Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2011 Jan;3(1):58-61. 10.4168/aair.2011.3.1.58.
In vitro Biphasic Effect of Honey Bee Venom on Basophils from Screened Healthy Blood Donors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology and Diagnostics, University of Verona, Verona, Italy. salvatore.chirumbolo@univr.it
- 2Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata-University Hospital-Service of Immunology-Policlinico GB Rossi, Verona, Italy.
- KMID: 2260379
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2011.3.1.58
Abstract
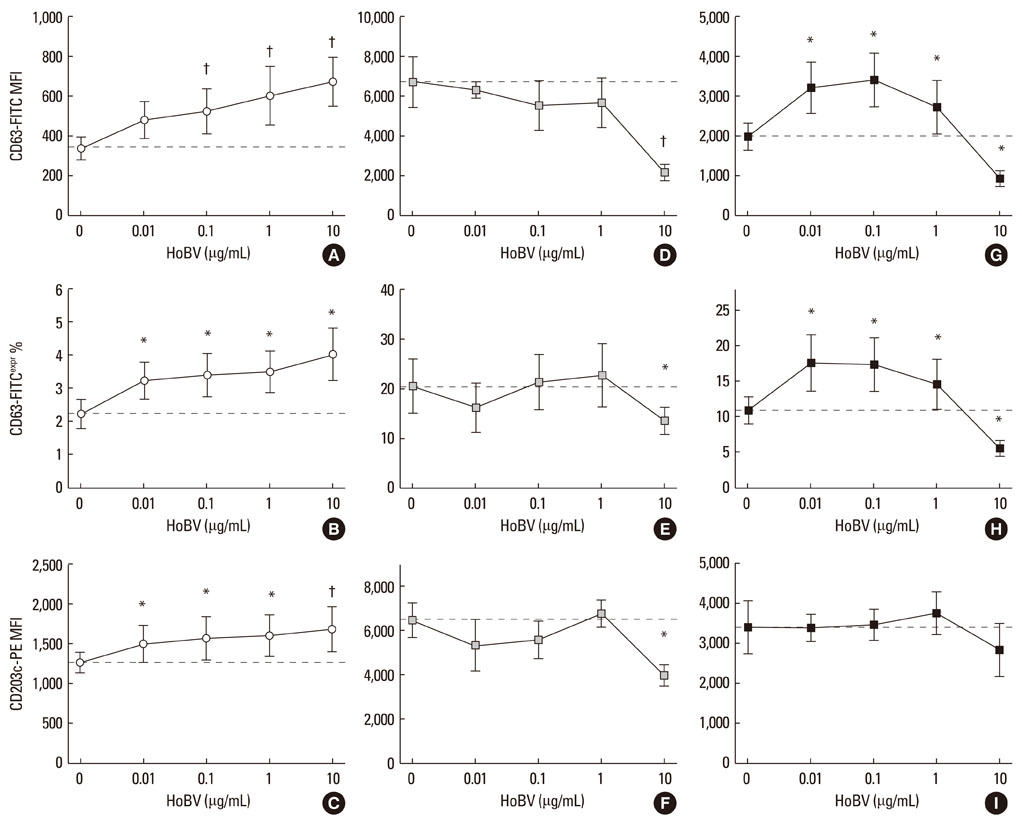
- Apis mellifera L. bee venom is the most studied hymenoptera allergen, but many aspects of its action on human basophils remain unclear. Allergologists seek evidence of the effectiveness of bee venom immunotherapy as this approach is the chosen treatment for systemic allergic reactions. The effect of bee venom on human basophils in vitro has not been studied in detail for many reasons, including the paucity of basophils in peripheral blood, inter-individual basophil response variability, and the reliability and predictability of basophil activation tests. We conducted a brief preliminary survey of the effect of Apis bee venom on healthy asymptomatic (non-allergic) subjects. A dose of an aqueous commercial extract of Apis bee venom as high as 10 microg/mL activated resting basophils (CD63=+80-90%, CD203c=+30%), while it inhibited the expression of CD63 (-50%) following basophil stimulation by the soluble agonists formyl-Met-Leu-Phe or anti-IgE. The activation of resting basophils appeared to be dose-related. Only when basophils were activated with an IgE-mediated agonist, did bee venom extract exhibit a possible priming mechanism at the lowest doses used only via CD63, while it was ineffective via CD203c. Autocrine interleukin-3 may play a role in the observed biphasic behavior.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adamic K, Zidarn M, Bajrovic N, Erzen R, Kopac P, Music E. The local and systemic side-effects of venom and inhaled-allergen subcutaneous immunotherapy. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2009. 121:357–360.2. Quercia O, Emiliani F, Pecora S, Burastero SE, Stefanini GF. Efficacy, safety, and modulation of immunologic markers by immunotherapy with honeybee venom: comparison of standardized quality depot versus aqueous extract. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2006. 27:151–158.3. Dubois AE. Mastocytosis and hymenoptera allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004. 4:291–295.4. Przybilla B, Ruëff F. Hymenoptera venom allergy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2010. 8:114–127.5. Chirumbolo S, Vella A, Ortolani R, De Gironcoli M, Solero P, Tridente G, Bellavite P. Differential response of human basophil activation markers: a multi-parameter flow cytometry approach. Clin Mol Allergy. 