Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwseo@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2276880
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.3.209
Abstract
- Obesity is significantly increasing in Korean adolescents and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is soon expected to be the most common chronic liver disease in children. The symptoms of NAFLD run a broad spectrum and NAFLD in children can lead to the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and can increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Definitive diagnosis can be achieved with liver biopsy. However, recent advances have shown alternative methods of screening and following patients with noninvasive biomarkers and radiologic imaging studies. The histopathology differs between children and adults, and the mechanism is expected to differ as well. Several factors, such as genes and environmental stressors work intricately to produce NAFLD. Promising medications have been reported for the management of NAFLD. However, their therapeutic effectiveness has yet to be determined. Dietary and exercise interventions remain the mainstay of treatment. By maintaining an interest in obesity and NALFD in children, NAFLD should be diagnosed early and appropriate lifestyle changes should be counseled and encouraged.
MeSH Terms
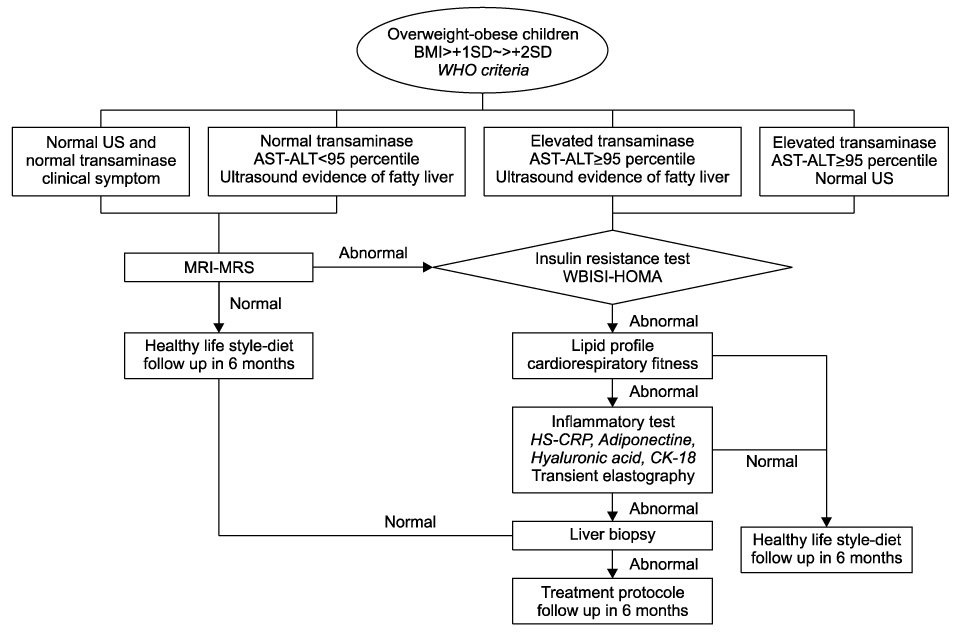
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
The Efficacy of Pharmacological Treatment in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Taeshik Cho, Yong Joo Kim, Seung Sam Paik
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012;15(4):256-265. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2012.15.4.256.Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Suspected Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in an Adolescent Population
Young Hoon Cho, Ju Whi Kim, Jung Ok Shim, Hye Ran Yang, Ju Young Chang, Jin Soo Moon, Jae Sung Ko
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2019;22(3):233-241. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.3.233.Pathologic Impact of Insulin Resistance and Sensitivity on the Severity of Liver Histopathology in Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Byung Han Park, Jung Min Yoon, Ja Hye Kim, Jin-Hwa Moon, Young Ho Lee, Se Min Jang, Yong Joo Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(4):756-762. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.4.756.
Reference
-
1. Mencin AA, Lavine JE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011. 14:151–157.
Article2. Alisi A, Locatelli M, Nobili V. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2010. 13:397–402.
Article3. Lindbäck SM, Gabbert C, Johnson BL, Smorodinsky E, Sirlin CB, Garcia N, et al. Pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a comprehensive review. Adv Pediatr. 2010. 57:85–140.
Article4. Widhalm K, Ghods E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a challenge for pediatricians. Int J Obes (Lond). 2010. 34:1451–1467.
Article5. Ko JS. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010. 56:6–14.
Article6. Lee KH. Update on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009. 12:Suppl 1. S62–S71.
Article7. Seo JW. Obesity in children and adolescents. Korean J Pediatr. 2009. 52:1311–1320.
