Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Feb;38(1):64-71. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.64.
Subclinical Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow in Diabetic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rmkdh@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2266542
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.64
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To demonstrate the prevalence and characteristics of subclinical ulnar neuropathy at the elbow in diabetic patients.
METHODS
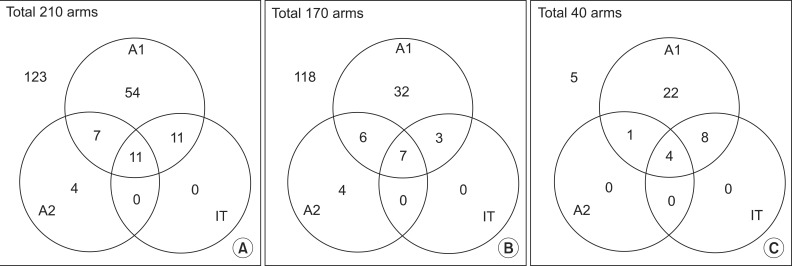
One hundred and five patients with diabetes mellitus were recruited for the study of ulnar nerve conduction analysis. Clinical and demographic characteristics were assessed. Electrodiagnosis of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow was based on the criteria of the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM1 and AANEM2). The inching test of the ulnar motor nerve was additionally performed to localize the lesion.
RESULTS
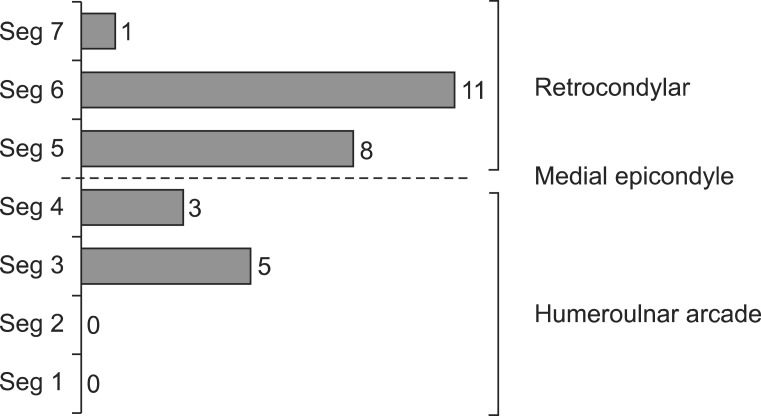
The duration of diabetes, the existence of diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) symptoms, the duration of symptoms, and HbA1C showed significantly larger values in the DPN group (p<0.05). Ulnar neuropathy at the elbow was more common in the DPN group. There was a statistically significant difference in the number of cases that met the three diagnostic criteria between the no DPN group and the DPN group. The most common location for ulnar mononeuropathy at the elbow was the retrocondylar groove.
CONCLUSION
Ulnar neuropathy at the elbow is more common in patients with DPN. If the conduction velocities of both the elbow and forearm segments are decreased to less than 50 m/s, it may be useful to apply the AANEM2 criteria and inching test to diagnose ulnar neuropathy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Partanen J, Niskanen L, Lehtinen J, Mervaala E, Siitonen O, Uusitupa M. Natural history of peripheral neuropathy in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:89–94. PMID: 7777034.
Article2. Vinik A, Mehrabyan A, Colen L, Boulton A. Focal entrapment neuropathies in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:1783–1788. PMID: 15220266.
Article3. Schady W, Abuaisha B, Boulton AJ. Observations on severe ulnar neuropathy in diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 1998; 12:128–132. PMID: 9618067.
Article4. Acosta JA, Hoffman SN, Raynor EM, Nardin RA, Rutkove SB. Ulnar neuropathy in the forearm: a possible complication of diabetes mellitus. Muscle Nerve. 2003; 28:40–45. PMID: 12811771.
Article5. Mondelli M, Aretini A, Rossi S. Ulnar neuropathy at the elbow in diabetes. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2009; 88:278–285. PMID: 19077671.
Article6. Hawley J, Capobianco J. Localizing ulnar nerve lesions by motor nerve conduction study. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1987; 27:385–392. PMID: 3428216.7. Kim DH, Kang YK, Hwang M, Jo HS, Kim KH. Localization of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow using new stimulator for the inching test. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004; 115:1021–1026. PMID: 15066525.
Article8. Kim DH, Kwon HK, Kwon KH, Kim WK, Kim CH. An evidence-based electrodignositc guidelines for the diagnosis of diabetic sensory and motor polyneuropathy. J Korean Assoc EMG Electrodiagn Med. 2012; 14:47–54.9. Kwon HK, Kim L, Park YK, Lee HJ. Frequency of carpal tunnel syndrome according to the severity of diabetic neuropathy. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 2005; 29:272–275.10. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive diabetes therapy on the development and progression of neuropathy. Ann Intern Med. 1995; 122:561–568. PMID: 7887548.11. Landau ME, Campbell WW. Clinical features and electrodiagnosis of ulnar neuropathies. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2013; 24:49–66. PMID: 23177030.
Article12. American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine. American Academy of Neurology. American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in ulnar neuropathy at the elbow: summary statement. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22:408–411. PMID: 10086904.13. Boonyapisit K, Katirji B, Shapiro BE, Preston DC. Lumbrical and interossei recording in severe carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 25:102–105. PMID: 11754192.
Article14. Park DS, Nam HS, Lee SE, Kim DH, Lee JG, Jeong HO. The usefulness of various electrodiagnostic parameters in mild carpal tunnel syndrome. J Korean Assoc EMG Electrodiagn Med. 2008; 10:135–143.15. Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts MJ. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Hanley & Belfus;2002.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis of Ulnar Neuropathy Caused by Intraneural Ganglion at Elbow with Ultrasound
- Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Ulnar Neuropathy Around the Elbow in Diabetes Mellitus
- Tardy Ulnar Nerve Palsy by Neurofibroma
- Ulnar Neuropathy Combined with Post-Traumatic Conditions of the Elbow
- Ultrasonographic Findings and Usefulness in Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow