Korean J Pain.
2014 Jan;27(1):86-89. 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.86.
Radiculopathy Caused by Discal Cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. mandell@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2278209
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.86
Abstract
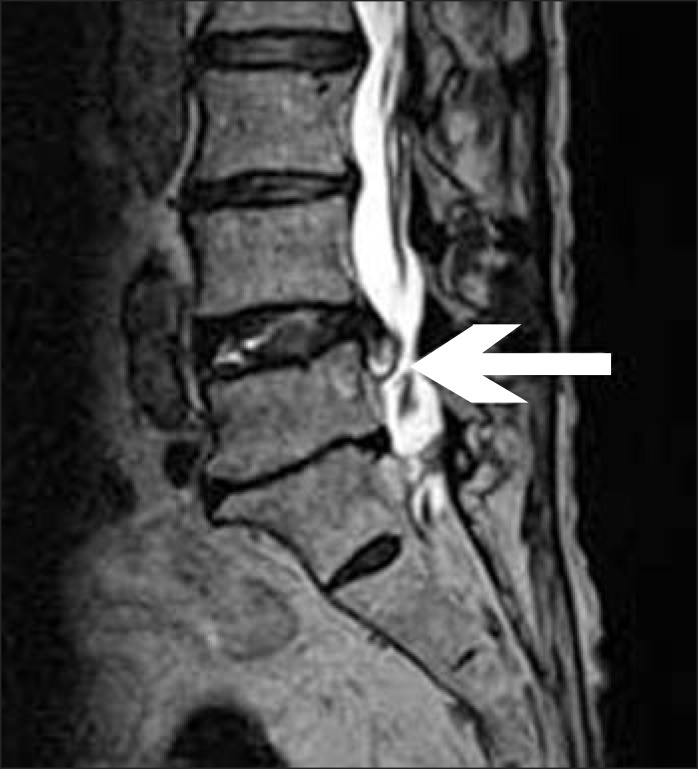
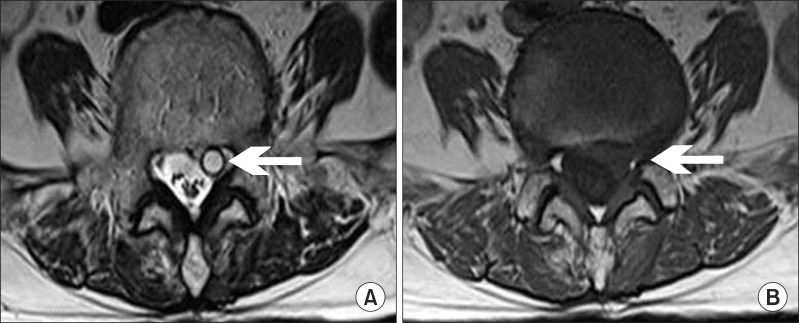
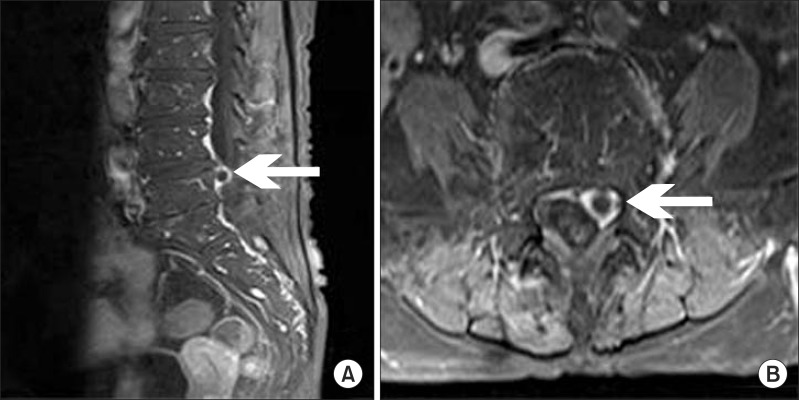
- Discal cyst is an intraspinal cyst with a distinct communication with the corresponding intervertebral disc. It is a rare condition and could present with radiculopathy similar to that caused by lumbar disc herniation. We present a patient with a large discal cyst in the ventrolateral epidural space of the 5th lumbar vertebral (L5) level that communicated with the adjacent 4th lumbar and 5th lumbar intervertebral disc, causing L5 radiculopathy. We alleviated the radiating pain with selective transforaminal epidural blocks.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Successful Treatment of a Symptomatic Discal Cyst by Percutaneous C-arm Guided Aspiration
Hyun Jeong Yu, Chan Jin Park, Kyoung Hoon Yim
Korean J Pain. 2016;29(2):129-135. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2016.29.2.129.
Reference
-
1. Chiba K, Toyama Y, Matsumoto M, Maruiwa H, Watanabe M, Nishizawa T. Intraspinal cyst communicating with the intervertebral disc in the lumbar spine: discal cyst. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:2112–2118. PMID: 11698889.
Article2. Coscia MF, Broshears JR. Lumbar spine intracanalicular discal cysts: two case reports. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2002; 15:431–435. PMID: 12394670.
Article3. Ishii K, Matsumoto M, Watanabe K, Nakamura M, Chiba K, Toyama Y. Endoscopic resection of cystic lesions in the lumbar spinal canal: a report of two cases. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2005; 48:240–243. PMID: 16172971.
Article4. Ha SW, Ju CI, Kim SW, Lee S, Kim YH, Kim HS. Clinical outcomes of percutaneous endoscopic surgery for lumbar discal cyst. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012; 51:208–214. PMID: 22737300.
Article5. Koga H, Yone K, Yamamoto T, Komiya S. Percutaneous CT-guided puncture and steroid injection for the treatment of lumbar discal cyst: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:E212–E216. PMID: 12782997.
Article6. Kono K, Nakamura H, Inoue Y, Okamura T, Shakudo M, Yamada R. Intraspinal extradural cysts communicating with adjacent herniated disks: imaging characteristics and possible pathogenesis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:1373–1377. PMID: 10473000.7. Lee HK, Lee DH, Choi CG, Kim SJ, Suh DC, Kahng SK, et al. Discal cyst of the lumbar spine: MR imaging features. Clin Imaging. 2006; 30:326–330. PMID: 16919553.
Article8. Demaerel P, Eerens I, Goffin J, Wilms G. Spontaneous regression of an intraspinal disc cyst. Eur Radiol. 2001; 11:2317–2318. PMID: 11702179.
Article9. Chou D, Smith JS, Chin CT. Spontaneous regression of a discal cyst. Case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 6:81–84. PMID: 17233298.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intraoperative Discography for Detecting Concealed Lumbar Discal Cysts
- Discal Cyst of Lumbar Spine: A Case Report
- Successful Treatment of a Symptomatic Discal Cyst by Percutaneous C-arm Guided Aspiration
- Discal Cyst of the Lumbar Spine: A Case Report
- Clinical Outcomes of Percutaneous Endoscopic Surgery for Lumbar Discal Cyst