stenfelt S, Tjellstrom A, Granstrom G. Transmission of bone-conducted sound in the human skull measured by cochlear vibrations. Int J Audiol. 2008; 12. 47(12):761–769. PMID: 19085400.
Article8. Hakansson B, Tjellstrom A, Rosenhall U. Hearing thresholds with direct bone conduction versus conventional bone conduction. Scand Audiol. 1984; 13(1):3–13. PMID: 6719012.9. Hillbratt ME, Asnes K. Customization of bone anchored hearing devices. 2008. Geneva: World Intellectual Property Organization;No. WO/2010/017579.10. Carlsson P, Hakansson B, Ringdahl A. Force threshold for hearing by direct bone conduction. J Acoust Soc Am. 1995; 2. 97(2):1124–1129. PMID: 7876434.
Article11. Snik AF, Mylanus EA, Proops DW, Wolfaardt JF, Hodgetts WE, Somers T, et al. Consensus statements on the BAHA system: where do we stand at present? Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl. 2005; 12. 195:2–12. PMID: 16619473.
Article12. Catlin FI. Guide for the evaluation of hearing handicap. American Academy of Otolaryngology Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1979; 8. 12(3):655–663. PMID: 157459.13. Hakansson B, Carlsson P, Tjellstrom A. The mechanical point impedance of the human head, with and without skin penetration. J Acoust Soc Am. 1986; 10. 80(4):1065–1075. PMID: 3771927.14. van der Pouw CT, Snik AF, Cremers CW. The BAHA HC200/300 in comparison with conventional bone conduction hearing aids. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1999; 6. 24(3):171–176. PMID: 10384840.
Article15. Guidelines for manual pure-tone threshold audiometry [Internet]. American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. 2005. cited 2012 Feb 20. Rockville: American Speech-Language-Hearing Association;Available from: http://www.asha.org/docs/html/GL2005-00014.html.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Experience of BAHA(Bone Anchored Hearing Aid) Surgery
- Subjective and Audiologic Results of Bone Anchored Hearing Aids (BAHA)
- A Novel Surgical Technique for BAHA® Attract Implantation
- Surgical and Audiologic Comparison Between Sophono and Bone-Anchored Hearing Aids Implantation
- Hearing Rehabilitation of Single-Sided Deafness: Benefit and Selection Criteria of Bone Anchored Hearing Aid and Contralateral Routing of Signal Hearing Aid