J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Jul;56(1):11-15. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.1.11.
Preoperative Identification of Facial Nerve in Vestibular Schwannomas Surgery Using Diffusion Tensor Tractography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Deagu, Korea. olkim@med.yu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Deagu, Korea.
- KMID: 2067070
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.1.11
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
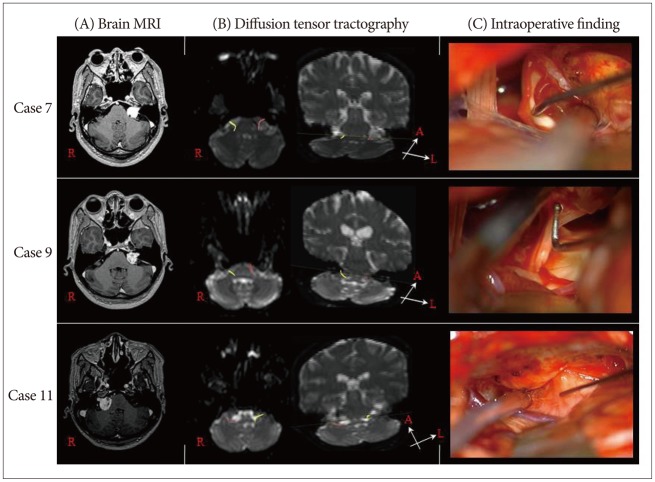
Facial nerve palsy is a common complication of treatment for vestibular schwannoma (VS), so preserving facial nerve function is important. The preoperative visualization of the course of facial nerve in relation to VS could help prevent injury to the nerve during the surgery. In this study, we evaluate the accuracy of diffusion tensor tractography (DTT) for preoperative identification of facial nerve.
METHODS
We prospectively collected data from 11 patients with VS, who underwent preoperative DTT for facial nerve. Imaging results were correlated with intraoperative findings. Postoperative DTT was performed at postoperative 3 month. Facial nerve function was clinically evaluated according to the House-Brackmann (HB) facial nerve grading system.
RESULTS
Facial nerve courses on preoperative tractography were entirely correlated with intraoperative findings in all patients. Facial nerve was located on the anterior of the tumor surface in 5 cases, on anteroinferior in 3 cases, on anterosuperior in 2 cases, and on posteroinferior in 1 case. In postoperative facial nerve tractography, preservation of facial nerve was confirmed in all patients. No patient had severe facial paralysis at postoperative one year.
CONCLUSION
This study shows that DTT for preoperative identification of facial nerve in VS surgery could be a very accurate and useful radiological method and could help to improve facial nerve preservation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Briggs RJ, Luxford WM, Atkins JS Jr, Hitselberger WE. Translabyrinthine removal of large acoustic neuromas. Neurosurgery. 1994; 34:785–790. discussion 790-791. PMID: 8052375.
Article2. Casselman JW, Kuhweide R, Deimling M, Ampe W, Dehaene I, Meeus L. Constructive interference in steady state-3DFT MR imaging of the inner ear and cerebellopontine angle. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1993; 14:47–57. PMID: 8427111.3. Chen DQ, Quan J, Guha A, Tymianski M, Mikulis D, Hodaie M. Three-dimensional in vivo modeling of vestibular schwannomas and surrounding cranial nerves with diffusion imaging tractography. Neurosurgery. 2011; 68:1077–1083. PMID: 21242825.
Article4. Gerganov VM, Giordano M, Samii M, Samii A. Diffusion tensor imaging-based fiber tracking for prediction of the position of the facial nerve in relation to large vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 2011; 115:1087–1093. PMID: 21962081.
Article5. Gjuric M, Rudic M. What is the best tumor size to achieve optimal functional results in vestibular schwannoma surgery? Skull Base. 2008; 18:317–325. PMID: 19240831.
Article6. Haberkamp TJ, Meyer GA, Fox M. Surgical exposure of the fundus of the internal auditory canal : anatomic limits of the middle fossa versus the retrosigmoid transcanal approach. Laryngoscope. 1998; 108(8 Pt 1):1190–1194. PMID: 9707242.
Article7. Hodaie M, Quan J, Chen DQ. In vivo visualization of cranial nerve pathways in humans using diffusion-based tractography. Neurosurgery. 2010; 66:788–795. discussion 795-796. PMID: 20305498.
Article8. House JW, Brackmann DE. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1985; 93:146–147. PMID: 3921901.
