Ann Rehabil Med.
2012 Aug;36(4):551-555. 10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.551.
Fornix Injury in a Patient with Rotavirus Encephalopathy: Diffusion Tensor Tractography Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu 705-717, Korea. pure0920@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu 705-717, Korea.
- KMID: 2266727
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.4.551
Abstract
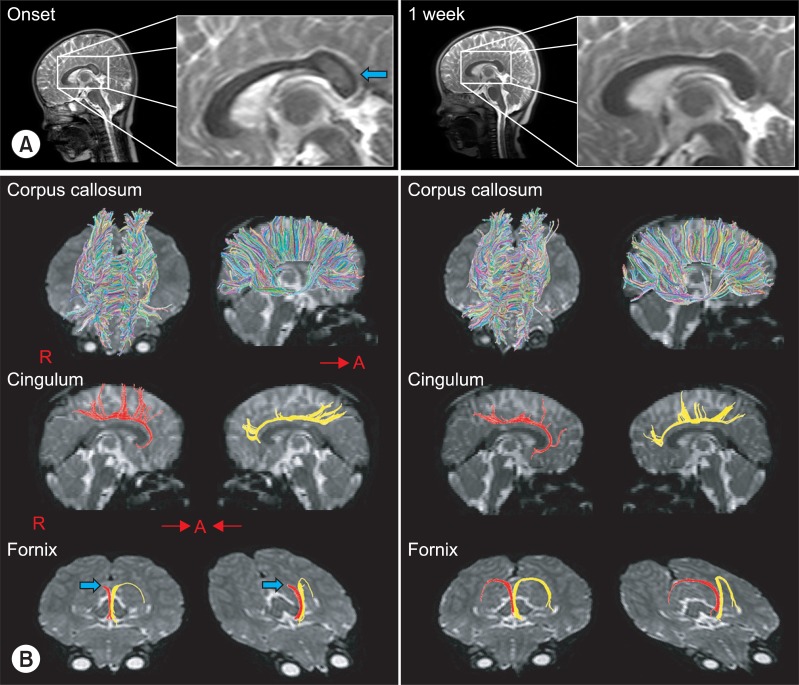
- Rotavirus encephalopathy (RE) is a benign afebrile seizure associated with acute gastroenteritis caused by rotavirus infection. We investigated the diffusion tensor tractography (DTT) findings of a patient with RE. The patient was a 30-month-old female that had experienced a brief, generalized convulsive seizure. On the day of admission, the patient had vomiting and experienced watery diarrhea. Her stool was positive for rotavirus antigen. At onset, the patient displayed a drowsy and delirious mental status; later, a splenial lesion of the corpus callosum was found on MRI. One week later, the patient's condition improved and the splenial lesion had disappeared by conventional MRI. Initial DTI showed decreased fractional anisotropy (FA) values of fornix, as well as of the corpus callosum. A follow-up DTT showed a restored interrupted right fonical crus and increased FA values of corpus callosum and fornix. These results highlight the implications of the probability of not only a corpus callosum injury, but a fornix injury as well, in this patient with RE.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Salmi TT, Arstila P, Koivikko A. Central nervous system involvement in patients with rotavirus gastroenteritis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1978; 10:29–31. PMID: 204984.
Article2. Fukuda S, Kishi K, Yasuda K, Sejima H, Yamaguchi S. Rotavirus-associated encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion. Pediatr Neurol. 2009; 40:131–133. PMID: 19135631.
Article3. Tada H, Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Oba H, Maeda M, Tsukahara H, Suzuki M, Yamamoto T, Shimono T, Ichiyama T, et al. Clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion. Neurology. 2004; 63:1854–1858. PMID: 15557501.
Article4. Takanashi J, Tada H, Kuroki H, Barkovich AJ. Delirious behavior in influenza is associated with a reversible splenial lesion. Brain Dev. 2009; 31:423–426. PMID: 18793826.
Article5. Malykhin N, Concha L, Seres P, Beaulieu C, Coupland NJ. Diffusion tensor imaging tractography and reliability analysis for limbic and paralimbic white matter tracts. Psychiatry Res. 2008; 164:132–142. PMID: 18945599.
Article6. Hong JH, Jang SH. Degeneration of cingulum and fornix in a patient with traumatic brain injury: diffuse tensor tractography study. J Rehabil Med. 2010; 42:979–981. PMID: 21031297.
Article7. Witelson SF. Hand and sex differences in the isthmus and genu of the human corpus callosum. A postmortem morphological study. Brain. 1989; 112:799–835. PMID: 2731030.8. Bulakbasi N, Kocaoglu M, Tayfun C, Ucoz T. Tansient splenial lesion of the corpus callosum in clinically mild influenza-associated encephalitis/encephalopathy. Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:1983–1986. PMID: 17032879.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Precommissural Fornix in the Human Brain: A Diffusion Tensor Tractography Study
- Reversible Psychosis Caused by Disconnection of the Limbic System: Clinical Reasoning Using Diffusion Tensor Tractography
- Hepatic Encephalopathy With Corticospinal Tract Involvement Demonstrated by Diffusion Tensor Tractography
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Exploring the Motor Networks and Clinical Applications
- Preoperative Identification of Facial Nerve in Vestibular Schwannomas Surgery Using Diffusion Tensor Tractography