Intense Pulsed Light and Low-Fluence Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser Treatment in Melasma Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University Boramae Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Dermatology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bell711@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2265298
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2012.24.3.267
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Recently, low fluence collimated Q-switched (QS) Nd:YAG laser has drawn attention for the treatment of melasma. However, it needs a lot of treatment sessions for the substantial results and repetitive laser exposures may end up with unwanted depigmentation.
OBJECTIVE
We evaluated the clinical effects and safety of the combinational treatment, using intense pulsed light (IPL) and low fluence QS Nd:YAG laser.
METHODS
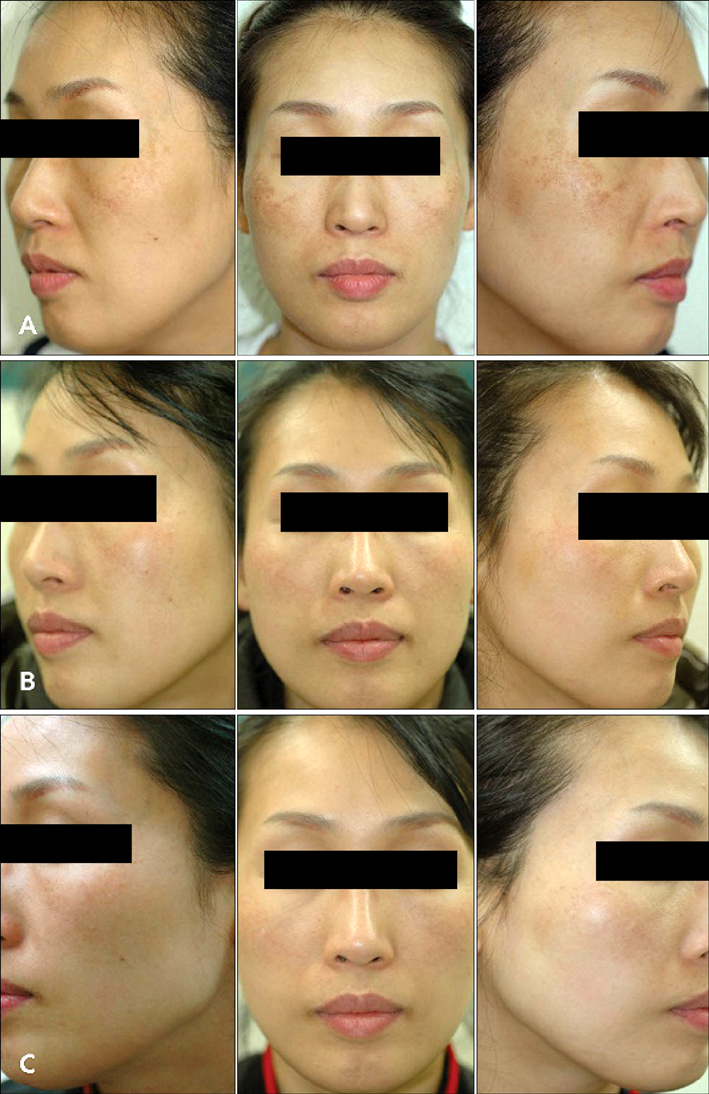
Retrospective case series of 20 female patients, with mixed type melasma, were analyzed using medical records. They were treated with IPL one time, and 4 times of weekly successive low fluence Nd:YAG laser treatments. At each visit, digital photographs were taken under the same condition. Melanin index (MI) and erythema index (EI) were measured on the highest point on the cheekbones. Modified melasma area and severity index (MASI) scores were calculated by two investigators using digital photographs.
RESULTS
The mean values of MI and EI decreased significantly after treatments. The modified MASI score has decreased by 59.35%, on average. Sixty percents of the participants did not require any more treatments, and no clinical aggravations were observed during the follow-up period (mean 5.9 months).
CONCLUSION
IPL and low fluence laser may elicit a clinical resolution in the mixed type melasma with long term benefits.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Treatment of Melasma with the Photoacoustic Twin Pulse Mode of Low-Fluence 1,064 nm Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser
Jee Young Kim, Misoo Choi, Chan Hee Nam, Ji Seok Kim, Myung Hwa Kim, Byung Cheol Park, Seung Phil Hong
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(3):290-296. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.290.Morphologic Changes of Zebrafish Melanophore after Intense Pulsed Light and Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser Irradiation
Hwa Jung Ryu, Ji Min Lee, Hee Won Jang, Hae Chul Park, Im Joo Rhyu, Il-Hwan Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(6):711-717. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.6.711.Beneficial Effect of Low Fluence 1,064 nm Q-Switched Neodymium:Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser in the Treatment of Senile Lentigo
Jae-Hui Nam, Han-Saem Kim, Ga-Young Lee, Won-Serk Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2017;29(4):427-432. doi: 10.5021/ad.2017.29.4.427.Treatment of Melasma with Pulsed-Dye Laser and 1,064-nm Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser: A Split-Face Study
Sook Hyun Kong, Ho Seok Suh, Yu Sung Choi
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(1):1-7. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Gupta AK, Gover MD, Nouri K, Taylor S. The treatment of melasma: a review of clinical trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 55:1048–1065.