Article9. Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, Pearlson GD, Mori S. DtiStudio : resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2006; 81:106–116. PMID: 16413083.
Article10. Kakizawa Y, Seguchi T, Kodama K, Ogiwara T, Sasaki T, Goto T, et al. Anatomical study of the trigeminal and facial cranial nerves with the aid of 3.0-tesla magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg. 2008; 108:483–490. PMID: 18312095.
Article11. Kartush JM. Intra-operative monitoring in acoustic neuroma surgery. Neurol Res. 1998; 20:593–596. PMID: 9785586.
Article12. Koos WT, Spetzler R. Color Atlas of Microneurosurgery: Microanatomy, Approaches, Techniques. ed 2. Stuttgart; New York: Thieme Medical Publishers;1993.13. Lanman TH, Brackmann DE, Hitselberger WE, Subin B. Report of 190 consecutive cases of large acoustic tumors (vestibular schwannoma) removed via the translabyrinthine approach. J Neurosurg. 1999; 90:617–623. PMID: 10193604.
Article14. Mori S, van Zijl PC. Fiber tracking : principles and strategies - a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002; 15:468–480. PMID: 12489096.15. Mukherjee P, Chung SW, Berman JI, Hess CP, Henry RG. Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: technical considerations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:843–852. PMID: 18339719.
Article16. Nadol JB Jr, Chiong CM, Ojemann RG, McKenna MJ, Martuza RL, Montgomery WW, et al. Preservation of hearing and facial nerve function in resection of acoustic neuroma. Laryngoscope. 1992; 102:1153–1158. PMID: 1405966.
Article17. Naganawa S, Koshikawa T, Fukatsu H, Ishigaki T, Fukuta T. MR cisternography of the cerebellopontine angle : comparison of three-dimensional fast asymmetrical spin-echo and three-dimensional constructive interference in the steady-state sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1179–1185. PMID: 11415916.18. Neff BA, Ting J, Dickinson SL, Welling DB. Facial nerve monitoring parameters as a predictor of postoperative facial nerve outcomes after vestibular schwannoma resection. Otol Neurotol. 2005; 26:728–732. PMID: 16015176.
Article19. Roundy N, Delashaw JB, Cetas JS. Preoperative identification of the facial nerve in patients with large cerebellopontine angle tumors using high-density diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurosurg. 2012; 116:697–702. PMID: 22283188.
Article20. Samii M, Gerganov V, Samii A. Improved preservation of hearing and facial nerve function in vestibular schwannoma surgery via the retrosigmoid approach in a series of 200 patients. J Neurosurg. 2006; 105:527–535. PMID: 17044553.
Article21. Samii M, Gerganov VM, Samii A. Functional outcome after complete surgical removal of giant vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg. 2010; 112:860–867. PMID: 19663543.
Article22. Sartoretti-Schefer S, Kollias S, Valavanis A. Spatial relationship between vestibular schwannoma and facial nerve on three-dimensional T2-weighted fast spin-echo MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:810–816. PMID: 10815653.23. Sluyter S, Graamans K, Tulleken CA, Van Veelen CW. Analysis of the results obtained in 120 patients with large acoustic neuromas surgically treated via the translabyrinthine-transtentorial approach. J Neurosurg. 2001; 94:61–66. PMID: 11147899.
Article24. Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage. 2004; 23(Suppl 1):S208–S219. PMID: 15501092.
Article25. Stuckey SL, Harris AJ, Mannolini SM. Detection of acoustic schwannoma : use of constructive interference in the steady state three-dimensional MR. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1219–1225. PMID: 8871702.26. Taoka T, Hirabayashi H, Nakagawa H, Sakamoto M, Myochin K, Hirohashi S, et al. Displacement of the facial nerve course by vestibular schwannoma : preoperative visualization using diffusion tensor tractography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006; 24:1005–1010. PMID: 17031835.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Significance of Preoperative Nerve Reconstruction Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Tractography for Facial Nerve Protection in Vestibular Schwannoma
- Preservation of Facial Nerve Function Repaired by Using Fibrin Glue-Coated Collagen Fleece for a Totally Transected Facial Nerve during Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery
- Surgical Findings to Differentiate Between Facial Nerve Schwannoma and Vestibular Schwannoma
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Exploring the Motor Networks and Clinical Applications
- Reversible Psychosis Caused by Disconnection of the Limbic System: Clinical Reasoning Using Diffusion Tensor Tractography