Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2013 Sep;5(5):337-339. 10.4168/aair.2013.5.5.337.
A Case of Fixed Drug Eruption Due to Doxycycline and Erythromycin Present in Food
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, College of Medicine, Dongguk University, Goyang, Korea. lay5604@naver.com
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, College of Medicine, Dongguk University, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2260816
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2013.5.5.337
Abstract
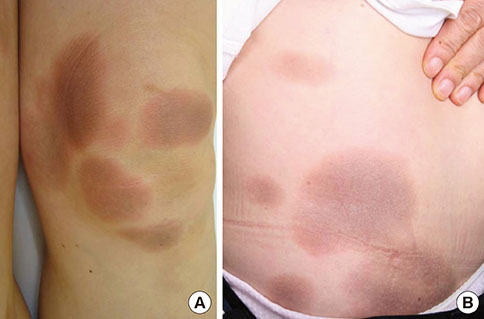
- A fixed drug eruption (FDE) is not difficult to diagnose, given its clinical characteristics. However, the causative agent can be difficult to identify, particularly when the patient denies ingestion of any drugs. To the best of our knowledge, we present herein the first reported case of an FDE caused by antibiotics taken in food; doxycycline and erythromycin contained in pork and fish. A 57-year-old female experienced repeated episodes of well-demarcated erythematous patches covering her entire body. She denied taking any medications, but she thought that the lesions appeared after consuming pork and/or fish. An oral provocation test showed positive results for doxycycline and erythromycin, commonly used antibiotics in live-stock farming and in the fishing industry. Because of the antibiotics' thermostability, cooking does not guarantee the elimination of residual drugs. From the patient's history, we concluded that doxycycline and erythromycin contained in the pork and fish that she ate were the cause of the FDE.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee AY. Fixed drug eruptions. Incidence, recognition, and avoidance. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000; 1:277–285.2. Benomar S, Ismaili N, Koufane J, Senouci K, Hassam B. Fixed food eruption caused by liquorice. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2010; 137:121–123.3. Tsuruta D, Sowa J, Kobayashi H, Ishii M. Fixed food eruption caused by Japanese sand lance. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009; 34:e309–e310.4. Fukushima S, Kidou M, Ihn H. Fixed food eruption caused by cashew nut. Allergol Int. 2008; 57:285–287.5. Shiohara T. Fixed drug eruption: pathogenesis and diagnostic tests. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:316–321.6. Kim MH, Shim EJ, Jung JW, Sohn SW, Kang HR. A case of allopurinol-induced fixed drug eruption confirmed with a lymphocyte transformation test. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:309–310.7. Ozkaya E. Polysensitivity in fixed drug eruption due to a novel drug combination-independent lesions due to piroxicam and cotrimoxazole. Eur J Dermatol. 2006; 16:591–592.8. Chan HL, Tan KC. Fixed drug eruption to three anticonvulsant drugs: an unusual case of polysensitivity. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997; 36:259.9. Ozkaya-Bayazit E. Independent lesions of fixed drug eruption caused by trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and tenoxicam in the same patient: a rare case of polysensitivity. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004; 51:S102–S104.10. del Río E, Guimaraens D, Aguilar A, Conde-Salazar L, Sánchez Yus E. Fixed exanthema induced by ultraviolet radiation. Dermatology. 1996; 193:54–55.11. Animal, Plant and Fisheries Quarantine and Inspection Agency. Animal quarantine [Internet]. Anyang: Animal, Plant and Fisheries Quarantine and Inspection Agency;2007. Available from: http://www.qia.go.kr/viewwebQiaCom.do?id=4266&type=1_23clyfjy.12. Shin HC. Veterinary drug residue monitoring [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Food & Drug Administration;2006. Available from: http://naver.nanet.go.kr/SearchDetailView.do?cn=MONO-1200710551.13. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Pig muscle. Veterinary drugs MRLs - sorted by food [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Food & Drug Administration;2012. Available from: http://fse.foodnara.go.kr/residue/vd/food/popup_food_mrl.jsp?countryCode=KR&foodCode=vd101020006.14. Korea Food & Drug Administration. Fish. Veterinary drugs MRLs - sorted by food [Internet]. Cheongwon: Korea Food & Drug Administration;2012. Available from: http://fse.foodnara.go.kr/residue/vd/food/popup_food_mrl.jsp?countryCode=KR&foodCode=vd199010009.15. Dewdney JM, Maes L, Raynaud JP, Blanc F, Scheid JP, Jackson T, Lens S, Verschueren C. Risk assessment of antibiotic residues of beta-lactams and macrolides in food products with regard to their immuno-allergic potential. Food Chem Toxicol. 1991; 29:477–483.16. Hsieh MK, Shyu CL, Liao JW, Franje CA, Huang YJ, Chang SK, Shih PY, Chou CC. Correlation analysis of heat stability of veterinary antibiotics by structural degradation, changes in antimicrobial activity and genotoxicity. Vet Med (Praha). 2011; 56:274–285.17. Hassani M, Lázaro R, Pérez C, Condón S, Pagán R. Thermostability of oxytetracycline, tetracycline, and doxycycline at ultrahigh temperatures. J Agric Food Chem. 2008; 56:2676–2680.18. Croubels S, Baert K, De Busser J, De Backer P. Residue study of doxycycline and 4-epidoxycycline in pigs medicated via-drinking water. Analyst. 1998; 123:2733–2736.19. Rose MD, Bygrave J, Farrington WH, Shearer G. The effect of cooking on veterinary drug residues in food: 4. Oxytetracycline. Food Addit Contam. 1996; 13:275–286.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Generalized Fixed Drug Eruption due to Mefenamic Acid
- Antimicrobial activity of erythromycin, doxycycline, pipemidic acid, and enoxacine against chlamydia trachomatis
- A Case of Fixed Drug Eruption induced by Chlorpropamide
- Generalized Multiple Fixed Drug Eruption
- Activities of Rifampicin, Erythromycin, Tetracycline and Doxycycline Against Clinical Isolates of Chlamydia Trachomatis in Korea