Ann Dermatol.
2010 May;22(2):186-190. 10.5021/ad.2010.22.2.186.
CD4-/CD56+/CD123+ Hematodermic Neoplasm Showing Early Liver Metastasis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. khkim@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2265390
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2010.22.2.186
Abstract
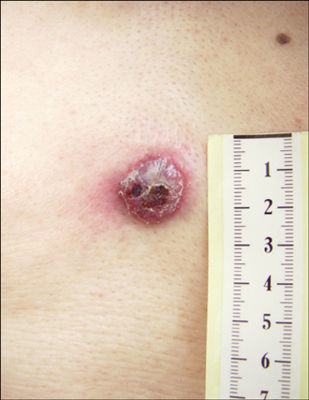
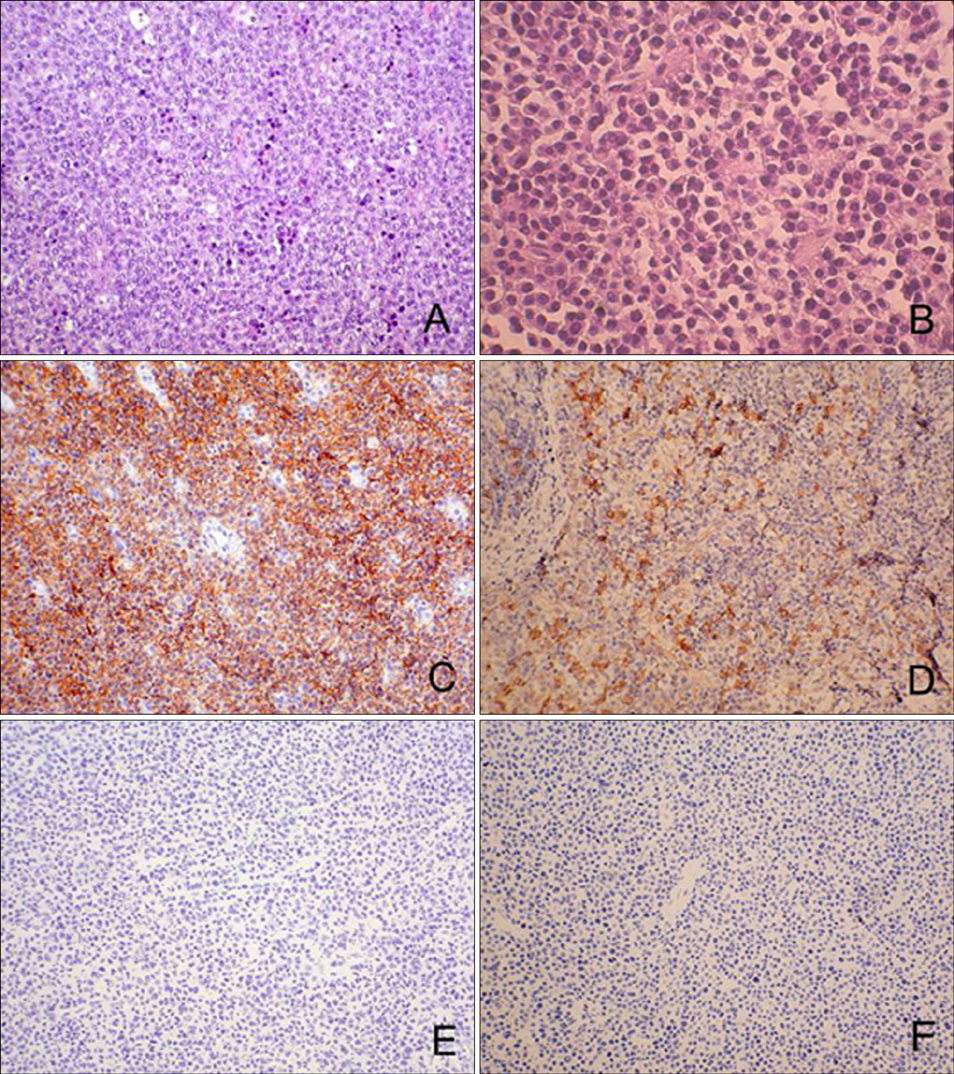
- Hematodermic neoplasm (HN) is a clinically aggressive neoplasm with a high incidence of cutaneous involvement and a risk of leukemic dissemination. In the recent WHO-EORTC classification, the term blastic natural killer cell lymphoma has been replaced with CD4+/CD56+ HN because of its derivation from a plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursor. Cases of HN that completely lack CD4 or CD56 expression, therefore represents a diagnostic problem. A 68-year-old Korean male was diagnosed with CD4-/CD56+ HN and treated with hyper-CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone) at initial treatment, and then switched to high dose methotrexate/cytarabine. His disease relapsed and resulted in death from bone and brain disease 6 months after complete clinical remission, despite diagnostic workups, including a radioisotope liver scan and ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy. Further cytogenetic studies such as comparative genomic hybridization could elucidate the genetic mechanisms in the development and progression of lymphomas. We report an unusual case of 'CD4-/CD56+/CD123+ HN' showing early liver metastasis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Willemze R, Jaffe ES, Burg G, Cerroni L, Berti E, Swerdlow SH, et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood. 2005. 105:3768–3785.
