Cancer Res Treat.
2006 Apr;38(2):61-65.
Number of Radiation Oncologists in Korea, Adequate or Surplus?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. kangjino@khmc.or.kr
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: The purpose of this research is to discern and address the issues related to the radiation oncology manpower supply and its distribution.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The statistical data of the Annual Report of the Korea Central Cancer Registry (KCCR) from 1997 to 2002 and the Annual Report of the Korean Society of Radiation Oncology (KOSTRO) from 1997 to 2004 were used to predict the status of the human resources in 2015. The estimated demand and supply were calculated with the Microsoft Excel(R) program (Microsoft, Redmond, WA).
RESULTS
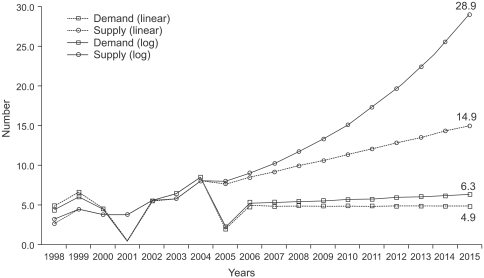
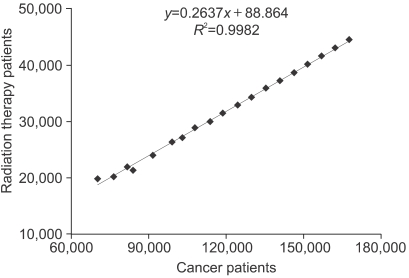
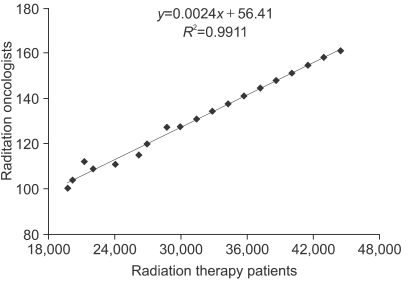
The demand for radiation oncologists is estimated to be 161 in 2015 and about 4.9 radiation oncologists will be in demand annually. In contrast, an average of 15 new radiation oncologists will be supplied annually so that the accumulated surplus of radiation oncologists until 2015 is estimated to be 74.1. The main reason for the surplus comes from the discrepancy between the increased number of radiation therapy patients and the need for radiation oncologists. When there is an increase of 1,000 radiation therapy patients, the demand for radiation oncologists increases only by 2.4. This phenomenon is especially evident in the top 10 hospitals where the average number of radiation therapy patients per radiation oncologist is 341, which is 58% higher than the average number (215) of other 46 hospitals.
CONCLUSION
To prevent a surplus and to maintain the quality of management, the number of radiation therapy patients per radiation oncologist should be limited. Furthermore, coordinate control of the number of residency positions should be seriously considered.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korea NCCo. National Cancer Statistics: National Cancer Center. 2003.2. Kim MS, Yoo SY, Cho CK, Yoo HJ, Yang KM, Ji YH, et al. The Stucture of Korean Radiation Oncology in 1997. J Korean Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 1999; 17:172–178.3. Yoo SY, Kim M, Ji YH, Cho CK, Yang KM, You HJ. Statistics for Department of Radiation Oncology 1999-2001. J Korean Soc Ther Radiol Oncol. 2004; 22:234–236.4. Excel Statistical Functions: TREND. Microsoft Corporation. 2006.5. Excel statistical functions: GROWTH. Microsoft Corporation. 2006.6. Davis LW, Cox J, Diamond J, Flynn D, Halberg F, Moss W. The manpower crisis facing radiation oncology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1986; 12:1873–1878. PMID: 3759539.
Article7. Sunshine JH. Too many radiation oncologists? An empirical report. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996; 35:851–854. PMID: 8690658.
Article8. Jagsi R, Buck DA, Singh AK, Engleman M, Thakkar V, Frank SJ, et al. Results of the 2003 Association of Residents in Radiation Oncology (ARRO) surveys of residents and chief residents in the United States. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 61:642–648. PMID: 15708241.
Article9. Hussey DH, Horton JL, Mendenhall NP, Munzenrider JE, Rose CM, Sunshine JH. Manpower needs for radiation oncology: a preliminary report of the ASTRO Human Resources Committee. American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996; 35:809–820. PMID: 8690651.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A carrier as a gynecologic oncologist in an academic hospital in a developing country
- Differential Perspectives by Specialty on Oligometastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Korean Oligometastasis Working Group’s Comparative Survey Study
- Survey of Medical Oncology Status in Korea (SOMOS-K): A National Survey of Medical Oncologists in the Korean Association for Clinical Oncology (KACO)
- Current Status of SCI & SCIE Publications in the Field of Radiation Oncology in Korea
- Physical and Biological Characteristics of Particle Therapy for Oncologists