Comparison between dental and basal arch forms in normal occlusion and Class III malocclusions utilizing cone-beam computed tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. kook2002@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Postgraduate Orthodontic Program, Arizona School of Dentistry & Oral Health, A.T. Still University, Mesa, AZ, USA.
- 3Graduate School of Dentistry, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Dentistry, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Dental Hygiene, Wonkwang Health Science University, Iksan, Korea.
- 6Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
- KMID: 2273464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2013.43.1.15
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
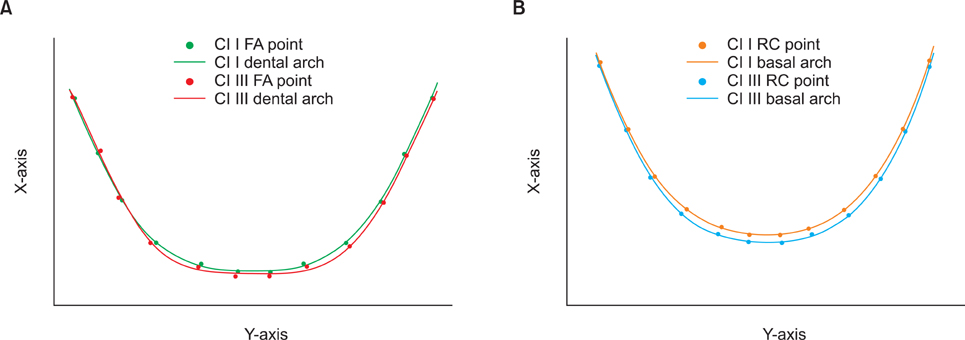
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between the mandibular dental and basal arch forms in subjects with normal occlusion and compare them with those of Class III malocclusion using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
METHODS
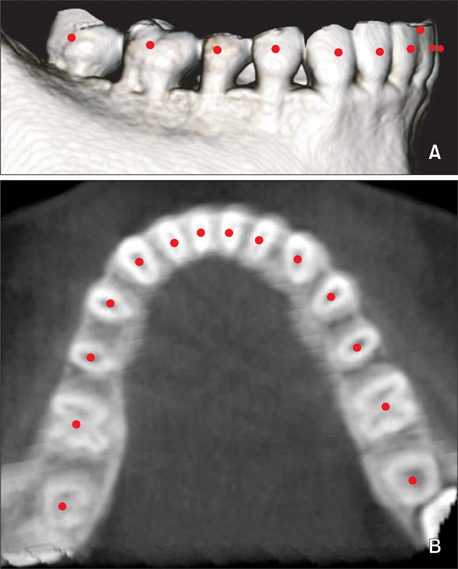
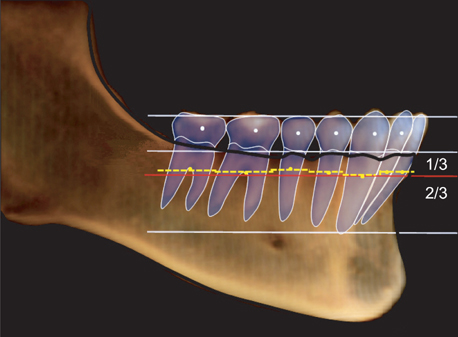
CBCT images of 32 normal occlusion (19 males, 13 females; 24.3 years) and 33 Class III malocclusion subjects (20 males, 13 females, 22.2 years) were selected. Facial axis and root center points were identified from the left to right mandibular first molars. Distances between the facial axis and root center points for each tooth were calculated, and 4 linear and 2 ratio variables were measured and calculated for each arch form. The variables were compared between groups by independent t-test. Pearson correlation coefficient was applied to assess the relationships between dental and basal variables within each group.