Article8. Oh KW, Jang MJ, Lee NY, Moon JS, Lee CG, Yoo MH, et al. Prevalence and trends in obesity among Korean children and adolescents in 1997 and 2005. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:950–955.
Article9. Tannapfel A, Denk H, Dienes HP, Langner C, Schirmacher P, Trauner M, et al. Histopathological diagnosis of non-alcoholic and alcoholic fatty liver disease. Virchows Arch. 2011. 458:511–523.
Article10. Schwimmer JB, Dunn W, Norman GJ, Pardee PE, Middleton MS, Kerkar N, et al. SAFETY study: alanine aminotransferase cutoff values are set too high for reliable detection of pediatric chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2010. 138:1357–1364.
Article11. Fraser A, Longnecker MP, Lawlor DA. Prevalence of elevated alanine aminotransferase among US adolescents and associated factors: NHANES 1999-2004. Gastroenterology. 2007. 133:1814–1820.
Article12. Manco M, Marcellini M, Devito R, Comparcola D, Sartorelli MR, Nobili V. Metabolic syndrome and liver histology in paediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008. 32:381–387.
Article13. Loomba R, Sirlin CB, Schwimmer JB, Lavine JE. Advances in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2009. 50:1282–1293.
Article14. Hwang SW, Kim DH, Kim HS. Prevalence of the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. Korean J Pediatr. 2005. 48:13–20.15. Nho HN, Kim CR, Uhm JH, Kim JT, Jin SM, Seo JY, et al. The prevalence of obesity and metabolic abnormalities in Korean pediatric population. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2009. 12:207–214.
Article16. Park HS, Han JH, Choi KM, Kim SM. Relation between elevated serum alanine aminotransferase and metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005. 82:1046–1051.
Article17. Schwimmer JB, Deutsch R, Kahen T, Lavine JE, Stanley C, Behling C. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2006. 118:1388–1393.
Article18. Kistler KD, Molleston J, Unalp A, Abrams SH, Behling C, Schwimmer JB. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network (NASH CRN). Symptoms and quality of life in obese children and adolescents with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010. 31:396–406.
Article19. Schwimmer JB, McGreal N, Deutsch R, Finegold MJ, Lavine JE. Influence of gender, race, and ethnicity on suspected fatty liver in obese adolescents. Pediatrics. 2005. 115:e561–e565.
Article20. Barshop NJ, Francis CS, Schwimmer JB, Lavine JE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a comorbidity of childhood obesity. Ped Health. 2009. 3:271–281.
Article21. Petersen KF, Dufour S, Feng J, Befroy D, Dziura J, Dalla Man C, et al. Increased prevalence of insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Asian-Indian men. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006. 103:18273–18277.
Article22. Louthan MV, Theriot JA, Zimmerman E, Stutts JT, McClain CJ. Decreased prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in black obese children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005. 41:426–429.
Article23. Ko JS, Yoon JM, Yang HR, Myung JK, Kim H, Kang GH, et al. Clinical and histological features of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Dig Dis Sci. 2009. 54:2225–2230.
Article24. Feldstein AE, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Treeprasertsuk S, Benson JT, Enders FB, Angulo P. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: a follow-up study for up to 20 years. Gut. 2009. 58:1538–1544.
Article25. Argo CK, Northup PG, Al-Osaimi AM, Caldwell SH. Systematic review of risk factors for fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2009. 51:371–379.
Article26. Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Caldwell SH. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: summary of an AASLD single topic conference. Hepatology. 2003. 37:1202–1219.
Article27. Schwimmer JB, Deutsch R, Rauch JB, Behling C, Newbury R, Lavine JE. Obesity, insulin resistance, and other clinicopathological correlates of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Pediatr. 2003. 143:500–505.
Article28. Starley BQ, Calcagno CJ, Harrison SA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: a weighty connection. Hepatology. 2010. 51:1820–1832.
Article29. Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Clark JM, Bass NM, Van Natta ML, Unalp-Arida A, Tonascia J, et al. Clinical, laboratory and histological associations in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010. 52:913–924.
Article30. Sanyal AJ, Banas C, Sargeant C, Luketic VA, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, et al. Similarities and differences in outcomes of cirrhosis due to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2006. 43:682–689.
