Ann Dermatol.
2016 Jun;28(3):290-296. 10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.290.
Treatment of Melasma with the Photoacoustic Twin Pulse Mode of Low-Fluence 1,064 nm Q-Switched Nd:YAG Laser
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. zamoo97@naver.com
- KMID: 2164635
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.290
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Low-fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser has been widely used for the treatment of melasma. Although new Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers with photoacoustic twin pulse (PTP) mode have been recently developed for high-efficiency, there is limited information available for the new technique.
OBJECTIVE
This study was designed to investigate the efficacy and adverse effects after few sessions of repeated low fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser treatment with PTP mode in Asian women with melasma.
METHODS
Twenty-two Korean women were treated with a total of five sessions of low-fluence PTP mode Nd:YAG laser treatment (Pastelle®) at 2 weeks interval. Responses to treatments were evaluated by using Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) scoring, colorimeter measurement, and the investigators' and patients' overall assessments. Adverse events were recorded at each visit.
RESULTS
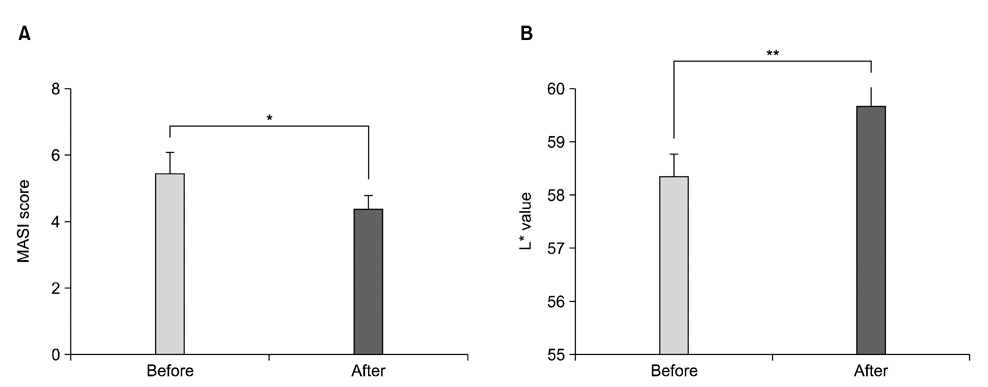
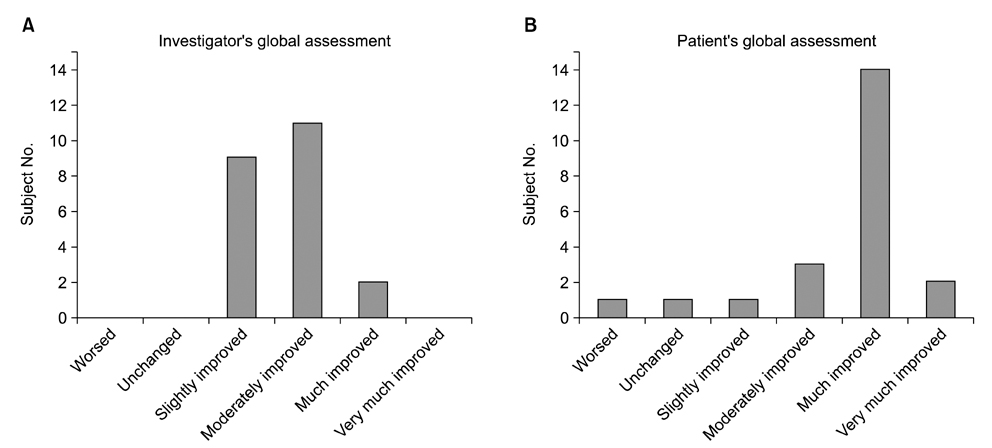
Investigators' and patients' overall assessment showed that 'significantly improved' was assessed by 13 (59.1%) and 19 of 22 patients (86.4%), respectively. MASI scores were significantly reduced by 20.4%. The lightness, measured by using a colorimeter, was significantly increased by 1.3 point. Notable adverse events were not observed.
CONCLUSION
After 5 sessions of laser therapy alone, about 60% of the subjects showed significant improvement. Few sessions of repeated laser toning treatment using the PTP mode is a safe and effective way to treat facial melasma.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ball Arefiev KL, Hantash BM. Advances in the treatment of melasma: a review of the recent literature. Dermatol Surg. 2012; 38:971–984.
Article2. Kauvar AN. Successful treatment of melasma using a combination of microdermabrasion and Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers. Lasers Surg Med. 2012; 44:117–124.