RESULTS
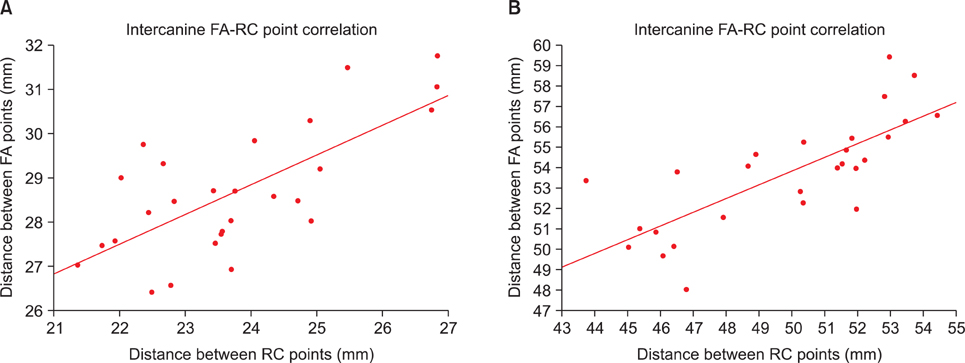
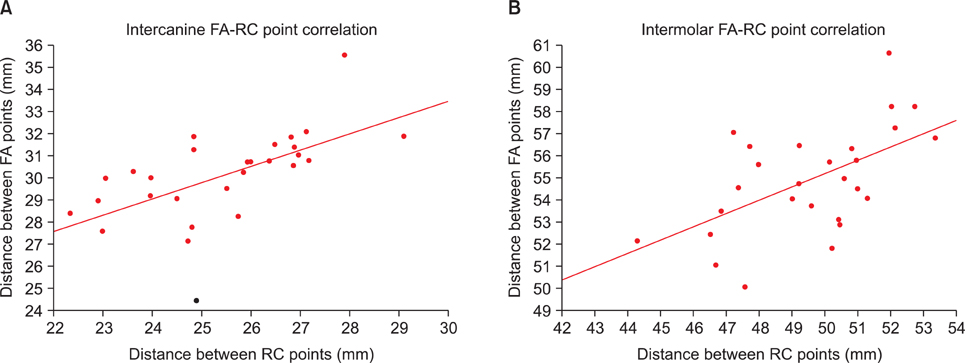
The mandibular dental and basal intercanine widths were significantly greater in the Class III group than in normal occlusion subjects (p < 0.05). The dental and basal intercanine widths as well as the dental and basal intermolar widths were strongly correlated in normal occlusion and moderately correlated in Class III malocclusion.
CONCLUSIONS
The dental arch form demon strated a strong positive correlation with the basal arch form in the normal occlusion group and moderate correlation in the Class III malocclusion group. These results might be helpful for clinicians to have a better understanding of the importance of basal arch form in the alveolar bone.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
New classification of lingual arch form in normal occlusion using three dimensional virtual models
Kyung Hee Park, Mohamed Bayome, Jae Hyun Park, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung-Hak Baek, Yoon-Ah Kook
Korean J Orthod. 2015;45(2):74-81. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2015.45.2.74.A novel classification of anterior alveolar arch forms and alveolar bone thickness: A cone-beam computed tomography study
Atcharee Bulyalert, Atiphan Pimkhaokham
Imaging Sci Dent. 2018;48(3):191-199. doi: 10.5624/isd.2018.48.3.191.Influence of the anterior arch shape and root position on root angulation in the maxillary esthetic area
Suweera Petaibunlue, Pravej Serichetaphongse, Atiphan Pimkhaokham
Imaging Sci Dent. 2019;49(2):123-130. doi: 10.5624/isd.2019.49.2.123.Maxillomandibular arch width differences at estimated centers of resistance: Comparison between normal occlusion and skeletal Class III malocclusion
Yun-Jin Koo, Sung-Hwan Choi, Byeong-Tak Keum, Hyung-Seog Yu, Chung-Ju Hwang, Birte Melsen, Kee-Joon Lee
Korean J Orthod. 2017;47(3):167-175. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2017.47.3.167.
Reference
-
1. Howes AE. Model analysis for treatment planning: a portion of a symposium on case analysis and treatment planning. Am J Orthod. 1952. 38:183–207.2. Rees DJ. A method for assessing the proportional relation of apical bases and contact diameters of the teeth. Am J Orthod. 1953. 39:695–707.
Article3. Stevens DR, Flores-Mir C, Nebbe B, Raboud DW, Heo G, Major PW. Validity, reliability, and reproducibility of plaster vs digital study models: comparison of peer assessment rating and Bolton analysis and their constituent measurements. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006. 129:794–803.
Article4. Quimby ML, Vig KW, Rashid RG, Firestone AR. The accuracy and reliability of measurements made on computer-based digital models. Angle Orthod. 2004. 74:298–303.5. Ball RL, Miner RM, Will LA, Arai K. Comparison of dental and apical base arch forms in Class II Division 1 and Class I malocclusions. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010. 138:41–50.
Article6. Gupta D, Miner RM, Arai K, Will LA. Comparison of the mandibular dental and basal arch forms in adults and children with Class I and Class II malocclusions. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010. 138:10.e1–10.e8.
Article7. Ronay V, Miner RM, Will LA, Arai K. Mandibular arch form: the relationship between dental and basal anatomy. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2008. 134:430–438.
