Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2014 May;2(2):134-137. 10.4168/aard.2014.2.2.134.
Drug hypersensitivity to various antihistamines with cross-reactions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. doc4u@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2261749
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2014.2.2.134
Abstract
- Antihistamines (histamine receptor antagonists) are widely prescribed medicines in the treatment of allergic disorders, especially the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions, mainly blocking the activity of vasoactive amines to their receptors. Drug adverse reactions such as sleepiness and dry mouth are frequently encountered. However, drug hypersensitivity provoking itchy hives by antihistamines were rarely reported. A 41-year-old female patient visited allergy clinic for generalized itchy hives from time to time, which had been aggravated 3 months before. Whenever she was exposed to antihistamines for treatment, she felt her hives got immediately full-blown. As a screening, she was tested with various antihistamines on her skin, then skin test-negative antihistamines were orally administered. Finally we failed to choose a safe antihistamine for the treatment of her symptoms. We report a case of drug hypersensitivity to various antihistamines with cross-reactions in a patient with chronic urticaria.
MeSH Terms
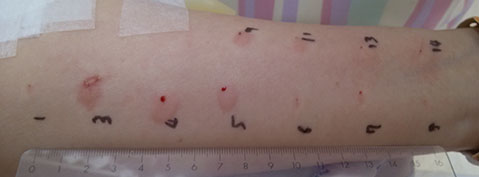
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Bepotastine-induced urticaria, cross-reactive with other antihistamines
Ju Wan Kang, Jaechun Lee
Asia Pac Allergy. 2016;6(4):253-256. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2016.6.4.253.
Reference
-
1. Estelle F, Simons R, Akdis CA. Histamine and H1-antihistamines. In : Adkinson NF, Bochner BS, Busse WW, Holgate ST, Lemanske RF, Simons FE, editors. Middleton's allergy principles & practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby;2008. p. 1517–1543.2. Rodríguez del Río P, Gonzalez-Gutierrez ML, Sanchez-Lopez J, Nunez-Acevedo B, Bartolome Alvarez JM, Martinez-Cocera C. Urticaria caused by antihistamines: report of 5 cases. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2009; 19:317–320.3. Afonso N, Shetgaonkar P, Dang A, Rataboli PV. Cetirizine-induced anaphylaxis: a rare adverse drug reaction. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009; 67:577–578.
Article4. Epstein E. Dermatitis due to antihistaminic agents. J Invest Dermatol. 1949; 12:151.
Article5. González de Olano D, Roan Roan J, de la Hoz Caballer B, Cuevas Agustin M, Hinojosa Macias M. Urticaria induced by antihistamines. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2006; 16:144–146.6. Chang YS, Kwon HS, Cho SH, Kim YY, Min KU. A case of urticaria induced by both hydroxyzine and cetirizine but not by levocetirizine. Allergy. 2007; 62:819–821.
Article7. Sánchez Morillas L, Rojas Perez-Ezquerra P, Reano Martos M, Sanz ML, Laguna Martinez JJ. Urticaria due to antihistamines. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011; 21:66–68.8. Cimbollek S, Ortega Camarero M, Avila R, Quiralte J, Prados M. NSAID-sensitive antihistamine-induced urticaria/angioedema. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011; 21:488–490.9. Kim MH, Lee SM, Lee SH, Kwon HS, Kim SH, Cho SH, et al. A case of chlorpheniramine maleate-induced hypersensitivity with aspirin intolerance. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3:62–64.
Article10. Choi GS, Sung JM, Lee JW, Park HJ, Ye YM, Nahm DH, et al. Two cases of urticaria induced by ebastine. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 29:64–68.11. Lee SW, Byun JY, Choi YW, Myung KB, Choi HY. Fexofenadine-induced urticaria. Ann Dermatol. 2011; 23:Suppl 3. S329–S332.
Article12. Inomata N, Tatewaki S, Ikezawa Z. Multiple H1-antihistamine-induced urticaria. J Dermatol. 2009; 36:224–227.
Article13. Hur H. A case of recurrent urticaria induced by tartrazine present in antihistamine. Korean J Dermatol. 1998; 36:742–744.14. Son BK, Lim DH. Allergic skin test. Korean J Pediatr. 2007; 50:409–415.
Article15. Maurer M, Rosen K, Hsieh HJ, Saini S, Grattan C, Gimenez-Arnau A, et al. Omalizumab for the treatment of chronic idiopathic or spontaneous urticaria. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:924–935.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bepotastine-induced urticaria, cross-reactive with other antihistamines
- Hypersensitivity Reactions to Antineoplastic Agents: Characteristics and Premedication Strategies
- Diagnosis and Management of Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions to Cephalosporins
- The efficacy of single premedication with antihistamines for radiocontrast media hypersensitivity
- An Overview of Multiple Drug Hypersensitivity Syndrome