Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Dec;38(6):852-855. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.6.852.
Churg-Strauss Syndrome Presented With Hearing Impairment and Facial Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical & Rehabilitation Medicine, Regional Cardiocerebrovascular Center, Chonnam National University Hospital, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. drchoiis@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2267098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.6.852
Abstract
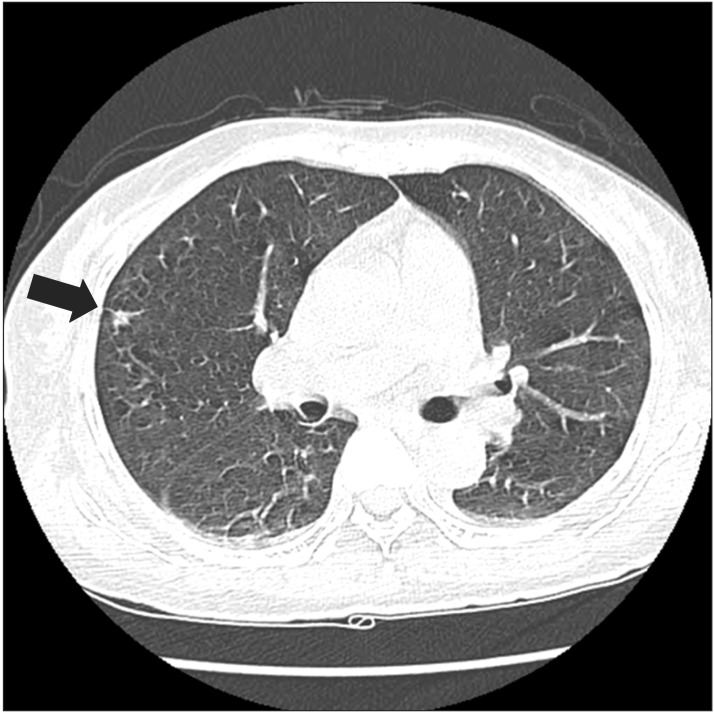
- Churg-Strauss syndrome (CSS) is a rare systemic necrotizing vasculitis. Cranial nerve involvement is very rare in CSS. A 59-year-old woman had complained of both hearing impairments for eight months and left facial palsy for three months. Left facial and cochlear neuropathies were detected in electrodiagnostic studies. Paranasal sinus computed tomography (CT) showed chronic pansinusitis. Chest CT revealed eosinophilic infiltration in the right upper lobe. Tissue biopsy of the right inferior turbinate displayed necrotizing vasculitis with eosinophilic infiltration. She was diagnosed as CSS, based on the presence of eosinophilia, pulmonary infiltration, paranasal sinusitis, and biopsy containing blood vessels with extravascular eosinophils. She was treated with intravenous and oral steroids and azathioprine, showing relatively good prognosis on facial palsy and hearing impairment. We report a very rare case of CSS presented with hearing impairment and facial palsy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Churg J, Strauss L. Allergic granulomatosis, allergic angiitis, and periarteritis nodosa. Am J Pathol. 1951; 27:277–301. PMID: 14819261.2. Wolf J, Bergner R, Mutallib S, Buggle F, Grau AJ. Neurologic complications of Churg-Strauss syndrome: a prospective monocentric study. Eur J Neurol. 2010; 17:582–588. PMID: 20050889.3. Sehgal M, Swanson JW, DeRemee RA, Colby TV. Neurologic manifestations of Churg-Strauss syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1995; 70:337–341. PMID: 7898138.
Article4. Ozaki Y, Tanaka A, Shimamoto K, Amuro H, Son Y, Ito T, et al. Effective intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for Churg-Strauss syndrome (allergic granulomatous angiitis) complicated by neuropathy of the eighth cranial nerve: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2012; 6:310. PMID: 22989316.
Article5. Oh MJ, Lee JY, Kwon NH, Choi DC. Churg-Strauss syndrome: the clinical features and long-term follow-up of 17 patients. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:265–271. PMID: 16614512.
Article6. Masi AT, Hunder GG, Lie JT, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Arend WP, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Churg-Strauss syndrome (allergic granulomatosis and angiitis). Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1094–1100. PMID: 2202307.
Article7. Comarmond C, Pagnoux C, Khellaf M, Cordier JF, Hamidou M, Viallard JF, et al. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): clinical characteristics and long-term followup of the 383 patients enrolled in the French Vasculitis Study Group cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65:270–281. PMID: 23044708.
Article8. Tsuda H, Ishikawa H, Majima T, Sawada U, Mizutani T. Isolated oculomotor nerve palsy in Churg-Strauss syndrome. Intern Med. 2005; 44:638–640. PMID: 16020896.
Article9. Ishiyama A, Canalis RF. Otological manifestations of Churg-Strauss syndrome. Laryngoscope. 2001; 111:1619–1624. PMID: 11568616.
Article10. Guillevin L, Pagnoux C, Seror R, Mahr A, Mouthon L, Le Toumelin P, et al. The Five-Factor Score revisited: assessment of prognoses of systemic necrotizing vasculitides based on the French Vasculitis Study Group (FVSG) cohort. Medicine (Baltimore). 2011; 90:19–27. PMID: 21200183.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of Churg-Strauss syndrome that underwent endoscopic sinus surgery under total intravenous anesthesia: A case report
- A Case of Churg-Strauss Syndrome Presenting Umbilicated Ulcerative Papules
- A Case of Churg-Strauss Syndrome with Endomyocardial Fibrosis
- Eosinophilic Annular Erythema in a Patient with Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss Syndrome)
- A Case of Chrug-Strauss Syndrome Complicated with Intestinal Perforation