Korean J Obstet Gynecol.
2010 Apr;53(4):346-353. 10.5468/kjog.2010.53.4.346.
Expression of aromatase in endometiosis and its relation to clinical laboratory and surgical parameters
- Affiliations
-
- 1Mire-I OB & GY Women's Clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimyb2@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 2273862
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/kjog.2010.53.4.346
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Aromatase is the key enzyme for the conversion of C19 steroids into estrogen in certain human tissues. We studied to evaluate the aromatase expression in eutopic endometirum and endometriotic lesion and its relationship to clinical and laboratory parameters.
METHODS
The study included 78 cases of endometriotic lesion and 14 cases of eutopic endometrium and 30 cases of normal uterine endometrium obtained through laparoscopic surgery and curettage. The frozen tissue specimens were examined by immunohistochemistry using aromatase. Clinical symptoms, laboratory findings, and operative findings were analyzed and compared in according to aromatase expression.
RESULTS
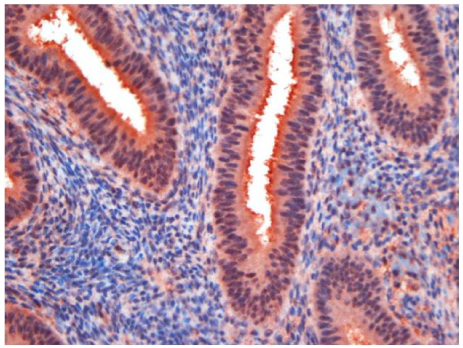
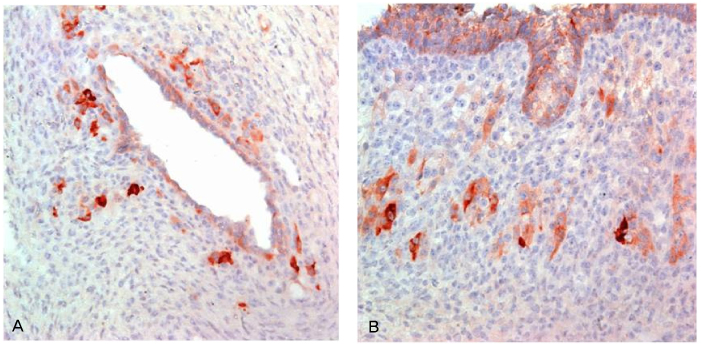
We observed positive immunohistochemical expression for aromatase in endometriotic lesion from 46/78 patients (59.0%). Aromatase expression was elevated in comparison to eutopic endometrium (5/14 patients, P=0.032) and the difference was more pronounced when eutopic endometriums from patients with endometriosis were compared with those of healthy controls (2/30 patients, P<0.001). Aromatase-positive patients had more moderate-to-severe chronic pelvic pain, higher CA-125 level significantly. Also in operative findings, severe grade endometriosis, bilateral endometriomas, and associated leiomyoma and adenomyosis were more frequent in aromatase positive patients. High values of white blood cell count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CA 19-9 were more frequent in aromatase positive patients notwithstanding insignificant differences.
CONCLUSION
Unopposed local biosynthesis of estrogens by increased expression of aromatase in eutopic endometrium and endometrial tissue could be involved in the development or maintenance of endometriosis and other uterine estrogen-triggered diseases. Our findings suggest increased expression of aromatase may be related with severity, activity, and chronic pelvic pain in patients with endometriosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lebovic DI, Mueller MD, Taylor RN. Immunobiology of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2001; 75:1–10.
Article2. Kitawaki J, Kado N, Ishihara H, Koshiba H, Kitaoka Y, Honjo H. Endometriosis: the pathophysiology as an estrogen-dependent disease. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002; 83:149–155.
Article3. Iwabe T, Harada T, Terakawa N. Role of cytokines in endometriosis-associated infertility. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2002; 53 Suppl 1:19–25.
Article4. Gómez-Torres MJ, Acién P, Campos A, Velasco I. Embryotoxicity of peritoneal fluid in women with endometriosis. Its relation with cytokines and lymphocyte populations. Hum Reprod. 2002; 17:777–781.5. Matsuzaki S, Canis M, Pouly JL, Déchelotte PJ, Mage G. Analysis of aromatase and 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 messenger ribonucleic acid expression in deep endometriosis and eutopic endometrium using laser capture microdissection. Fertil Steril. 2006; 85:308–313.6. Dheenadayalu K, Mak I, Gordts S, Campo R, Higham J, Puttemans P, et al. Aromatase P450 messenger RNA expression in eutopic endometrium is not a specific marker for pelvic endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2002; 78:825–829.
