Korean J Community Nutr.
2011 Aug;16(4):511-524. 10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.4.511.
Korean and Chinese University Students' Importance and Performance Analysis for Quality Attributes by Coffee Type in Daejeon
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Education, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Nutrition Services, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Food and Nutrition, Sangji University, Wonju, Korea. hy1317@sangji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2266123
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.4.511
Abstract
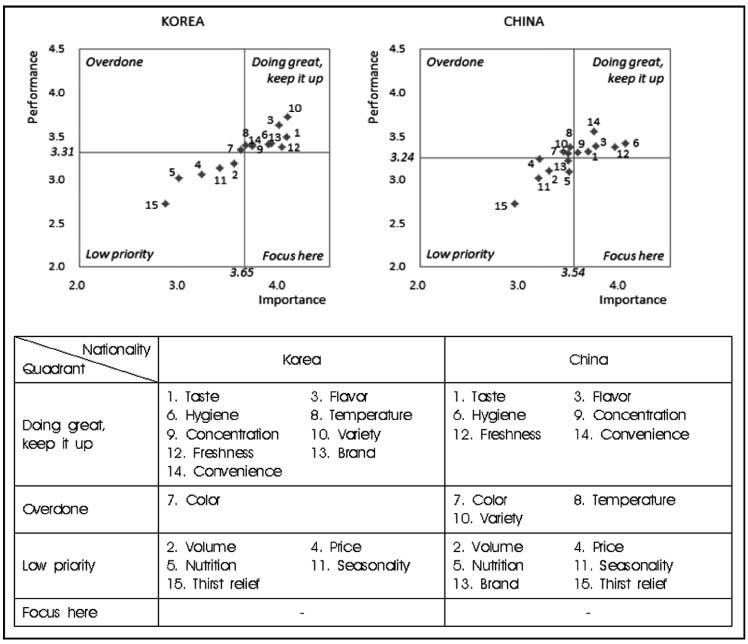
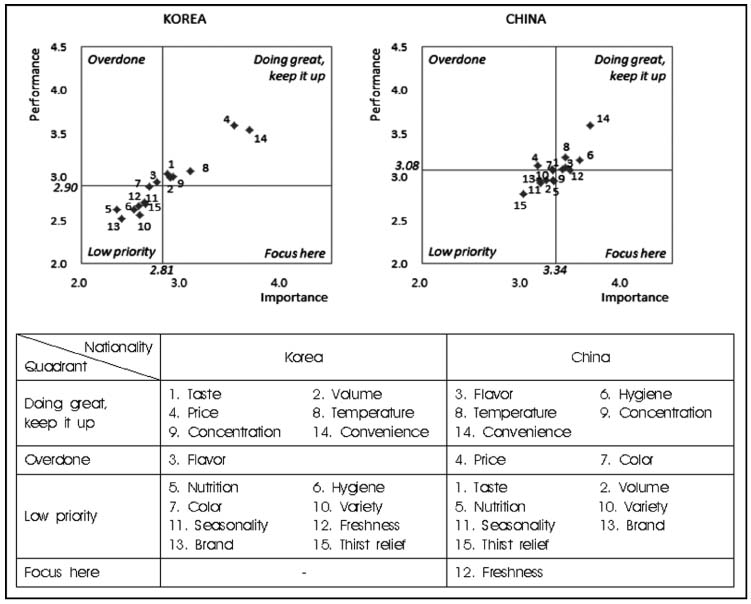
- The purposes of this study was to investigate importance and performance for coffee quality attributes in Korean and Chinese university students by 3 types of coffee; coffee in coffee houses, coffee in vending machines and canned/bottled coffee. Survey was done for 360 students in Daejeon with developed questionnaires including general information, favorite type of coffee and 15 quality attributes of coffee. Finally, data from 168 Korean and 126 Chinese university students was used for statistical analysis by SPSS 18.0 package program. Results of this study were as follows: for favorite type of coffee, the rates of coffee in coffee houses, coffee in vending machines and canned/bottled coffee were 43.0% 34.8% and 22.2% in Korean students and 8.7%, 78.0%, and 12.2% in Chinese students, respectively. Comparing Chinese students and Korean students showed higher importance for several quality attributes of coffee in coffee house (p < 0.05), but lower importance for most quality-attributes of coffee in vending machine (p < 0.05) and canned/bottled coffee (p < 0.05). According to importance and performance analysis, strategies for increasing satisfaction were to improve 'price' of canned/bottled coffee in Korean students, and 'taste', 'volume', 'concentration' and 'variety' of canned/bottled coffee and 'freshness' of coffee in vending machine in Chinese students. These results suggested that differentiated marketing plans between Korean and Chinese university students should be needed in coffee industry.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Antecedents of Coffee Satisfaction by Lifestyle Segments for Korean and Chinese University Students in Korea
Hye-Kyung Chung, Hye-Young Kim, Hae-Young Lee
Korean J Community Nutr. 2011;16(6):782-793. doi: 10.14253/kjcn.2011.16.6.782.