Article8. Cha BK, Lee YH, Lee NK, Choi DS, Baek SH. Soft tissue thickness for placement of an orthodontic miniscrew using an ultrasonic device. Angle Orthod. 2008. 78:403–408.
Article9. Berco M, Rigali PH Jr, Miner RM, DeLuca S, Anderson NK, Will LA. Accuracy and reliability of linear cephalometric measurements from cone-beam computed tomography scans of a dry human skull. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009. 136:17.e1–17.e9.
Article10. Damstra J, Fourie Z, Huddleston Slater JJ, Ren Y. Accuracy of linear measurements from cone-beam computed tomography-derived surface models of different voxel sizes. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010. 137:16.e1–16.e11.
Article11. Tai K, Hotokezaka H, Park JH, Tai H, Miyajima K, Choi M, et al. Preliminary cone-beam computed tomography study evaluating dental and skeletal changes after treatment with a mandibular Schwarz appliance. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010. 138:262.e1–262.e11.
Article12. Bayome M. Evaluation of three-dimensional relationships among skeletal, dentoalveolar, and soft tissue variables in normal occlusion sample [doctorial dissertation]. 2011. Seoul, Korea: The Catholic University of Korea.13. Kuntz TR, Staley RN, Bigelow HF, Kremenak CR, Kohout FJ, Jakobsen JR. Arch widths in adults with Class I crowded and Class III malocclusions compared with normal occlusions. Angle Orthod. 2008. 78:597–603.
Article14. Al-Khateeb SN, Abu Alhaija ES. Tooth size discrepancies and arch parameters among different malocclusions in a Jordanian sample. Angle Orthod. 2006. 76:459–465.15. Uysal T, Usumez S, Memili B, Sari Z. Dental and alveolar arch widths in normal occlusion and Class III malocclusion. Angle Orthod. 2005. 75:809–813.16. Slaj M, Spalj S, Pavlin D, Illes D, Slaj M. Dental archforms in dentoalveolar Class I, II and III. Angle Orthod. 2010. 80:919–924.
Article17. Braun S, Hnat WP, Fender DE, Legan HL. The form of the human dental arch. Angle Orthod. 1998. 68:29–36.18. Andrews LF. The six keys to normal occlusion. Am J Orthod. 1972. 62:296–309.
Article19. Andrews LF, Andrews WA. The six elements of orofacial harmony. Andrews J. 2000. 1:13–22.20. Sarikaya S, Haydar B, Ciğer S, Ariyürek M. Changes in alveolar bone thickness due to retraction of anterior teeth. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002. 122:15–26.
Article21. Shelley AM, Brunton P, Horner K. Subjective image quality assessment of cross sectional imaging methods for the symphyseal region of the mandible prior to dental implant placement. J Dent. 2011. 39:764–770.
Article22. Howes AE. A polygon portrayal of coronal and basal arch dimensions in the horizontal plane. Am J Orthod. 1954. 40:811–831.
Article23. Kim KY, Bayome M, Kim K, Han SH, Kim Y, Baek SH, et al. Three-dimensional evaluation of the relationship between dental and basal arch forms in normal occlusion. Korean J Orthod. 2011. 41:288–296.
Article24. Sergl HG, Kerr WJ, McColl JH. A method of measuring the apical base. Eur J Orthod. 1996. 18:479–483.
Article25. Ludlow JB, Ivanovic M. Comparative dosimetry of dental CBCT devices and 64-slice CT for oral and maxillofacial radiology. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008. 106:106–114.
Article26. Scheid RC, Weiss G, Woelfel JB. Woelfel's dental anatomy. 2012. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.27. Bayome M, Sameshima GT, Kim Y, Nojima K, Baek SH, Kook YA. Comparison of arch forms between Egyptian and North American white populations. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2011. 139:e245–e252.
Article28. Kook YA, Nojima K, Moon HB, McLaughlin RP, Sinclair PM. Comparison of arch forms between Korean and North American white populations. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2004. 126:680–686.
Article29. Nojima K, McLaughlin RP, Isshiki Y, Sinclair PM. A comparative study of Caucasian and Japanese mandibular clinical arch forms. Angle Orthod. 2001. 71:195–200.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Maxillomandibular arch width differences at estimated centers of resistance: Comparison between normal occlusion and skeletal Class III malocclusion
- A Study on Basal and Dental Arch Width in Skeletal Class III Malocclusion
- Posterior dental compensation and occlusal function in adults with different sagittal skeletal malocclusions
- Location and shape of the mandibular lingula: Comparison of skeletal class I and class III patients using panoramic radiography and cone-beam computed tomography
- Three dimensional structural analysis between dental arch and basal bone in normal occlusion