Article7. Noble LS, Takayama K, Zeitoun KM, Putman JM, Johns DA, Hinshelwood MM, et al. Prostaglandin E2 stimulates aromatase expression in endometriosis- derived stromal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997; 82:600–606.8. Bulun SE, Noble LS, Takayama K, Michael MD, Agarwal V, Fisher C, et al. Endocrine disorders associated with inappropriately high aromatase expression. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1997; 61:133–139.
Article9. Ebert AD, Bartley J, David M. Aromatase inhibitors and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors in endometriosis: new questions-old answers? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2005; 122:144–150.
Article10. Attar E, Bulun SE. Aromatase and other steroidogenic genes in endometriosis: translational aspects. Hum Reprod Update. 2006; 12:49–56.
Article11. Acién P, Quereda FJ, Gómez-Torres MJ, Bermejo R, Gutierrez M. GnRH analogues, transvaginal ultrasound-guided drainage and intracystic injection of recombinant interleukin-2 in the treatment of endometriosis. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2003; 55:96–104.
Article12. Revised American Fertility Society classification of endometriosis: 1985. Fertil Steril. 1985; 43:351–352.13. Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil Steril. 1997; 67:817–821.14. Velasco I, Rueda J, Acién P. Aromatase expression in endometriotic tissues and cell cultures of patients with endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 2006; 12:377–381.
Article15. Bulun SE, Simpson ER, Word RA. Expression of the CYP19 gene and its product aromatase cytochrome P450 in human uterine leiomyoma tissues and cells in culture. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994; 78:736–743.
Article16. Mousa NA, Bedaiwy MA, Casper RF. Aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of severe endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol. 2007; 109:1421–1423.
Article17. Bulun SE, Zeitoun KM, Takayama K, Sasano H. Molecular basis for treating endometriosis with aromatase inhibitors. Hum Reprod Update. 2000; 6:413–418.
Article18. Maia H Jr, Pimentel K, Casoy J, Correia T, Freitas LA, Zausner B, et al. Aromatase expression in the eutopic endometrium of myomatous uteri: the influence of the menstrual cycle and oral contraceptive use. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2007; 23:320–324.
Article19. Berstein LM, Tchernobrovkina AE, Gamajunova VB, Kovalevskij AJ, Vasilyev DA, Chepik OF, et al. Tumor estrogen content and clinico- morphological and endocrine features of endometrial cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2003; 129:245–249.20. Acién P. Miomas y reproducción. In: Remohí J, Pellicer A, Simón C, Navarro J, editors. Reproducción humana. 2nd ed. Madrid: McGraw-Hill Interamericana; 2002. pp. 245-262.21. Bulun SE, Imir G, Utsunomiya H, Thung S, Gurates B, Tamura M, et al. Aromatase in endometriosis and uterine leiomyomata. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005; 95:57–62.
Article22. Heilier JF, Donnez O, Van Kerckhove V, Lison D, Donnez J. Expression of aromatase (P450 aromatase/CYP19) in peritoneal and ovarian endometriotic tissues and deep endometriotic (adenomyotic) nodules of the rectovaginal septum. Fertil Steril. 2006; 85:1516–1518.
Article23. Acién P, Velasco I, Gutiérrez M, Marítnez-Beltrán M. Aromatase expression in endometriotic tissues and its relationship to clinical and analytical findings. Fertil Steril. 2007; 88:32–38.
Article24. Kitawaki J, Ishihara H, Koshiba H, Kiyomizu M, Teramoto M, Kitaoka Y, et al. Usefulness and limits of CA-125 in diagnosis of endometriosis without associated ovarian endometriomas. Hum Reprod. 2005; 20:1999–2003.
Article25. Somigliana E, Viganò P, Tirelli AS, Felicetta I, Torresani E, Vignali M, et al. Use of the concomitant serum dosage of CA 125, CA 19-9 and interleukin-6 to detect the presence of endometriosis. Results from a series of reproductive age women undergoing laparoscopic surgery for benign gynaecological conditions. Hum Reprod. 2004; 19:1871–1876.26. Zhang X, Wen J, Deng L, Lin J. Decreased levels of peritoneal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in patients with endometriosis and disease-related dysmenorrhea. Fertil Steril. 2007; 88:594–599.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Appropriate Testosterone-to-Estradiol Ratios for Aromatase Inhibitor Usage in Oligoasthenospermic Men
- Aromatase inhibition in ovarian cancer: repeated signals of efficacy but tools for patient selection remain elusive
- Effects of the Expression of Leptin and Leptin Receptor (OBR) on the Prognosis of Early-stage Breast Cancers
- Survival Benefit of Zoledronic Acid in Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Aromatase Inhibitors
- Effect of Potent Aromatase Inhibitor (Letrozole) on Bone Maturation and Predicted Adult Height in Boys with Early Puberty