Article31. Caserta CA, Pendino GM, Amante A, Vacalebre C, Fiorillo MT, Surace P, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and carotid artery intima-media thickness in an adolescent population in southern Italy. Am J Epidemiol. 2010. 171:1195–1202.
Article32. Schwimmer JB, Pardee PE, Lavine JE, Blumkin AK, Cook S. Cardiovascular risk factors and the metabolic syndrome in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Circulation. 2008. 118:277–283.
Article33. Zivkovic AM, German JB, Sanyal AJ. Comparative review of diets for the metabolic syndrome: implications for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007. 86:285–300.
Article34. Donnelly KL, Smith CI, Schwarzenberg SJ, Jessurun J, Boldt MD, Parks EJ. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest. 2005. 115:1343–1351.
Article35. Kelishadi R, Cook SR, Amra B, Adibi A. Factors associated with insulin resistance and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among youths. Atherosclerosis. 2009. 204:538–543.
Article36. Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two "hits"? Gastroenterology. 1998. 114:842–845.
Article37. Cole LK, Jacobs RL, Vance DE. Tamoxifen induces triacylglycerol accumulation in the mouse liver by activation of fatty acid synthesis. Hepatology. 2010. 52:1258–1265.
Article38. Newbold RR, Padilla-Banks E, Jefferson WN. Environmental estrogens and obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009. 304:84–89.
Article39. Hu FB, Malik VS. Sugar-sweetened beverages and risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes: epidemiologic evidence. Physiol Behav. 2010. 100:47–54.
Article40. Kohli R, Kirby M, Xanthakos SA, Softic S, Feldstein AE, Saxena V, et al. High-fructose, medium chain trans fat diet induces liver fibrosis and elevates plasma coenzyme Q9 in a novel murine model of obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2010. 52:934–944.
Article41. Schwimmer JB, Celedon MA, Lavine JE, Salem R, Campbell N, Schork NJ, et al. Heritability of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2009. 136:1585–1592.
Article42. Tilg H, Moschen A. Update on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: genes involved in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and associated inflammation. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2010. 13:391–396.
Article43. Kheirandish-Gozal L, Sans Capdevila O, Kheirandish E, Gozal D. Elevated serum aminotransferase levels in children at risk for obstructive sleep apnea. Chest. 2008. 133:92–99.
Article44. Burke JP, Hale DE, Hazuda HP, Stern MP. A quantitative scale of acanthosis nigricans. Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:1655–1659.
Article45. Schwimmer JB, Behling C, Newbury R, Deutsch R, Nievergelt C, Schork NJ, et al. Histopathology of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005. 42:641–649.
Article46. Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005. 41:1313–1321.
Article47. Lee SH, Kim HJ, Oh JC, Han HJ, Kim HS, Tchach H, et al. Diagnosis of fatty liver complicated by simple obesity in children: serum ALT and its correlation with abdominal CT and liver biopsy. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999. 2:153–163.
Article48. Jarrar MH, Baranova A, Collantes R, Ranard B, Stepanova M, Bennett C, et al. Adipokines and cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008. 27:412–421.
Article49. Patton HM, Lavine JE, Van Natta ML, Schwimmer JB, Kleiner D, Molleston J. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Clinical correlates of histopathology in pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2008. 135:1961–1971.
Article50. Nobili V, Alkhouri N, Alisi A, Ottino S, Lopez R, Manco M, et al. Retinol-binding protein 4: a promising circulating marker of liver damage in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 7:575–579.
Article51. Feldstein AE, Wieckowska A, Lopez AR, Liu YC, Zein NN, McCullough AJ. Cytokeratin-18 fragment levels as noninvasive biomarkers for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a multicenter validation study. Hepatology. 2009. 50:1072–1078.
Article52. Nobili V, Parkes J, Bottazzo G, Marcellini M, Cross R, Newman D, et al. Performance of ELF serum markers in predicting fibrosis stage in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2009. 136:160–167.
Article53. Alkhouri N, Carter-Kent C, Lopez R, Rosenberg WM, Pinzani M, Bedogni G, et al. A combination of the pediatric NAFLD fibrosis index and enhanced liver fibrosis test identifies children with fibrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. 9:150–155.
Article54. Shah AG, Lydecker A, Murray K, Tetri BN, Contos MJ, Sanyal AJ. Nash Clinical Research Network. Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009. 7:1104–1112.
