Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Jun;36(3):400-403. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.400.
The Change of Intrinsic Stiffness in Gastrocnemius after Intensive Rehabilitation with Botulinum Toxin A Injection in Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu 705-718, Korea. kjunggus01@naver.com
- KMID: 2266747
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.400
Abstract
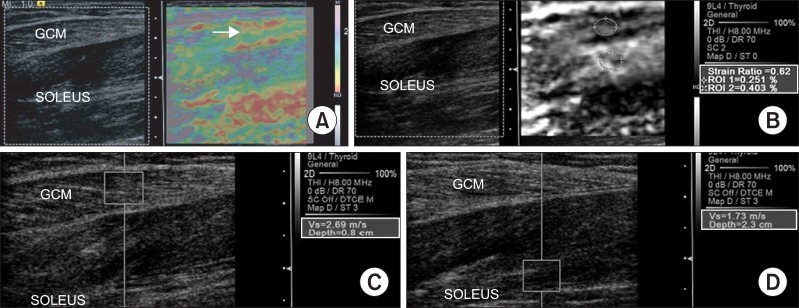
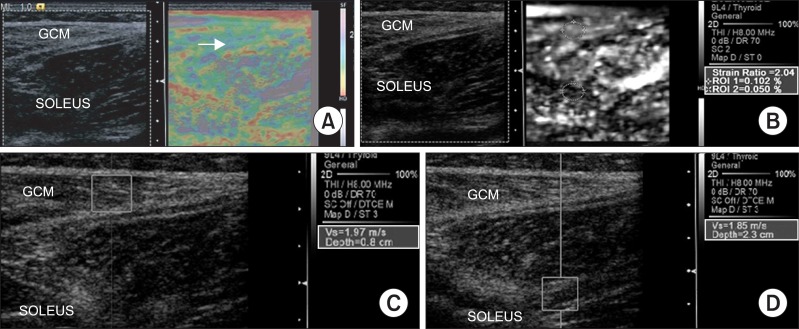
- A recent study claimed that botulinum toxin A (BTX-A) injection into the calf muscle of cerebral palsy (CP) children did not change the intrinsic stiffness. Contrary to this recent report, in our case, decreased muscle spasticity, which was measured using a modified Ashworth scale, and increased Gross Motor Function Measure score were demonstrated at 4 weeks after intensive rehabilitation treatment (IRT) with BTX-A injection to the medial gastrocnemius muscle in a child with spastic CP. Additionally, we indentified decreased muscle stiffness which was demonstrated by a decrease in the color-coded scale and shear velocity, and an increase in the strain ratio using dynamic sonoelastography.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of Treatment Effects Between Children With Spastic Cerebral Palsy Under and Over Five Years After Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection
Won-Yub Lee, Gi-Young Park, Dong Rak Kwon
Ann Rehabil Med. 2014;38(2):200-208. doi: 10.5535/arm.2014.38.2.200.Therapeutic Effect of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy According to Treatment Session on Gastrocnemius Muscle Spasticity in Children With Spastic Cerebral Palsy: A Pilot Study
Dong-Soon Park, Dong Rak Kwon, Gi-Young Park, Michael Y. Lee
Ann Rehabil Med. 2015;39(6):914-921. doi: 10.5535/arm.2015.39.6.914.
Reference
-
1. Fung YC. Biomechanics: mechanical properties of living tissues. 1988. 1st ed. New York: Springer.2. Murayama M, Nosaka K, Yoneda T, Minamitani K. Changes in hardness of the human elbow flexor muscles after eccentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000; 82:361–367. PMID: 10985588.
Article3. Park GY, Kwon DR. Application of Real-Time Sonoelastography in Musculoskeletal Diseases Related to Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011; 90:875–886.
Article4. Alhusaini AA, Crosbie J, Shepherd RB, Dean CM, Scheinberg A. No change in calf muscle passive stiffness after botulinum toxin injection in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011; 53:553–558. PMID: 21574991.
Article5. Kim HJ, Yum KW, Lee SS, Heo MS, Seo K. Effect of botulinum toxin type A on bilateral masseteric hypertrophy evaluated with computed tomographic measurement. Dermatol Surg. 2003; 29:484–489. PMID: 12752515.6. Chang CS, Bergeron L, Yu CC, Chen PK, Chen YR. Mandible changes evaluated by computed tomography following Botulinum Toxin A injections in square-faced patients. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2011; 35:452–455. PMID: 21103871.
Article7. Chen CM, Stott NS, Smith HK. Effects of botulinum toxin A injection and exercise on the growth of juvenile rat gastrocnemius muscle. J Appl Physiol. 2002; 93:1437–1447. PMID: 12235045.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Change of Dynamic Gastrocnemius Length after the Block of Spastic Gastrocnemius Muscle in Cerebral Palsy
- Electrophysiological Changes after Botulinum Toxin Type A in Children with Cerebral Palsy
- Effects of Botulinum Toxin A Treatment in Cerebral Palsy
- Is Electrical Stimulation Beneficial for Improving the Paralytic Effect of Botulinum Toxin Type A in Children with Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy?
- Effects of Botulinum Toxin A Therapy on Gastrocnemius in Spastic Cerebral Palsied Children