Novel Risk Factors for Allergic Rhinitis in Korean Elementary School Children: ARCO-kids Phase II in a Community
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. csrhee@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Biomedical Science, Seoul National University Graduate School, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Food and Nutrition, Kyung Hee University College of Human Ecology, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Graduate School of Immunology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Sensory Organ Research Institute, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2260460
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.3.234
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a multifactorial disease whose genetic and environmental risk factors have been studied for decades. Many pediatric studies have pointed out the familial history of allergy, hygiene hypothesis, breast-feeding, pet ownership, and diets as risk factors of AR. However, most of factors are still up for debate. This preliminary report aimed to confirm the known risk factors and find the novel risk factors for AR in the Korean pediatric population.
METHODS
A bi-seasonal, winter and summer, study in 2 elementary schools included all students whose parents completed the questionnaire of medical and social histories, quality of life, infant and early-childhood history, and the living styles. Skin prick tests and endoscopic examinations were conducted on all participants.
RESULTS
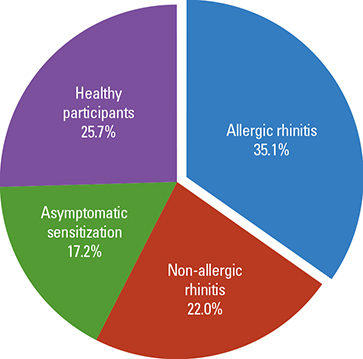
Among total 1,020 children, 338 participants had AR. The multivariate logistic regression analysis highlighted 6 factors: male gender (OR, 2.10; 95% CI, 1.32-3.33), older age (1.65; 1.03-2.65), previous history of allergic conjunctivitis (14.25; 4.99-40.74), asthma (2.73; 0.96-7.76) and pneumonia (0.39; 0.19-0.82), and an hour increase in daily playing time (0.90; 0.80-1.00).
CONCLUSIONS
Lack of pneumonia in early childhood and short playing time are newly found risk factors for Korean pediatric AR in this study confirming male gender, older age and previous history of allergic conjunctivitis and asthma as the risk factors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
The prevalence and risk factors of allergic rhinitis from a nationwide study of Korean elementary, middle, and high school students
Yeongho Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Ji-Won Kwon, Eun Lee, Song-I Yang, Hyun-Ju Cho, Mina Ha, Eunae Burm, Kee-Jae Lee, Hwan-Cheol Kim, Sinye Lim, Hee-Tae Kang, Mia Son, Soo-Young Kim, Hae-Kwan Cheong, Yu-Mi Kim, Gyung-Jae Oh, Joon Sakong, Chul-Gab Lee, Sue Jin Kim, Yong-Wook Beak, Soo-Jong Hong
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(4):272-280. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.4.272.Efficacy of Nasal Cellulose Powder in the Symptomatic Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Wiparat Manuyakorn, Natchanun Klangkalya, Wasu Kamchaisatian, Suwat Benjaponpita, Cherapat Sasisakulporn, Wanlapa Jotikasthira
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(5):446-452. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.5.446.Early-Life Environmental Factors Can Increase the Risk of Allergic Rhinitis
Doo Hee Han, Chae-Seo Rhee
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;12(3):239-240. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2019.00689.