Article55. Carter-Kent C, Yerian LM, Brunt EM, Angulo P, Kohli R, Ling SC, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in children: a multicenter clinicopathological study. Hepatology. 2009. 50:1113–1120.
Article56. Nobili V, Alkhouri N, Bartuli A, Manco M, Lopez R, Alisi A, et al. Severity of liver injury and atherogenic lipid profile in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatr Res. 2010. 67:665–670.
Article57. Patton HM, Yates K, Unalp-Arida A, Behling CA, Huang TT, Rosenthal P, et al. Association between metabolic syndrome and liver histology among children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010. 105:2093–2102.
Article58. Needleman L, Kurtz AB, Rifkin MD, Cooper HS, Pasto ME, Goldberg BB. Sonography of diffuse benign liver disease: accuracy of pattern recognition and grading. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986. 146:1011–1015.
Article59. Cassidy FH, Yokoo T, Aganovic L, Hanna RF, Bydder M, Middleton MS, et al. Fatty liver disease: MR imaging techniques for the detection and quantification of liver steatosis. Radiographics. 2009. 29:231–260.
Article60. Tomita K, Tanimoto A, Irie R, Kikuchi M, Yokoyama H, Teratani T, et al. Evaluating the severity of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008. 28:1444–1450.
Article61. Nobili V, Vizzutti F, Arena U, Abraldes JG, Marra F, Pietrobattista A, et al. Accuracy and reproducibility of transient elastography for the diagnosis of fibrosis in pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2008. 48:442–448.
Article62. Wong VW, Vergniol J, Wong GL, Abraldes JG, Marra F, Pietrobattista A, et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010. 51:454–462.
Article63. Bohte AE, van Werven JR, Bipat S, Stoker J. The diagnostic accuracy of US, CT, MRI and 1H-MRS for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis compared with liver biopsy: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2011. 21:87–97. Epub 2010 Jul 31.
Article64. Shannon A, Alkhouri N, Carter-Kent C, Monti L, Devito R, Lopez R, et al. Ultrasonographic quantitative estimation of hepatic steatosis in children with NAFLD. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011. 53:190–195.
Article65. Reinehr T, Schmidt C, Toschke AM, Andler W. Lifestyle intervention in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: 2-year follow-up study. Arch Dis Child. 2009. 94:437–442.
Article66. Nobili V, Manco M, Devito R, Di Ciommo V, Comparcola D, Sartorelli MR, et al. Lifestyle intervention and antioxidant therapy in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology. 2008. 48:119–128.
Article67. Nobili V, Marcellini M, Devito R, Ciampalini P, Piemonte F, Comparcola D, et al. NAFLD in children: a prospective clinical-pathological study and effect of lifestyle advice. Hepatology. 2006. 44:458–465.
Article68. Houmard JA, Tanner CJ, Slentz CA, Duscha BD, McCartney JS, Kraus WE. Effect of the volume and intensity of exercise training on insulin sensitivity. J Appl Physiol. 2004. 96:101–106.
Article69. Lavine JE, Schwimmer JB, Van Natta ML, Molleston JP, Murray KF, Rosenthal P, et al. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Effect of vitamin E or metformin for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: the TONIC randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2011. 305:1659–1668.
Article70. Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, Kowdley KV, McCullough A, Diehl AM, Bass NM, et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2010. 362:1675–1685.
Article71. Lindor KD, Kowdley KV, Heathcote EJ, Harrison ME, Jorgensen R, Angulo P, et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid for treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: results of a randomized trial. Hepatology. 2004. 39:770–778.
Article72. Leuschner UF, Lindenthal B, Herrmann G, Arnold JC, Rössle M, Cordes HJ, et al. NASH Study Group. High-dose ursodeoxycholic acid therapy for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology. 2010. 52:472–479.
Article73. Ratziu V, de Ledinghen V, Oberti F, Mathurin P, Wartelle-Bladou C, Renou C, et al. A randomized controlled trial of high-dose ursodesoxycholic acid for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2011. 54:1011–1019.
Article74. Nobili V, Bedogni G, Alisi A, Pietrobattista A, Risé P, Galli C, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid supplementation decreases liver fat content in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: double-blind randomised controlled clinical trial. Arch Dis Child. 2011. 96:350–353.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of the Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Children
- Noninvasive serum biomarkers for liver steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Current and future developments
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathogenesis and treatment
- Elevated serum bilirubin levels are inversely associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Noninvasive diagnosis of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease