Korean J Nutr.
2010 Dec;43(6):570-577. 10.4163/kjn.2010.43.6.570.
Effect of the Magnetized Water Supplementation on Lymphocyte DNA Damage in Mice Treated with Diethylnitrosamine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food & Nutrition, Daedeok Valley Campus, Hannam University, Daejeon 305-811, Korea. mhkang@hnu.kr
- KMID: 2268053
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4163/kjn.2010.43.6.570
Abstract
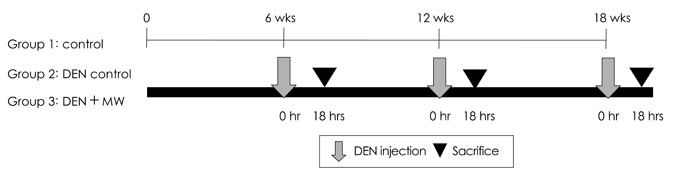
- Water gets magnetically charged when it is contacted with a magnet. Although magnetic water products have been promoted since the 1930's, they have received very little recognition due to questionable effectiveness. Diethylnitrosamine (DEN) is a widely occurring nitrosamine that is one of the most important environmental carcinogens primarily inducing tumors of liver. In this study, the effect of magnetized water supplementation on lymphocyte DNA damage in ICR mice treated with DEN was evaluated using the Comet assay. Mice were divided into 3 groups: control, DEN, and DEN + magnetized water group. Fifteen mice were maintained in each group for the entire experimental period of 6, 12 and 18 weeks. Five mice in each group were sacrificed at 6, 12, and 18th weeks, followed by the Comet assay using the blood obtained from heart puncture of the mice. The level of lymphocyte DNA damage reflected by tail moment and other DNA damage indices of tail DNA (%) or tail length of the magnetized water group were significantly decreased after the 6th, 12th and 18th weeks of supplementation compared with the positive control, the DEN group. The relative DNA damage of the magnetized water groups compared to the DEN control group after 6th, 12th, and 18th weeks of supplementation were 42.2%, 40.8%, and 32.9% for DNA in tail, 31.2%, 32.6%, and 21.3% for tail length, and 33.8%, 33.8%, and 24.6% for tail moment, respectively. This is the first report demonstrating that magnetized water may be involved in the lowering effect of the DNA damage in DEN-treated ICR mice. This result suggests that the magnetized water might have minimized the DNA damage by improving the antioxidant status of the mice. However, further studies are needed to characterize the condition of the magnetization and examine the long-term effect of the water product.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Effect of the magnetized water supplementation on blood glucose, lymphocyte DNA damage, antioxidant status, and lipid profiles in STZ-induced rats
Hye-Jin Lee, Myung-Hee Kang
Nutr Res Pract. 2013;7(1):34-42. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2013.7.1.34.Four months of magnetized water supplementation improves glycemic control, antioxidant status, and cellualr DNA damage in db/db mice
Hye-Jin Lee, Myung-Hee Kang
J Nutr Health. 2016;49(6):401-410. doi: 10.4163/jnh.2016.49.6.401.
Reference
-
1. Poulsen HE, Prieme H, Loft S. Role of oxidative DNA damage in cancer initiation and promotion. Eur J Cancer Prev. 1998. 7(1):9–16.2. Wogan GN. Detection of DNA damage in studies on cancer etiology and prevention. IARC Sci Publ. 1988. 89:32–51.3. Santella RM. DNA damage as an intermediate biomarker in intervention studies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1997. 216(2):166–171.
Article4. Bonassi S, Neri M, Puntoni R. Validation of biomarkers as early predictors of disease. Mutat Res. 2001. 480-481:349–358.
Article5. National Bureau of Statistics, Republic of Korea. Annual report on the cause of death statistics (Based on vital registration). 2009. Seoul:6. Kang BJ. Magnetized Water. 2005. Seoul: Soe-Um Media Pub Co;49–63.7. Johnson KE, Sanders JJ, Gellin RG, Palesch YY. The effectiveness of a magnetized water oral irrigator (Hydro Floss) on plaque, calculus and gingival health. J Clin Periodontol. 1998. 25(4):316–321.
Article8. Ma YL, Ren H, Ren S, Zhen EK, Hao G, Zhao YW. A study of the effect of magnetized water on enzyme activities by potentiometric enzyme electrode method. J Tongji Med Univ. 1992. 12(4):193–196.
Article9. Wu J. Further observations on the therapeutic effect of magnets and magnetized water against ascariasis in children--analysis of 114 cases. J Tradit Chin Med. 1989. 9(2):111–112.10. Zhang YS, Wu HW. Effect of magnetic water on urinary calculi--an experimental and clinical study. Z Urol Nephrol. 1987. 80(9):517–523.11. Watt D, Sutton CD. The effect of oral irrigation with a magnetic water treatment device on plaque and calculus. J Clin Periodontol. 1993. 20(5):314–317.
Article12. Zhang YS, Wu HW. Effect of magnetized water on urinary calculi: an experimental and clinical study. Acta Acad Med Wuhan. 1984. 4(1):31–37.13. Akintonwa DA. The derivation of nitrosamines from some therapeutic amines in the human environment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 1985. 9(1):64–70.
Article14. Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr. AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr. 1993. 123(11):1939–1951.
Article15. Park YK, Kim JS, Jeon EJ, Kang MH. The Improvement of Chaga mushroom (Inonotus Obliquus) extract supplementation on the blood glucose and cellular DNA damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Korean J Nutr. 2009. 42(1):5–13.16. Singh PN, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988. 175(1):184–191.
Article17. Xu YB, Sun SY. Effect of stable weak magnetic field on Cr (VI) bio-removal in anaerobic SBR system. Biodegradation. 2008. 19(3):455–462.
Article18. Gonet B. Influence of constant magnetic fields on certain physiochemical properties of water. Bioelectromagnetics. 1985. 6(2):169–175.
Article19. Lednev VV. Possible mechanism for the influence of weak magetic field on biological system. Bioelectromagnetics. 1991. 12(2):71–75.
Article20. Miyakoshi J. Effects of static magnetic fields at the cellular level. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2005. 87(2-3):213–223.
Article21. Zhang JX, Yu JY. The effect of magnetic field on soil microorganism and enzymic activity. Chin J Soil Sci. 1999. 30(1):26–28.22. Liboff AR, Cherng S, Jenrow KA, Bull A. Calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity is altered by 20 µT magnetostatic fields. Bioelectromagnetics. 2003. 24(1):32–38.
Article23. Grutsch JF, McClintock JW. Corrosion and deposit control in alkaline cooling water using magnetic water treatment at amoco's largest refinery. Corrosion. 1984. 84:Paper No. 330.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of the magnetized water supplementation on blood glucose, lymphocyte DNA damage, antioxidant status, and lipid profiles in STZ-induced rats
- Four months of magnetized water supplementation improves glycemic control, antioxidant status, and cellualr DNA damage in db/db mice
- The Effect of Alpha-tocopherol Supplementation on the Improvement of Antioxidant Status and Lymphocyte DNA Damage in Postmenopausal Women
- Increase of proliferation and DNA damage in mouse hepatocytes treated with diethylnitrosamine
- The effect of carrot juice, beta-carotene supplementation on lymphocyte DNA damage, erythrocyte antioxidant enzymes and plasma lipid profiles in Korean smoker