Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2014 May;2(2):103-107. 10.4168/aard.2014.2.2.103.
Relationship between breast-feeding and wheeze risk in early childhood in Korean children: based on the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010-2012
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yhrha@khu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2261744
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2014.2.2.103
Abstract
- PURPOSE
There is conflicting evidence concerning the relationship between breast-feeding and development of wheezing in early childhood. Epidemiological evidence for a role of breast-feeding on risk of wheezing is inconclusive. The objective of this study was to investigate the associations between breast feeding and risk of current wheezing in early childhood in Korea.
METHODS
We combined the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data collected from 2010 to 2012 and analyzed 1,011 children from 1 to 3 years olds who had been surveyed in regards to breast-feeding. Multivariate regression analysis was used to identify association among the following variables: presence of current wheezing, feeding types and duration of breast-feeding.
RESULTS
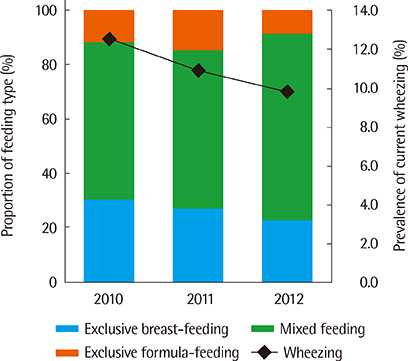
Prevalence of exclusive breast-feeding and current wheezing decreased both annually from 2010 to 2012. In the univariate analysis, breast-feeding, formula-feeding, duration of breast-feeding were not associated significantly with current wheezing of children younger than 3 years old. No measureable statistically significant relation was observed among breast-feeding, formula-feeding, duration of breast-feeding and risk of current wheezing in the multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSION
The present study showed no statistically significant relationship between breast-feeding and the risk of wheeze in early childhood in Korean children. National prospective study is needed to clarify the role of breast-feeding in development of current wheezing.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Does Breast-feeding Relate to Development of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Korean Children?: Based on the Fourth and Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2012
Kyung Suk Lee, Yeong-Ho Rha, In-Hwan Oh, Yong Sung Choi, Young-Eun Kim, Sun Hee Choi
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(4):307-313. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.307.
Reference
-
1. Nwaru BI, Takkinen HM, Niemela O, Kaila M, Erkkola M, Ahonen S, et al. Timing of infant feeding in relation to childhood asthma and allergic diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:78–86.
Article2. Yum HY. Association of brestfeeding and allergic diseases. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009; 19:325–328.3. Lee HB. Effects of breastfeeding on the development of allergies. Hanyang Med Rev. 2010; 30:49–59.
Article4. Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012; 129:e827–e841.5. Shin JW, Kim WK, Yoon HS. Association of breast-feeding and allergic diseases in preschool aged children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2009; 19:374–382.6. Greer FR, Sicherer SH, Burks AW. American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Allergy and Immunology. Effects of early nutritional interventions on the development of atopic disease in infants and children: the role of maternal dietary restriction, breastfeeding, timing of introduction of complementary foods, and hydrolyzed formulas. Pediatrics. 2008; 121:183–191.
Article7. Hong SJ, Lee MS, Lee SY, Ahn KM, Oh JW, Kim KE, et al. High body mass index and dietary pattern are associated with childhood asthma. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006; 41:1118–1124.
Article8. Miyake Y, Tanaka K, Sasaki S, Kiyohara C, Ohya Y, Fukushima W, et al. Breastfeeding and the risk of wheeze and asthma in Japanese infants: the Osaka Maternal and Child Health Study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008; 19:490–496.
Article9. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-1) 2010. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2011.10. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-2) 2011. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2012.11. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-3) 2012. Cheongwon: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2013.12. Lai CK, Beasley R, Crane J, Foliaki S, Shah J, Weiland S, et al. Global variation in the prevalence and severity of asthma symptoms: phase three of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). Thorax. 2009; 64:476–483.
Article13. Pedersen SE, Hurd SS, Lemanske RF Jr, Becker A, Zar HJ, Sly PD, et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis and management of asthma in children 5 years and younger. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2011; 46:1–17.
Article14. Kim YH, Urm SH, Kim WK. Prevalence of allergic diseases and risk factors in preschool children, 2009. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2011; 21:165–175.
Article15. Matheson MC, Allen KJ, Tang ML. Understanding the evidence for and against the role of breastfeeding in allergy prevention. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:827–851.
Article16. Qu F, Weschler LB, Sundell J, Zhang Y. Increasing prevalence of asthma and allergy in Beijing pre-school children: is exclusive breastfeeding for more than 6 months protective? Chin Sci Bull. 2013; 58:4190–4202.
Article17. Kramer MS. Breastfeeding and allergy: the evidence. Ann Nutr Metab. 2011; 59:Suppl 1. 20–26.
Article18. Brew BK, Allen CW, Toelle BG, Marks GB. Systematic review and meta-analysis investigating breast feeding and childhood wheezing illness. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2011; 25:507–518.
Article19. Wright AL, Holberg CJ, Taussig LM, Martinez FD. Factors influencing the relation of infant feeding to asthma and recurrent wheeze in childhood. Thorax. 2001; 56:192–197.
Article20. Patandin S, Weisglas-Kuperus N, de Ridder MA, Koopman-Esseboom C, van Staveren WA, van der Paauw CG, et al. Plasma polychlorinated biphenyl levels in Dutch preschool children either breast-fed or formula-fed during infancy. Am J Public Health. 1997; 87:1711–1714.
Article21. Castro-Rodriguez JA. The Asthma Predictive Index: a very useful tool for predicting asthma in young children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:212–216.
Article22. Lodge CJ, Zaloumis S, Lowe AJ, Gurrin LC, Matheson MC, Axelrad C, et al. Early-life risk factors for childhood wheeze phenotypes in a high-risk birth cohort. J Pediatr. 2014; 164:289–294.e1-2.
Article23. Writing Committee of the WHO Consultation on Clinical Aspects of Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 Influenza. Bautista E, Chotpitayasunondh T, Gao Z, Harper SA, Shaw M, et al. Clinical aspects of pandemic 2009 influenza A (H1N1) virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1708–1719.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Does Breast-feeding Relate to Development of Atopic Dermatitis in Young Korean Children?: Based on the Fourth and Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2012
- Relationship between Complementary Feeding Introduction and Early Childhood Caries: Results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2015
- Breast-feeding and Obesity in Early Childhood: Based on the KNHANES 2008 through 2011
- Association of Infant Feeding Characteristics With Dietary Patterns and Obesity in Korean Childhood
- The Association between Socioeconomic Status and Obesity in Korean Children: An Analysis of the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2010-2012)