Article2. Rendon M, Berneburg M, Arellano I, Picardo M. Treatment of melasma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006. 54:S272–S281.
Article3. Jeong SY, Shin JB, Yeo UC, Kim WS, Kim IH. Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser for melasma with pre- or post-treatment triple combination cream. Dermatol Surg. 2010. 36:909–918.
Article4. Wattanakrai P, Mornchan R, Eimpunth S. Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (1,064 nm) laser for the treatment of facial melasma in Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2010. 36:76–87.
Article5. Haddad AL, Matos LF, Brunstein F, Ferreira LM, Silva A, Costa D Jr. A clinical, prospective, randomized, double-blind trial comparing skin whitening complex with hydroquinone vs. placebo in the treatment of melasma. Int J Dermatol. 2003. 42:153–156.
Article6. Wang CC, Hui CY, Sue YM, Wong WR, Hong HS. Intense pulsed light for the treatment of refractory melasma in Asian persons. Dermatol Surg. 2004. 30:1196–1200.
Article7. Negishi K, Kushikata N, Tezuka Y, Takeuchi K, Miyamoto E, Wakamatsu S. Study of the incidence and nature of "very subtle epidermal melasma" in relation to intense pulsed light treatment. Dermatol Surg. 2004. 30:881–886.
Article8. Polnikorn N. Treatment of refractory dermal melasma with the MedLite C6 Q-switched Nd:YAG laser: two case reports. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2008. 10:167–173.
Article9. Choi M, Choi JW, Lee SY, Choi SY, Park HJ, Park KC, et al. Low-dose 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser for the treatment of melasma. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010. 21:224–228.
Article10. Chan NP, Ho SG, Shek SY, Yeung CK, Chan HH. A case series of facial depigmentation associated with low fluence Q-switched 1,064 nm Nd:YAG laser for skin rejuvenation and melasma. Lasers Surg Med. 2010. 42:712–719.
Article11. Kim MJ, Kim JS, Cho SB. Punctate leucoderma after melasma treatment using 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with low pulse energy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009. 23:960–962.
Article12. Kang WH, Chun SC, Lee S. Intermittent therapy for melasma in Asian patients with combined topical agents (retinoic acid, hydroquinone and hydrocortisone): clinical and histological studies. J Dermatol. 1998. 25:587–596.
Article13. Kang WH, Yoon KH, Lee ES, Kim J, Lee KB, Yim H, et al. Melasma: histopathological characteristics in 56 Korean patients. Br J Dermatol. 2002. 146:228–237.
Article14. Kim EH, Kim YC, Lee ES, Kang HY. The vascular characteristics of melasma. J Dermatol Sci. 2007. 46:111–116.
Article15. Li YH, Chen JZ, Wei HC, Wu Y, Liu M, Xu YY, et al. Efficacy and safety of intense pulsed light in treatment of melasma in Chinese patients. Dermatol Surg. 2008. 34:693–700.16. Yamashita T, Negishi K, Hariya T, Kunizawa N, Ikuta K, Yanai M, et al. Intense pulsed light therapy for superficial pigmented lesions evaluated by reflectance-mode confocal microscopy and optical coherence tomography. J Invest Dermatol. 2006. 126:2281–2286.17. Jeong SY, Chang SE, Bak H, Choi JH, Kim IH. New melasma treatment by collimated low fluence Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:1163–1170.
Article18. Kim JH, Kim H, Park HC, Kim IH. Subcellular selective photothermolysis of melanosomes in adult zebrafish skin following 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser irradiation. J Invest Dermatol. 2010. 130:2333–2335.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Split-face Comparison of Pulse-in-pulse Type Intense Pulsed Light Versus Low-fluence Multi-pass 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser in the Treatment of Facial Melasma
- Treatment of Melasma with the Photoacoustic Twin Pulse Mode of Low-Fluence 1,064 nm Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser
- New Melasma Treatment by Collimated Low Fluence Q-switched Nd : YAG Laser
- Treatment of Melasma with Pulsed-Dye Laser and 1,064-nm Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser: A Split-Face Study
- Effective Treatment of Suspicious Riehl's Melanosis Using Low Fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser and 595 nm Pulsed Dye Laser