Korean J Pain.
2011 Sep;24(3):131-136. 10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.131.
Participation of KATP Channels in the Antinociceptive Effect of Pregabalin in Rat Formalin Test
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ywleepain@yuhs.ac
- 2Anesthesia and Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2278100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.131
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Pregabalin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic agent that interacts selectively with the voltage-sensitive-Ca(2+)-channel alpha-2-delta subunit. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether the analgesic action of intrathecal (IT) pregabalin is associated with KATP channels in the rat formalin test.
METHODS
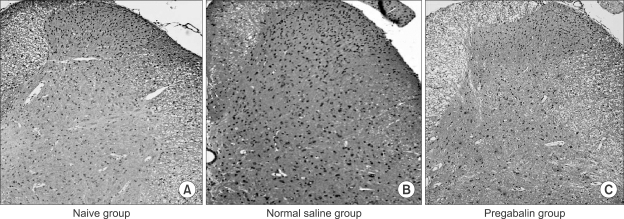
IT PE-10 catheters were implanted in male Sprague-Dawley rats (250-300 g) under inhalation anesthesia using enflurane. Nociceptive behavior was defined as the number of hind paw flinches during 60 min after formalin injection. Ten min before formalin injection, IT drug treatments were divided into 3 groups: normal saline (NS) 20 microl (CON group); pregabalin 0.3, 1, 3 and 10 microg in NS 10 microl (PGB group); glibenclamide 100 microg in DMSO 5 microl with pregabalin 0.3, 1, 3 and 10 microg in NS 5 microl (GBC group). All the drugs were flushed with NS 10 microl. Immunohistochemistry for the KATP channel was done with a different set of rats divided into naive, NS and PGB groups.
RESULTS
IT pregabalin dose-dependently decreased the flinching number only in phase 2 of formalin test. The log dose response curve of the GBC group shifted to the right with respect to that of the PGB group. Immunohistochemistry for the KATP channel expression on the spinal cord dorsal horn showed no difference among the groups 1 hr after the formalin test.
CONCLUSIONS
The antinociceptive effect of pregabalin in the rat formalin test was associated with the activation of the KATP channel. However, pregabalin did not induce KATP channel expression in the spinal cord dorsal horn.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Anesthesia, Inhalation
Animals
Catheters
Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Enflurane
Formaldehyde
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
Glyburide
Horns
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
KATP Channels
Male
Pain Measurement
Prostaglandins B
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Spinal Cord
Thienamycins
Pregabalin
Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Enflurane
Formaldehyde
Glyburide
KATP Channels
Prostaglandins B
Thienamycins
gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Evidence for the Participation of ATP-sensitive Potassium Channels in the Antinociceptive Effect of Curcumin
Marco Antonio De Paz-Campos, Aracely Evangelina Chávez-Piña, Mario I Ortiz, Gilberto Castañeda-Hernández
Korean J Pain. 2012;25(4):221-227. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2012.25.4.221.
Reference
-
1. Beydoun A, Uthman BM, Kugler AR, Greiner MJ, Knapp LE, Garofalo EA, et al. Safety and efficacy of two pregabalin regimens for add-on treatment of partial epilepsy. Neurology. 2005; 64:475–480. PMID: 15699378.
Article2. Yaksh TL. Calcium channels as therapeutic targets in neuropathic pain. J Pain. 2006; 7(1 Suppl 1):S13–S30. PMID: 16426997.
Article3. Joshi I, Taylor CP. Pregabalin action at a model synapse: binding to presynaptic calcium channel alpha2-delta subunit reduces neurotransmission in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006; 553:82–88. PMID: 17064682.
Article4. Dooley DJ, Taylor CP, Donevan S, Feltner D. Ca2+ channel alpha2delta ligands: novel modulators of neurotransmission. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007; 28:75–82. PMID: 17222465.5. Bauer CS, Tran-Van-Minh A, Kadurin I, Dolphin AC. A new look at calcium channel α2δ subunits. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010; 20:563–571. PMID: 20579869.
Article6. Quintero JE, Dooley DJ, Pomerleau F, Huettl P, Gerhardt GA. Amperometric measurement of glutamate release modulation by gabapentin and pregabalin in rat neocortical slices: role of voltage-sensitive Ca2+ alpha2delta-1 subunit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011; 338:240–245. PMID: 21464332.
