Korean J Orthod.
2012 Apr;42(2):56-63. 10.4041/kjod.2012.42.2.56.
Three-dimensional soft tissue analysis for the evaluation of facial asymmetry in normal occlusion individuals
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthodontics, 2nd Stage of Brain Korea 21, School of Dentistry, Dental Science Research Institute, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea. hhwang@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea; Department of Stomatology, Bethune International Peace Hospital, Shijiazhuang, PR China.
- 3School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 4Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 5Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, School of Dentistry, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2273256
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4041/kjod.2012.42.2.56
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To identify the right and left difference of the facial soft tissue landmarks three-dimensionally from the subjects of normal occlusion individuals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
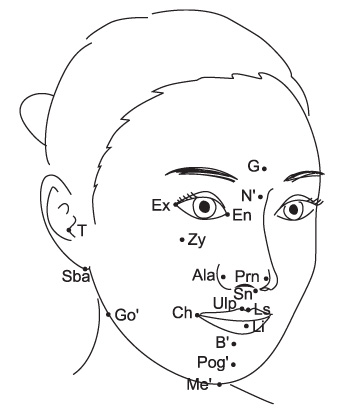
Cone-beam computed tomography (CT) scans were obtained in 48 normal occlusion adults (24 men, 24 women), and reconstructed into 3-dimensional (3D) models by using a 3D image soft ware. 3D position of 27 soft tissue landmarks, 9 midline and 9 pairs of bilateral landmarks, were identified in 3D coordination system, and their right and left differences were calculated and analyzed.
RESULTS
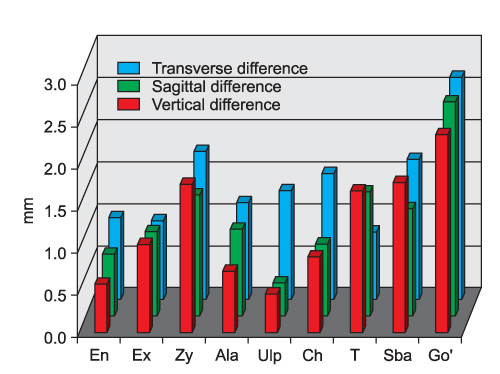
The right and left difference values derived from the study ranged from 0.6 to 4.6 mm indicating a high variability according to the landmarks. In general, the values showed a tendency to increase according to the lower and lateral positioning of the landmarks in the face. Overall differences were determined not only by transverse differences but also by sagittal and vertical differences, indicating that 3D evaluation would be essential in the facial soft tissue analysis.
CONCLUSIONS
Means and standard deviations of the right and left difference of facial soft tissue landmarks derived from this study can be used as the diagnostic standard values for the evaluation of facial asymmetry.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
3-Dimensional analysis for class III malocclusion patients with facial asymmetry
Eun-Ja Kim, Eun-Jung Ki, Hae-Myung Cheon, Eun-Joo Choi, Kyung-Hwan Kwon
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;39(4):168-174. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.4.168.Evaluation of soft tissue asymmetry using cone-beam computed tomography after open reduction and internal fixation of zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture
Dong Hyuck Kim, Rae Hyong Kim, Jun Lee, Young Deok Chee, Kyoung-Hwan Kwon
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;40(3):103-110. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.3.103.
Reference
-
1. Proffit WR, Fields HW Jr, Sarver DM. Contemporary orthodontics. 2007. 4th ed. St Louis: Mosby;5.2. Bittner C, Pancherz H. Facial morphology and malocclusions. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1990. 97:308–315.
Article3. Kim WS, Lee KH, Hwang HS. Comparison of asymmetric degree between maxillofacial hard and soft tissue in facial asymmetric subjects using three-dimensional computed tomography. Korean J Orthod. 2005. 35:163–173.4. Katsumata A, Fujishita M, Maeda M, Ariji Y, Ariji E, Langlais RP. 3D-CT evaluation of facial asymmetry. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005. 99:212–220.
Article5. Maeda M, Katsumata A, Ariji Y, Muramatsu A, Yoshida K, Goto S, et al. 3D-CT evaluation of facial asymmetry in patients with maxillofacial deformities. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006. 102:382–390.
Article6. Hwang HS, Hwang CH, Lee KH, Kang BC. Maxillofacial 3-dimensional image analysis for the diagnosis of facial asymmetry. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2006. 130:779–785.
Article7. Alavi DG, BeGole EA, Schneider BJ. Facial and dental arch asymmetries in Class II subdivision malocclusion. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1988. 93:38–46.
Article8. Peck S, Peck L, Kataja M. Skeletal asymmetry in esthetically pleasing faces. Angle Orthod. 1991. 61:43–48.9. Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Miani A Jr, Serrao G. Dental arch asymmetry in young healthy human subjects evaluated by Euclidean distance matrix analysis. Arch Oral Biol. 1993. 38:189–194.
Article10. Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Miani A, Tartaglia G. Craniofacial morphometry by photographic evaluations. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993. 103:327–337.
Article11. Farkas LG. Anthropometry of the head and face. 1994. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press;103–111.12. Ras F, Habets LL, van Ginkel FC, Prahl-Andersen B. Method for quantifying facial asymmetry in three dimensions using stereophotogrammetry. Angle Orthod. 1995. 65:233–239.13. Ras F, Habets LL, van Ginkel FC, Prahl-Andersen B. Three-dimensional evaluation of facial asymmetry in cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1994. 31:116–121.
Article14. Ras F, Habets LL, van Ginkel FC, Prahl-Andersen B. Longitudinal study on three-dimensional changes of facial asymmetry in children between 4 to 12 years of age with unilateral cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1995. 32:463–468.
Article15. Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Ciusa V, Dellavia C, Tartaglia GM. The effect of sex and age on facial asymmetry in healthy subjects: a cross-sectional study from adolescence to mid-adulthood. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001. 59:382–388.
Article16. Baik HS, Lee HJ, Lee KJ. A proposal for soft tissue landmarks for craniofacial analysis using 3-dimensional laser scan imaging. World J Orthod. 2006. 7:7–14.17. Baik HS, Jeon JM, Lee HJ. Facial soft-tissue analysis of Korean adults with normal occlusion using a 3-dimensional laser scanner. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007. 131:759–766.
Article18. Gwilliam JR, Cunningham SJ, Hutton T. Reproducibility of soft tissue landmarks on three-dimensional facial scans. Eur J Orthod. 2006. 28:408–415.
Article19. Severt TR, Proffit WR. The prevalence of facial asymmetry in the dentofacial deformities population at the University of North Carolina. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1997. 12:171–176.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of asymmetric degree between maxillofacial hard and soft tissue in facial asymmetric subjects using three-dimensional computed tomography
- Three dimensional CT analysis of facial asymmetry
- Three-dimensional surgical simulation for facial asymmetry: soft tissue-, skeleton-, and occlusion-based planning
- Three-dimensional symmetry and parallelism of the skeletal and soft-tissue poria in patients with facial asymmetry
- Quantification of three-dimensional facial asymmetry for diagnosis and postoperative evaluation of orthognathic surgery