Article3. Polnikorn N. Treatment of refractory dermal melasma with the medLite C6 Q-switched Nd:YAG laser: two case reports. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2008; 10:167–173.
Article4. Sim JH, Park YL, Lee JS, Lee SY, Choi WB, Kim HJ, et al. Treatment of melasma by low-fluence 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. J Dermatolog Treat. 2014; 25:212–217.
Article5. Na SY, Cho S, Lee JH. Intense pulsed light and low-fluence Q-switched Nd:YAG laser treatment in melasma patients. Ann Dermatol. 2012; 24:267–273.
Article6. Park GH, Lee JH, Choi JR, Chang SE. The degree of erythema in melasma lesion is associated with the severity of disease and the response to the low-fluence Q-switched 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser treatment. J Dermatolog Treat. 2013; 24:297–299.
Article7. Bansal C, Naik H, Kar HK, Chauhan A. A comparison of low-fluence 1064-nm Q-switched Nd: YAG laser with topical 20% azelaic acid cream and their combination in melasma in Indian patients. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2012; 5:266–272.
Article8. Brown AS, Hussain M, Goldberg DJ. Treatment of melasma with low fluence, large spot size, 1064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) laser for the treatment of melasma in Fitzpatrick skin types II-IV. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2011; 13:280–282.
Article9. Jeong SY, Shin JB, Yeo UC, Kim WS, Kim IH. Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser for melasma with pre- or post-treatment triple combination cream. Dermatol Surg. 2010; 36:909–918.
Article10. Wattanakrai P, Mornchan R, Eimpunth S. Low-fluence Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (1,064 nm) laser for the treatment of facial melasma in Asians. Dermatol Surg. 2010; 36:76–87.
Article11. Choi M, Choi JW, Lee SY, Choi SY, Park HJ, Park KC, et al. Low-dose 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser for the treatment of melasma. J Dermatolog Treat. 2010; 21:224–228.
Article12. Pandya AG, Hynan LS, Bhore R, Riley FC, Guevara IL, Grimes P, et al. Reliability assessment and validation of the Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) and a new modified MASI scoring method. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011; 64:78–83. 83.e1–83.e2.
Article13. Kimbrough-Green CK, Griffiths CE, Finkel LJ, Hamilton TA, Bulengo-Ransby SM, Ellis CN, et al. Topical retinoic acid (tretinoin) for melasma in black patients. A vehicle-controlled clinical trial. Arch Dermatol. 1994; 130:727–733.
Article14. Kim JH, Kim H, Park HC, Kim IH. Subcellular selective photothermolysis of melanosomes in adult zebrafish skin following 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser irradiation. J Invest Dermatol. 2010; 130:2333–2335.
Article15. Mun JY, Jeong SY, Kim JH, Han SS, Kim IH. A low fluence Q-switched Nd:YAG laser modifies the 3D structure of melanocyte and ultrastructure of melanosome by subcellular-selective photothermolysis. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2011; 60:11–18.
Article16. Polnikorn N. Treatment of refractory melasma with the medLite C6 Q-switched Nd:YAG laser and alpha arbutin: a prospective study. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2010; 12:126–131.
Article17. Suh KS, Sung JY, Roh HJ, Jeon YS, Kim YC, Kim ST. Efficacy of the 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser in melasma. J Dermatolog Treat. 2011; 22:233–238.
Article18. Kim T, Cho SB, Oh SH. Punctate leucoderma after 1,064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser with low-fluence therapy: is it melanocytopenic or melanopenic? Dermatol Surg. 2010; 36:1790–1791.
Article19. Kim MJ, Kim JS, Cho SB. Punctate leucoderma after melasma treatment using 1064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG laser with low pulse energy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009; 23:960–962.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Split-face Comparison of Pulse-in-pulse Type Intense Pulsed Light Versus Low-fluence Multi-pass 1064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser in the Treatment of Facial Melasma
- Beneficial Effect of Low Fluence 1,064 nm Q-Switched Neodymium:Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet Laser in the Treatment of Senile Lentigo
- Effective Treatment of Suspicious Riehl's Melanosis Using Low Fluence 1,064 nm Q-switched Nd:YAG Laser and 595 nm Pulsed Dye Laser
- New Melasma Treatment by Collimated Low Fluence Q-switched Nd : YAG Laser
- Hypopigmentation Induced by Frequent Low-Fluence, Large-Spot-Size QS Nd:YAG Laser Treatments