Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2014 Sep;2(4):302-305. 10.4168/aard.2014.2.4.302.
Penicillamine-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient with Wilson disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. choisw@uuh.ulsan.kr
- 2Department of Dermatology, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2262400
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2014.2.4.302
Abstract
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is rare but life-threatening severe cutaneous adverse reaction, which is mostly induced by drugs. It characterized by widespread epidermal necrosis, resulting in bullae with sloughing and frequent involvement of the mucous membrane. Due to high mortality, management of patients requires prompt withdrawal of the causative drug, appropriate supportive care, and consideration of immune-modulating agents, such as intravenous immunoglobulin or corticosteroids. Wilson disease is an inherited disorder of copper transport that results in excessive accumulation of copper in the body. Copper chelation with penicillamine is an effective first line therapy in most patients. We present a 20-year-old man with Wilson disease who developed TEN following administration of penicillamine. He was successfully treated with systemic corticosteroid, intravenous immunoglobulin, and supportive management.
MeSH Terms
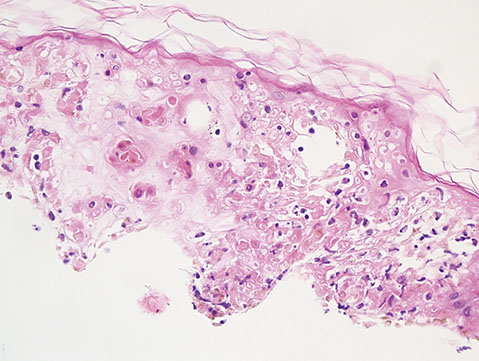
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pereira FA, Mudgil AV, Rosmarin DM. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007; 56:181–200.
Article2. Roujeau JC, Stern RS. Severe adverse cutaneous reactions to drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331:1272–1285.
Article3. Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Rzany B, Stern RS, Anderson T, et al. Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:1600–1607.
Article4. Downey A, Jackson C, Harun N, Cooper A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: review of pathogenesis and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012; 66:995–1003.
Article5. Seo JK. Wilson disease: an update. Korean J Hepatol. 2006; 12:333–363.6. Levy RS, Fisher M, Alter JN. Penicillamine: review and cutaneous manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1983; 8:548–558.
Article7. Ishak R, Abbas O. Penicillamine revisited: historic overview and review of the clinical uses and cutaneous adverse effects. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013; 14:223–233.
Article8. Letko E, Papaliodis DN, Papaliodis GN, Daoud YJ, Ahmed AR, Foster CS. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a review of the literature. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005; 94:419–436.
Article9. Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau JC. Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol. 1993; 129:92–96.
Article10. Viard I, Wehrli P, Bullani R, Schneider P, Holler N, Salomon D, et al. Inhibition of toxic epidermal necrolysis by blockade of CD95 with human intravenous immunoglobulin. Science. 1998; 282:490–493.
Article11. Abe R, Shimizu T, Shibaki A, Nakamura H, Watanabe H, Shimizu H. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome are induced by soluble Fas ligand. Am J Pathol. 2003; 162:1515–1520.
Article12. Trent J, Halem M, French LE, Kerdel F. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and intravenous immunoglobulin: a review. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2006; 25:91–93.
Article13. Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M, Roujeau JC, Revuz J, Wolkenstein P. SCORTEN: a severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol. 2000; 115:149–153.
Article14. Roberts EA, Schilsky ML. Division of Gastroenterology and Nutrition, Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. A practice guideline on Wilson disease. Hepatology. 2003; 37:1475–1492.
Article15. Greer KE, Askew FC, Richardson DR. Skin lesions induced by penicillamine. Occurrence in a patient with hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson Disease). Arch Dermatol. 1976; 112:1267–1269.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Carbamazepine- Induced- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- Penicillamine Induced Breast Enlargement in a Patient with Wilson's Disease
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Due to Contact of Paraquat(Gramoxone(R))
- A Case of Complete Vaginal Ostruction Following Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- Macromastia with Multiple Fibroadenomas in a Wilson's Disease Patient