Article2. Niakosari F, Sur M. Agranular CD4+/CD56+ hematodermic neoplasm: a distinct entity described in the recent World Health Organization-European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2007. 131:149–151.
Article3. Petrella T, Comeau MR, Maynadie M, Couillault G, De Muret A, Maliszewski CR, et al. 'Agranular CD4+ CD56+ hematodermic neoplasm' (blastic NK-cell lymphoma) originates from a population of CD56+ precursor cells related to plasmacytoid monocytes. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002. 26:852–862.
Article4. Ascani S, Massone C, Ferrara G, Rongioletti F, Papini M, Pileri S, et al. CD4-negative variant of CD4+/CD56+ hematodermic neoplasm: description of three cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2008. 35:911–915.
Article5. Argyrakos T, Rontogianni D, Karmiris T, Kapsimali V, Grigoriou E, Tsantekidou M, et al. Blastic natural killer (NK)-cell lymphoma: report of an unusual CD4 negative case and review of the CD4 negative neoplasms with blastic features in the literature. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. 45:2127–2133.
Article6. Kato N, Yasukawa K, Kimura K, Sugawara H, Aoyagi S, Mishina T, et al. CD2- CD4+ CD56+ hematodermic/hematolymphoid malignancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001. 44:231–238.7. Khoury JD, Medeiros LJ, Manning JT, Sulak LE, Bueso-Ramos C, Jones D. CD56(+) TdT(+) blastic natural killer cell tumor of the skin: a primitive systemic malignancy related to myelomonocytic leukemia. Cancer. 2002. 94:2401–2408.
Article8. Urosevic M, Conrad C, Kamarashev J, Asagoe K, Cozzio A, Burg G, et al. CD4+CD56+ hematodermic neoplasms bear a plasmacytoid dendritic cell phenotype. Hum Pathol. 2005. 36:1020–1024.
Article9. DiGiuseppe JA, Louie DC, Williams JE, Miller DT, Griffin CA, Mann RB, et al. Blastic natural killer cell leukemia/lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997. 21:1223–1230.
Article10. Petrella T, Dalac S, Maynadie M, Mugneret F, Thomine E, Courville P, et al. Groupe Francais d'Etude des Lymphomes Cutanes (GFELC). CD4+ CD56+ cutaneous neoplasms: a distinct hematological entity? Am J Surg Pathol. 1999. 23:137–146.
Article11. Jacob MC, Chaperot L, Mossuz P, Feuillard J, Valensi F, Leroux D, et al. CD4+ CD56+ lineage negative malignancies: a new entity developed from malignant early plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Haematologica. 2003. 88:941–955.12. Assaf C, Gellrich S, Whittaker S, Robson A, Cerroni L, Massone C, et al. CD56-positive haematological neoplasms of the skin: a multicentre study of the Cutaneous Lymphoma Project Group of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2007. 60:981–989.
Article13. Li K, Cho KH, Kim CW, Kim YC. A case of blastic NK-cell lymphoma. Korean J Dermatol. 2003. 41:1381–1384.14. Petrella T, Meijer CJ, Dalac S, Willemze R, Maynadie M, Machet L, et al. TCL1 and CLA expression in agranular CD4/CD56 hematodermic neoplasms (blastic NK-cell lymphomas) and leukemia cutis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004. 122:307–313.
Article15. Chang SE, Choi HJ, Huh J, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, et al. A case of primary cutaneous CD56+, TdT+, CD4+, blastic NK-cell lymphoma in a 19-year-old woman. Am J Dermatopathol. 2002. 24:72–75.
Article16. Hahtola S, Burghart E, Jeskanen L, Karenko L, Abdel-Rahman WM, Polzer B, et al. Clinicopathological characterization and genomic aberrations in subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. 128:2304–2309.
Article17. Dijkman R, Tensen CP, Jordanova ES, Knijnenburg J, Hoefnagel JJ, Mulder AA, et al. Array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis reveals recurrent chromosomal alterations and prognostic parameters in primary cutaneous large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:296–305.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CD 4+/CD56+ Hematodermic Neoplasm in Infancy: Case Report
- A Case of Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm in Child
- Plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms
- CD4+CD56+Lineage Negative Hematopoietic Neoplasm: So Called Blastic NK Cell Lymphoma
- A Case of Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm with Mutations in DNMT3A, TET2, SRSF2, and ATRX Genes