Korean J Community Nutr.
2011 Apr;16(2):253-264. 10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.2.253.
Government-Funded Meal Support Program for Low-Income Children through Convenience Stores : Current Status and Nutritional Quality of Available Meal Items in Seoul
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. hoonyoon@snu.ac.kr
- 2Research Institute of Human Ecology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2264399
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5720/kjcn.2011.16.2.253
Abstract
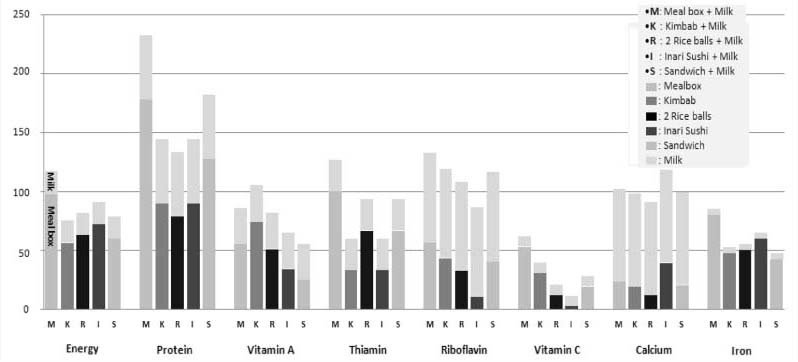
- The objectives of this study were to investigate the current status of the Korean government-funded meal support program for low-income children through convenience stores and to evaluate the nutritional quality of the meal items available under the program. The POS data of three convenient stores where children had used their electronic meal cards most often in Seoul during January 2010 and the kinds and amounts of ingredients of the meals items available to the children were obtained from the headquarter of the convenient stores. A total of 5,081 transactions by 693 children included in the POS data was analyzed. In addition, nutritional contents of meal items, which were meal boxes (11 kinds), kimbab (13 kinds), rice balls (27 kinds), inari sushi (1 kind), and sandwiches (26 kinds), were analyzed with Can Pro 3.0. The results showed that children had purchased flavored-milk products most often. Children tended to purchase meal items together with drinks (60.9% of transactions), but some purchased drinks (27.6%) or meal items only (11.5%). Except for meal boxes, none of the meal items satisfied 1/3 of Estimated Energy Requirements of the 9-11 year-old boys per day. The average energy contents of different kinds of meal boxes, kimbabs, rice balls, and sandwiches were 619, 357, 200, and 380 kcal, respectively, and the energy content of a package of Inari sushi was 457 kcal. Vitamin C amount was found to be deficient in all the meal items, compared to 1/3 of Recommended Intake of the 9-11 year-old boys per day. The results of this study could be useful to develop nutritionally appropriate meal items for the convenient stores participating in the government-funded meal support program for children from low-income families.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alaimo K, Olson CM, Frongillo EA. Family food insufficiency, but not low family income, is positively associated with dysthymia and suicide symptoms in adolescents. J Nutr. 2002. 132:719–725.2. Asano K, Yoon J, Yoon B. Appropriate size and dish combination of nutritional-balanced lunch boxes delivered to children under the government-funded meal service program in Korea. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009. 14(5):565–575.3. Bae EJ, Kwon JH, Yoon HJ, Lee SK. Nutritional status of school lunch supported students in an elementary school. J Korean Diet Assoc. 2001. 7(4):349–360.4. Black RE, Williams SM, Jones IE, Goulding A. Children who avoid drinking cow milk are at increased risk for prepubertal bone fractures. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004. 104:250–253.5. Cooper C, Cawley M, Bhalla A, Egger P, Ring F, Morton L, Barker D. Childhood growth, physical activity, and peak bone mass in women. J Bone Miner Res. 1995. 10(6):940–947.6. Government changes meal coupon into electronic card. Hankookilbo. 2009. cited 2010 June 20. Available from http://news.hankooki.com/lpage/society/200904/h2009040203004784110.htm.7. Chungnam introduced the electronic card for the government-funded meal support program for children from low-income families. Hankookilbo. 2010. cited 2010 September 22. Available from http://news.hankooki.com/lpage/society/201004/h2010042015312774990.htm.8. Kim ES. A study on improving the efficiency of the free feeding system for poorly-fed children in Gangwon province. 2007a. Gangwon: Gangwon Development Research Institute;87–111.9. Kim MS. Survey of current status on foodservice program for children from low-income families. 