Reference
-
1. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63:Suppl 86. 8–160.2. Portelli MA, Hodge E, Sayers I. Genetic risk factors for the development of allergic disease identified by genome wide association. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014.3. Dold S, Wjst M, von Mutius E, Reitmeir P, Stiepel E. Genetic risk for asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis. Arch Dis Child. 1992; 67:1018–1022.4. Barnes KC, Marsh DG. The genetics and complexity of allergy and asthma. Immunol Today. 1998; 19:325–332.5. Joki-Erkkilä VP, Karjalainen J, Hulkkonen J, Pessi T, Nieminen MM, Aromaa A, et al. Allergic rhinitis and polymorphisms of the interleukin 1 gene complex. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003; 91:275–279.6. Nieters A, Linseisen J, Becker N. Association of polymorphisms in Th1, Th2 cytokine genes with hayfever and atopy in a subsample of EPIC-Heidelberg. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:346–353.7. Nakamura H, Higashikawa F, Miyagawa K, Nobukuni Y, Endo T, Imai T, et al. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the eosinophil peroxidase gene with Japanese cedar pollinosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2004; 135:40–43.8. Mercer MJ, Joubert G, Ehrlich RI, Nelson H, Poyser MA, Puterman A, et al. Socioeconomic status and prevalence of allergic rhinitis and atopic eczema symptoms in young adolescents. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2004; 15:234–241.9. Almqvist C, Pershagen G, Wickman M. Low socioeconomic status as a risk factor for asthma, rhinitis and sensitization at 4 years in a birth cohort. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:612–618.10. Durkin MS, Islam S, Hasan ZM, Zaman SS. Measures of socioeconomic status for child health research: comparative results from Bangladesh and Pakistan. Soc Sci Med. 1994; 38:1289–1297.11. Park YB, Mo EK, Lee JY, Kim JH, Kim CH, Hyun IG, et al. Association between pet ownership and the sensitization to pet allergens in adults with various allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:295–300.12. Roost HP, Künzli N, Schindler C, Jarvis D, Chinn S, Perruchoud AP, et al. Role of current and childhood exposure to cat and atopic sensitization. European Community Respiratory Health Survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 104:941–947.13. Hesselmar B, Aberg N, Aberg B, Eriksson B, Björkstén B. Does early exposure to cat or dog protect against later allergy development? Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:611–617.14. Zhumambayeva S, Rozenson R, Tawfik A, Awadalla NJ, Zhumambayeva R. Date of birth and hay fever risk in children and adolescents of Kazakhstan. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2014; 78:214–217.15. Seaton A, Godden DJ, Brown K. Increase in asthma: a more toxic environment or a more susceptible population? Thorax. 1994; 49:171–174.16. Bodner C, Godden D, Brown K, Little J, Ross S, Seaton A. Aberdeen WHEASE Study Group. Antioxidant intake and adult-onset wheeze: a case-control study. Eur Respir J. 1999; 13:22–30.17. Hodge L, Salome CM, Peat JK, Haby MM, Xuan W, Woolcock AJ. Consumption of oily fish and childhood asthma risk. Med J Aust. 1996; 164:137–140.18. Black PN, Sharpe S. Dietary fat and asthma: is there a connection? Eur Respir J. 1997; 10:6–12.19. Skoner DP. Allergic rhinitis: definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, detection, and diagnosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:S2–S8.20. Wahn U, Lau S, Bergmann R, Kulig M, Forster J, Bergmann K, et al. Indoor allergen exposure is a risk factor for sensitization during the first three years of life. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997; 99:763–769.21. Sibbald B. Epidemiology of allergic rhinitis. Monogr Allergy. 1993; 31:61–79.22. Lee JE, Ahn JC, Han DH, Kim DY, Kim JW, Cho SH, et al. Variability of offending allergens of allergic rhinitis according to age: optimization of skin prick test allergens. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2014; 6:47–54.23. Shaheen SO, Aaby P, Hall AJ, Barker DJ, Heyes CB, Shiell AW, et al. Measles and atopy in Guinea-Bissau. Lancet. 1996; 347:1792–1796.24. Lewis SA, Britton JR. Measles infection, measles vaccination and the effect of birth order in the aetiology of hay fever. Clin Exp Allergy. 1998; 28:1493–1500.25. Bodner C, Godden D, Seaton A. The Aberdeen WHEASE Group. Family size, childhood infections and atopic diseases. Thorax. 1998; 53:28–32.26. de Marco R, Pesce G, Girardi P, Marchetti P, Rava M, Ricci P, et al. Foetal exposure to maternal stressful events increases the risk of having asthma and atopic diseases in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012; 23:724–729.27. Wamboldt MZ, Laudenslager M, Wamboldt FS, Kelsay K, Hewitt J. Adolescents with atopic disorders have an attenuated cortisol response to laboratory stress. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:509–514.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Geographical and Sociodemographic Risk Factors for Allergic Diseases in Korean Children
- Environmental Factors Affecting Prevalence of Allergic Diseases in Elementary School Children in a Province
- Effects of wheezing in early childhood in the development of allergic rhinitis in later years
- Research on pediatric allergic rhinitis in Korea
- Prevalence of Allergic Disease in Kindergarten Age Children in Korea