Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Dec;37(6):824-831. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.824.
Efficacy of Epidural Neuroplasty Versus Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Radiating Pain Caused by a Herniated Lumbar Disc
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Sun General Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. rmactksk@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Sun General Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2266561
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.824
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To compare the treatment effects of epidural neuroplasty (NP) and transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) for the radiating pain caused by herniated lumbar disc.
METHODS
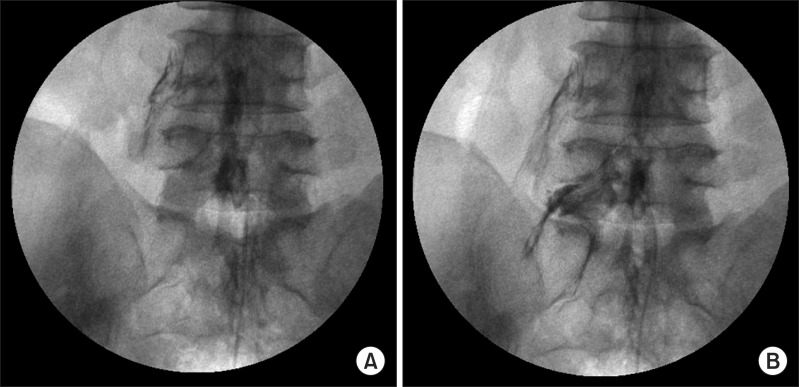
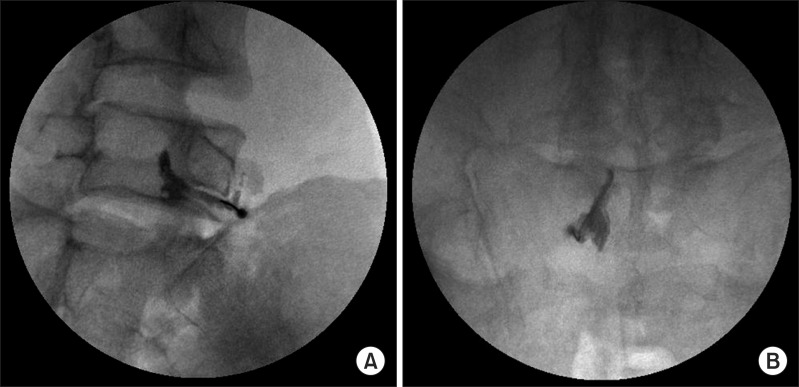
Thirty-two patients diagnosed with herniated lumbar disc through magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography were included in this study. Fourteen patients received an epidural NP and eighteen patients had a TFESI. The visual analogue scale (VAS) and functional rating index (FRI) were measured before the treatment, and at 2 weeks, 4 weeks and 8 weeks after the treatment.
RESULTS
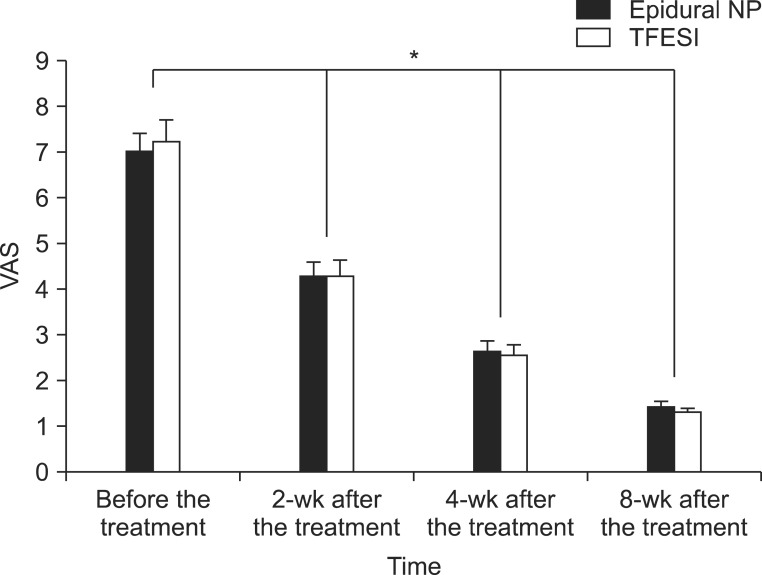
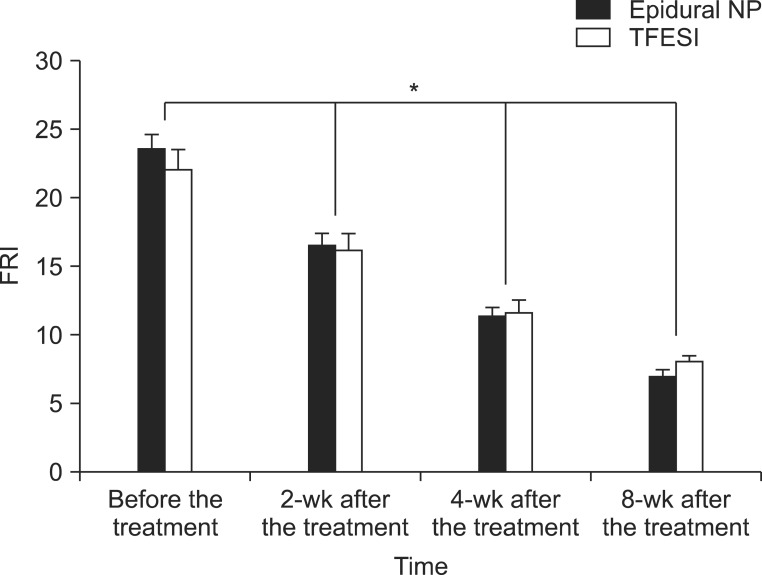
In the epidural NP group, the mean values of the VAS before the treatment, and at 2 weeks, 4 weeks and 8 weeks after the treatment were 7.00+/-1.52, 4.29+/-1.20, 2.64+/-0.93, 1.43+/-0.51 and those of FRI were 23.57+/-3.84, 16.50+/-3.48, 11.43+/-2.44, 7.00+/-2.15. In the TFESI group, the mean values of the VAS before the treatment, and at 2 weeks, 4 weeks and 8 weeks after the treatment were 7.22+/-2.05, 4.28+/-1.67, 2.56+/-1.04, 1.33+/-0.49 and those of FRI were 22.00+/-6.64, 16.22+/-5.07, 11.56+/-4.18, 8.06+/-1.89. During the follow-up period, the values of VAS and FRI within each group were significantly reduced (p<0.05) after the treatment. But there were no significant differences between the two groups statistically.