2007b. Seoul: National Human Rights Commission of Korea;100–224.10. To introduce the purumi welfare card. Kyonggidominilbo. 2009. cited 2010 June 20. Available from http://www.kgdomin.com/news/122675.11. Ministry for Health and Welfare [MHW]. 2009 Winter statistics about child foodservice program. 2009a. Unpublished raw data.12. Eat absentmindedly? No! Healthy food is a privilege for children. Ministry for Health and Welfare [MHW]. 2009b. cited 2010 June 22. Available from http://www.mw.go.kr/front/al/sal0301ls.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=04&MENU_ID=0403.13. Ministry for Health and Welfare [MHW]. 2010 The child welfare program guide. 2010. Seoul: 144.14. Neumann CG, Murphy SP, Gewa C, Grillenberger M, Bwibo NO. Meat supplementation improves growth, cognitive, and behavioral outcomes in Kenyan children. J Nutr. 2007. 137:1119–1123.15. Park ND. Analysis of the status of foodservice program for children from low-income families in Daejeon and improvement plan for the support system. 2008. Daejeon: Daejeon Development Institute;39–107.16. Government changes meal coupon into electronic card for the government-funded meal support program for children from low-income families. Segyeilbo. 2009. cited 2010 June 10. Available from http://www.segye.com/Articles/NEWS/WHOLECOUNTRY/Article.asp?aid=20090401005564&subctg1=01&subctg2=.17. GS25 launched the government-funded meal support program for children from low-income families. Segyeilbo. 2010. cited 2010 June 15. Available from http://www.segye.com/Articles/NEWS/ECONOMY/Article.asp?aid=20100728000722&subctg1=&subctg2=.18. Seoul Metropolitan Government. 2010 Statistics about Child Foodservice Program. 2010. Unpublished raw data.19. Schaible UE, Kaufmann SHE. Malnutrition and infection: Complex mechanisms and global impacts. Plos Med. 2007. 4(5):e115.20. Shim JE, Yoon J, Lee K, Kwon S. Evaluation of dietary intake of Korean school-aged children from low-income families by comparing with the Korean food guide: Analysis of the data from the 2001 National Health and Nutrition Survey. Korean J Nutr. 2009. 42(8):691–701.21. Sigfusdottir ID, Kristjansson AL, Allegrante JP. Health behaviour and academic achivement in Icelandic school children. Health Educ Res. 2006. 22(1):70–80.22. SPSS Inc. PASW Statistics 18.0 [Predictive analytics software]. 2009.23. The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary reference intakes for Koreans. 2005a. Seoul: Hanareum Publishing Co.;15–341.24. The Korean Nutrition Society. CAN Pro 3.0 [Computer software]. 2005b.25. Child & Adult Care Food Program. United States Department of Agriculture [USDA]. 2009. cited 2010 June 23. Available from http://www.fns.usda.gov/cnd/care/programbasics/meals/meal_patterns.htm.26. WIC food packages-regulatory requirements for WIC-eligible foods. United States Department of Agriculture [USDA]. 2010. cited 2010 June 23. Available from http://www.fns.usda.gov/wic/benefitsandservices/foodpkgregs.htm.27. Yoon B, Yoon J, Shim JE, Kwon S. Current status of meal box service management for children from low-income familiesduring summer vacation. Korean J Community Nutr. 2009. 14(2):206–215.28. Youn HJ, Han YH, Hyun TS. Amounts and food sources of nutrients of elementary school lunch menus by the type of foodservice and the percent energy from fat. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007. 12(1):90–105.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diet of children under the government-funded meal support program in Korea
- The Current Status of Foodservice Management in the Restaurants Participating in the Government-funded Children's Model Program in Korea during Summer Vacation
- Current Status of Meal Box Service Management for Children from Low-income Families During Summer Vacation
- Efficiency of Purchase Management as Determined by the Adoption of School Meal Service Support Center in Gyeonggi Area
- Evaluation of Nutritional Quality of Convenience Store Meal Boxes according to Store Company and Meal Price