2008. 6:12.6. Binder M, Fierlbeck G, King T, Valent P, Bühring HJ. Individual hymenoptera venom compounds induce upregulation of the basophil activation marker ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 3 (CD203c) in sensitized patients. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002. 129:160–168.7. Sturm EM, Kranzelbinder B, Heinemann A, Groselj-Strele A, Aberer W, Sturm GJ. CD203c-based basophil activation test in allergy diagnosis: characteristics and differences to CD63 upregulation. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2010. 78(5):308–318.8. Schroeder JT, Chichester KL, Bieneman AP. Human basophils secrete IL-3: evidence of autocrine priming for phenotypic and functional responses in allergic disease. J Immunol. 2009. 182:2432–2438.9. Mustafa FB, Ng FS, Nguyen TH, Lim LH. Honeybee venom secretory phospholipase A2 induces leukotriene production but not histamine release from human basophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008. 151:94–100.10. Okayama Y, Begishvili TB, Church MK. Comparison of mechanisms of IL-3 induced histamine release and IL-3 priming effect on human basophils. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993. 23:901–910.11. Neel NF, Creasy BM, Rankin JN, Pierce EM, McCoy ME, Daner RH, Fowler JA, Daniel JC, Lantz CS. Absence of interleukin-3 does not affect the severity of local and systemic anaphylaxis but does enhance eosinophil infiltration in a mouse model of allergic peritonitis. Immunol Lett. 2004. 95:37–44.12. Verweij MM, Bridts CH, De Clerck LS, Stevens WJ, Ebo DG, De Knop KJ. P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction in the diagnosis and follow up of immunotherapy of wasp venom allergy. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2010. 78(5):302–307.13. Aerts NE, Dombrecht EJ, Bridts CH, Hagendorens MM, de Clerck LS, Stevens WJ, Ebo DG. Simultaneous flow cytometric detection of basophil activation marker CD63 and intracellular phosphorylated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in birch pollen allergy. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2008. 76B:8–17.14. Ebo DG, Dombrecht EJ, Bridts CH, Aerts NE, de Clerck LS, Stevens WJ. Combined analysis of intracellular signalling and immunophenotype of human peripheral blood basophils by flow cytometry: a proof of concept. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007. 37:1668–1675.15. MacGlashan D Jr, Undem BJ. Inducing an anergic state in mast cells and basophils without secretion. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. 121:1500–1506.e4.16. Denyer J, Patel V. Syk kinase inhibitors in allergic diseases. Drug News Perspect. 2009. 22:146–150.17. Uermösi C, Beerli RR, Bauer M, Manolova V, Dietmeier K, Buser RB, Kündig TM, Saudan P, Bachmann MF. Mechanisms of allergen-specific desensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. 126:375–383.