CONCLUSION
Epidural NP and TFESI are equally effective treatments for the reduction of radiating pain and for improvement of function in patients with a herniated lumbar disc. We recommend that TFESI should be primarily applied to patients who need interventional spine treatment, because it is easier and more cost-effective than epidural NP.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Epidural neuroplasty/epidural adhesiolysis
Se Hee Kim, Sang Sik Choi
Anesth Pain Med. 2016;11(1):14-22. doi: 10.17085/apm.2016.11.1.14.Percutaneous epidural balloon neuroplasty: a narrative review of current evidence
Doo-Hwan Kim, Jin-Woo Shin, Seong-Soo Choi
Anesth Pain Med. 2022;17(4):361-370. doi: 10.17085/apm.22237.
Reference
-
1. Boden SD, Davis DO, Dina TS, Patronas NJ, Wiesel SW. Abnormal magnetic-resonance scans of the lumbar spine in asymptomatic subjects: a prospective investigation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990; 72:403–408. PMID: 2312537.
Article2. Saal JS, Franson RC, Dobrow R, Saal JA, White AH, Goldthwaite N. High levels of inflammatory phospholipase A2 activity in lumbar disc herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990; 15:674–678. PMID: 2218714.
Article3. Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, Skinner JS, Hanscom B, Tosteson AN, et al. Surgical vs nonoperative treatment for lumbar disk herniation: the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT) observational cohort. JAMA. 2006; 296:2451–2459. PMID: 17119141.4. Weinstein JN, Tosteson TD, Lurie JD, Tosteson AN, Hanscom B, Skinner JS, et al. Surgical vs nonoperative treatment for lumbar disk herniation: the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT): a randomized trial. JAMA. 2006; 296:2441–2450. PMID: 17119140.5. Lutz GE, Vad VB, Wisneski RJ. Fluoroscopic transforaminal lumbar epidural steroids: an outcome study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1998; 79:1362–1366. PMID: 9821894.
Article6. Vad VB, Bhat AL, Lutz GE, Cammisa F. Transforaminal epidural steroid injections in lumbosacral radiculopathy: a prospective randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:11–16. PMID: 11805628.7. McCarron RF, Wimpee MW, Hudkins PG, Laros GS. The inflammatory effect of nucleus pulposus: a possible element in the pathogenesis of low-back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1987; 12:760–764. PMID: 2961088.8. Racz GB, Holubec JT. Lysis of adhesion in the epidural space. In : Racz GB, editor. Techniques of neurolysis. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publisher;1989. p. 57–72.9. Racz GB, Heavner JE, Diede JH. Lysis of epidural adhesions utilizing the epidural approach. Waldman SD, Winnie AP. Interventional pain management. Philadelphia: Saunders;1996. p. 339–351.10. Racz GB, Heavner JE, Trescot A. Percutaneous lysis of epidural adhesions: evidence for safety and efficacy. Pain Pract. 2008; 8:277–286. PMID: 18503627.11. Manchikanti L, Rivera JJ, Pampati V, Damron KS, McManus CD, Brandon DE, et al. One day lumbar epidural adhesiolysis and hypertonic saline neurolysis in treatment of chronic low back pain: a randomized, double-blind trial. Pain Physician. 2004; 7:177–186. PMID: 16868590.12. Manchikanti L, Pampati V, Fellows B, Rivera J, Beyer CD, Damron KS. Role of one day epidural adhesiolysis in management of chronic low back pain: a randomized clinical trial. Pain Physician. 2001; 4:153–166. PMID: 16902688.13. Fenton DS, Czervionke LF. Image-guided spine intervention. Philadelphia: Saunders;2003.14. Chansirinukor W, Maher CG, Latimer J, Hush J. Comparison of the functional rating index and the 18-item Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire: responsiveness and reliability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:141–145. PMID: 15626994.
Article15. Grotle M, Brox JI, Vollestad NK. Functional status and disability questionnaires: what do they assess? A systematic review of back-specific outcome questionnaires. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:130–140. PMID: 15626993.16. Feise RJ, Michael Menke J. Functional rating index: a new valid and reliable instrument to measure the magnitude of clinical change in spinal conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:78–86. PMID: 11148650.17. Veihelmann A, Devens C, Trouillier H, Birkenmaier C, Gerdesmeyer L, Refior HJ. Epidural neuroplasty versus physiotherapy to relieve pain in patients with sciatica: a prospective randomized blinded clinical trial. J Orthop Sci. 2006; 11:365–369. PMID: 16897200.
Article18. Heavner JE, Racz GB, Raj P. Percutaneous epidural neuroplasty: prospective evaluation of 0.9% NaCl versus 10% NaCl with or without hyaluronidase. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 1999; 24:202–207. PMID: 10338168.19. LaRocca H, Macnab I. The laminectomy membrane. Studies in its evolution, characteristics, effects and prophylaxis in dogs. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974; 56:545–550. PMID: 4421702.20. Burton CV. Lumbosacral arachnoiditis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1978; 3:24–30. PMID: 148106.
Article21. Benner B, Ehni G. Spinal arachnoiditis: the postoperative variety in particular. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1978; 3:40–44. PMID: 644391.22. Manchikanti L, Malla Y, Wargo BW, Cash KA, Pampati V, Fellows B. A prospective evaluation of complications of 10,000 fluoroscopically directed epidural injections. Pain Physician. 2012; 15:131–140. PMID: 22430650.23. Woodward JL, Herring SA, Windsor RE, Dreyer SJ, Lester JP, Lagattuta FP. Epidural procedures in spine pain management. In : Lennard TA, editor. Physiatric procedures in clinical practice. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;1995. p. 260–291.24. Woodward JL, Weinstein SM. Epidural injections for the diagnosis and management of axial and radicular pain syndromes. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 1995; 6:691–714.
Article25. Lee HM, Weinstein JN, Meller ST, Hayashi N, Spratt KF, Gebhart GF. The role of steroids and their effects on phospholipase A2: an animal model of radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23:1191–1196. PMID: 9636970.26. Kawakami M, Matsumoto T, Tamaki T. Roles of thromboxane A2 and leukotriene B4 in radicular pain induced by herniated nucleus pulposus. J Orthop Res. 2001; 19:472–477. PMID: 11398862.
Article27. Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Bernand TN. A comprehensive outline of treatment. In : Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Bernand TN, editors. Managing low back pain. New York: Churchill Livingstone;1983. p. 147–60.28. Evans W. Intrasacral epidural injection in the treatment of sciatica. Lancet. 1930; 216:1225–1229.
Article29. Winkel D, Aufdemkampe G, Matthijs O, Meijer OG, Phelps V. Diagnosis and treatment of the spine. Gaithersburg: Aspen Publishers;1996.30. Manchikanti L. Transforaminal lumbar epidural steroid injections. Pain Physician. 2000; 3:374–398. PMID: 16906179.
Article31. Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Molonoff PB, Ruddon RW, Gilman AG. Goodman & Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;1996.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection and Lumbar/Caudal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Treatment of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
- Epidural neuroplasty/epidural adhesiolysis
- The Effect of Transforaminal Epidural Block with Hyaluronidase and Triamcinolone
- Comparison of the Effects between Interlaminar Epidural Block and Transforaminal Epidural Block under C-arm Guide in Lumbar Disc Herniated Radiculopathy
- Radiculopathy Caused by Discal Cyst