Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Oct;38(5):694-697. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.5.694.
Effect of Ultrasonography-Guided Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Holmes' Tremor Secondary to Pontine Hemorrhage: Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Rehabilitation Hospital, National Rehabilitation Center, Seoul, Korea. asfreelyas@gmail.com
- 2Division of Education & Public Relations, National Rehabilitation Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2266505
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.5.694
Abstract
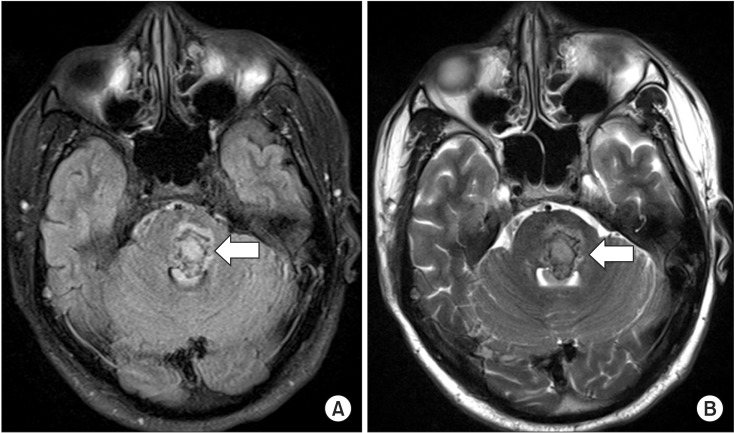
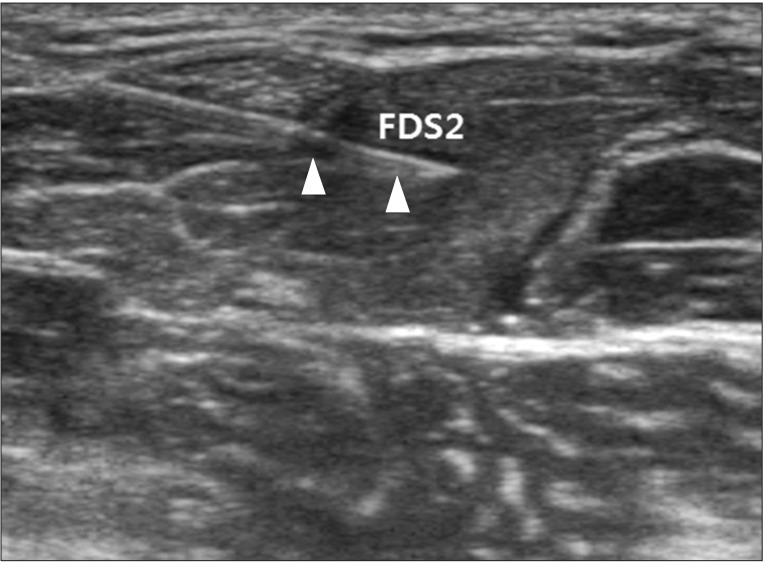
- Holmes' tremor is a low-frequency rest and intentional tremor secondary to various insults, including cerebral ischemia, hemorrhage, trauma, or neoplasm. Pharmacologic treatment is usually unsuccessful, and some cases require surgical intervention. We report a rare case of Holmes' tremor secondary to left pontine hemorrhage in a 29-year-old Asian male patient who developed 1.6-Hz postural and rest tremor of the right hand. He responded markedly to ultrasonography-guided botulinum toxin type A injection. To our knowledge, this is the first report of Homes' tremor treated with ultrasonography-guided botulinum toxin type A injection with favorable results.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ultrasonography for Assessment and Intervention With Botulinum Toxin Injection for Tremors
So-Hyun Park, Joon-Ho Shin
Ann Rehabil Med. 2024;48(6):396-404. doi: 10.5535/arm.240065.
Reference
-
1. Holmes G. On certain tremors in organic cerebral lesions. Brain. 1904; 27:327–375.
Article2. Deuschl G, Bergman H. Pathophysiology of nonparkinsonian tremors. Mov Disord. 2002; 17(Suppl 3):S41–S48. PMID: 11948754.
Article3. Acar G, Acar F, Bir LS, Kizilay Z, Cırak B. Vim stimulation in Holmes' tremor secondary to subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res. 2010; 32:992–994. PMID: 20546686.
Article4. Seidel S, Kasprian G, Leutmezer F, Prayer D, Auff E. Disruption of nigrostriatal and cerebellothalamic pathways in dopamine responsive Holmes' tremor. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009; 80:921–923. PMID: 18450789.
Article5. Kim MC, Son BC, Miyagi Y, Kang JK. Vim thalamotomy for Holmes' tremor secondary to midbrain tumour. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002; 73:453–455. PMID: 12235320.
Article6. Striano P, Elefante A, Coppola A, Tortora F, Zara F, Minetti C, et al. Dramatic response to levetiracetam in post-ischaemic Holmes' tremor. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007; 78:438–439. PMID: 17369598.
Article7. Zeuner KE, Deuschl G. An update on tremors. Curr Opin Neurol. 2012; 25:475–482. PMID: 22772877.
Article8. Simpson DM, Blitzer A, Brashear A, Comella C, Dubinsky R, Hallett M, et al. Assessment : Botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of movement disorders (an evidence-based review): report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2008; 70:1699–1706. PMID: 18458230.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasonography for Assessment and Intervention With Botulinum Toxin Injection for Tremors
- The Complications Developed after Repeated Botulinum Toxin Injection
- Botulinum Toxin Injection Therapy for Lingual Dystonia: A Case Report
- Holmes' Tremor Associated with Bilateral Hypertrophic Olivary Degeneration Following Brain Stem Hemorrhage: A Case Report
- Improvement of Lingual Dystonia Following Cerebellar Infarction through Botulinum Toxin Injection: a Case Report