Reference
-
1. Byun GI, Lee SY, Cho WJ. Study on the importance and customer satisfaction of coffee-shop type according to the choice attributes by university students : Focused on Daegu. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2009. 19(4):503–514.2. Choi JO. The current analysis of consumer behaviors using the coffee vending machine. 2000. Andong University;39. MS thesis.3. Choi YS, Kim YT, Jhee OH. A study on university students' coffee shop use in the Seoul area. Korean J Culinary Res. 2009. 15(1):287–295.4. Green CG. Using customer survey data to develop marketing strategies in college/university food services. Journal of College & University Foodservice. 1992. 1(1):39–51.5. Ha KH. Survey of Korean food acknowledgement and preference by Chinese students in Daejeon. . Korean J Food Nutr. 2010. 23(2):186–195.6. Ha TS, Park MH, Choi YS, Sho SH. A study on beverage consumption pattern associated with food and nutrient intakes of college students. J Korean Diet Assoc. 1999. 5(1):21–28.7. Han ES, Rho SN. An analysis of consumption and preferences of the Korean traditional drinks by women indifferent age groups. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2004. 14(5):397–397.8. Jiang L. Comparison of salty taste assessment and eating behaviors among university students in Daegu, South Korea and in Shenyang, China. 2010. Kyungpook National University;65–68. MS thesis.9. Jung HY, Jeon ER. Preference for Korean food and satisfaction of dormitory foodservice by Chinese students studying at Mokpo National University. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2011. 40(2):283–289.10. Jung YW. A study on the factors of customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in coffee houses. Korean J Culinary Res. 2006a. 12(4):1–17.11. Jung YW. A study on the positioning strategy of coffee house. Korean J Hosp Adm. 2006b. 15(1):269–289.12. Kang SY. Coffee: Trends in 2006 and forecasting 2007. Food Industry. 2007. 195(1):37–45.13. Khoe KI, Sul WS. A study on the entering strategies of Korean traditional food in Chinese market. Korean J Food Mark Econ. 2008. 25(2):125–152.14. Kim HA. Importance-performance analysis of service quality of in campus specialty coffee shop. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2008. 37(8):1069–1078.15. Kim HB, Lee JW, Ro YJ. Impacts of choice attributes on customer loyalty in the coffee-shop restaurant. J Foodserv Manage. 2007. 10(4):237–252.16. Kim HJ. The survey of beverage preference and sales trends. 2004. Sookmyung Women's University;8–9. MS thesis.17. Kim KH, Kim KM. A study on Chinese consumers' Korean food consumption behavior based on food-related lifestyle. Korean J Food Mark Econ. 2010. 27(1):41–62.18. Kim SS, Kim BK, Park JO. Identification of selection attributions and assessment of brand equity of take-out coffee shops using conjoint analysis. Journal of Foodservice Management. 2006. 9(4):49–69.19. Kim WS, Oh KN, Lee YH, Cho KO. Marketing strategy for service quality improvement of specialty Starbucks coffeeshop: A case study. Journal of Foodservice Management. 2002. 5(1):3–22.20. Kim YO. A study on the choice attributes and customer satisfaction of a take-out coffee shop. Korean J Culinary Res. 2003. 9(3):141–154.21. Ko JY, Seo HJ. A study on the selection attribute of coffee consumer's. Journal of Hotel and Resort. 2009. 8(2):23–41.22. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The forth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV). 2008. Seoul: 127. 143.23. Korea Joongang Daily (2007): Visiting specialty coffee shops that is hitting university campuses. cited 2011 June 20. Available from http://article.joinsmsn.com/news/article/article.asp?total_id=2675242.24. Lee YN, Kim JY. Differences in purchase behavior and choice attributes according to characteristics of specialty coffee shop customers. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2009. 19(2):265–277.25. Martilla JA, James JC. Importance-performance analysis. The Journal of Marketing. 1977. 41(1):77–79.26. Park KH, Yoon JH. Coffee SERV: Multiple-item scale for measuring service quality of specialty coffee shop. J Foodserv Manage. 2006. 10(2):249–265.27. Seo GH, Shin MJ. Importance and satisfaction with the service of Korean restaurants for Japanese and Chinese students in Korea. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2006. 16(6):753–762.28. Shin SY, Chung LN. Analysis of customer perception for quality attributes according to consumers' coffee consumption types. Korean J Food Cult. 2007a. 22(6):748–756.29. Shin SY, Chung LN. The preference and frequency of beverages related to health factor in university students. Korean J Food Cult. 2007b. 22(4):420–433.30. Sohn KH, Lee MJ, Min SH, Lee HJ. A study on the factors affecting the consumption of coffee and tea among female in Seoul. Korean J Food Cult. 2000. 15(5):398–412.31. The Chosunilbo (2011): Private colleges lure poorly qualified Chinese students. cited 2011 June 20. Available from http://news.chosun.com/site/data/html_dir/2011/04/04/2011040400188.html.32. The Korea Economic Daily (2003): 'A boom' of franchise store location in campus. cited 2011 June 20. Available from http://www.hankyung.com/news/app/newsview.php?aid=2003051890411&intype=1.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Students' Satisfaction with Middle School Foodservice by Region in Gangwon Province
- Customer Perception Levels towards Service Quality Attributes of University Residence Hall Foodservice by Importance-Performance Analysis
- Comparison of Importance and performance to the school lunch service according of male and female middle school students in the Gangwon province.
- Comparative Analysis of the Quality Attributes Affecting Students' Satisfaction on School Lunch Service of Middle School by Year
- The Antecedents of Coffee Satisfaction by Lifestyle Segments for Korean and Chinese University Students in Korea