Article7. McClelland D, Evans RM, Barkworth L, Martin DJ, Scott RH. A study comparing the actions of gabapentin and pregabalin on the electrophysiological properties of cultured DRG neurones from neonatal rats. BMC Pharmacol. 2004; 4:14. PMID: 15294026.8. Ocaña M, Cendán CM, Cobos EJ, Entrena JM, Baeyens JM. Potassium channels and pain: present realities and future opportunities. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004; 500:203–219. PMID: 15464034.
Article9. Marker CL, Luján R, Loh HH, Wickman K. Spinal G-protein-gated potassium channels contribute in a dose-dependent manner to the analgesic effect of mu- and delta- but not kappa-opioids. J Neurosci. 2005; 25:3551–3559. PMID: 15814785.
Article10. Seward E, Hammond C, Henderson G. Mu-opioid-receptor-mediated inhibition of the N-type calcium-channel current. Proc Biol Sci. 1991; 244:129–135. PMID: 1679547.11. Mixcoatl-Zecuatl T, Medina-Santillán R, Reyes-García G, Vidal-Cantú GC, Granados-Soto V. Effect of K+ channel modulators on the antiallodynic effect of gabapentin. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004; 484:201–208. PMID: 14744604.
Article12. Yaksh TL, Rudy TA. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976; 17:1031–1036. PMID: 14677603.
Article13. Reshef A, Sperling O, Zoref-Shani E. Opening of ATP-sensitive potassium channels by cromakalim confers tolerance against chemical ischemia in rat neuronal cultures. Neurosci Lett. 1998; 250:111–114. PMID: 9697931.
Article14. Soares AC, Leite R, Tatsuo MA, Duarte ID. Activation of ATP-sensitive K(+) channels: mechanism of peripheral antinociceptive action of the nitric oxide donor, sodium nitroprusside. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000; 400:67–71. PMID: 10913586.
Article15. Fehrenbacher JC, Taylor CP, Vasko MR. Pregabalin and gabapentin reduce release of substance P and CGRP from rat spinal tissues only after inflammation or activation of protein kinase C. Pain. 2003; 105:133–141. PMID: 14499429.
Article16. Zhang J, Ho KY, Wang Y. Efficacy of pregabalin in acute postoperative pain: a meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2011; 106:454–462. PMID: 21357616.
Article17. Fink K, Dooley DJ, Meder WP, Suman-Chauhan N, Duffy S, Clusmann H, et al. Inhibition of neuronal Ca(2+) influx by gabapentin and pregabalin in the human neocortex. Neuropharmacology. 2002; 42:229–236. PMID: 11804619.
Article18. Huang CW, Huang CC, Wu SN. The opening effect of pregabalin on ATP-sensitive potassium channels in differentiated hippocampal neuron-derived H19-7 cells. Epilepsia. 2006; 47:720–726. PMID: 16650138.
Article19. Mixcoatl-Zecuatl T, Flores-Murrieta FJ, Granados-Soto V. The nitric oxide-cyclic GMP-protein kinase G-K+ channel pathway participates in the antiallodynic effect of spinal gabapentin. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006; 531:87–95. PMID: 16438951.
Article20. Soares AC, Duarte ID. Dibutyryl-cyclic GMP induces peripheral antinociception via activation of ATP-sensitive K(+) channels in the rat PGE2-induced hyperalgesic paw. Br J Pharmacol. 2001; 134:127–131. PMID: 11522604.
Article21. Widmer HA, Rowe IC, Shipston MJ. Conditional protein phosphorylation regulates BK channel activity in rat cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Physiol. 2003; 552:379–391. PMID: 14561822.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evidence for the Participation of ATP-sensitive Potassium Channels in the Antinociceptive Effect of Curcumin
- The Analgesic Effects of Intrathecal Pregabalin in Rat Formalin Tests: Comparison between Pre- and Post-treatment
- Effect of Cisapride on ATP-sensitive K Channel of Ventricular Cell
- Cause of Intracellular ATP dependency on Zn2++ Blockade of KATP Channels in Pancreatic Beta Cells
- Antinociceptive drug interaction between intrathecal vitamin E and gabapentin in the rat formalin test